An artificial lake anti-seepage structure
An artificial lake and soil layer technology, applied in marine engineering, water conservancy engineering, construction, etc., can solve the problems of inconvenient jet dredging, damage to the water quality of artificial lakes, and inconvenience of artificial lake dredging, etc., to avoid algae growth, avoid rich Oxidation process, the effect of reducing the leakage rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
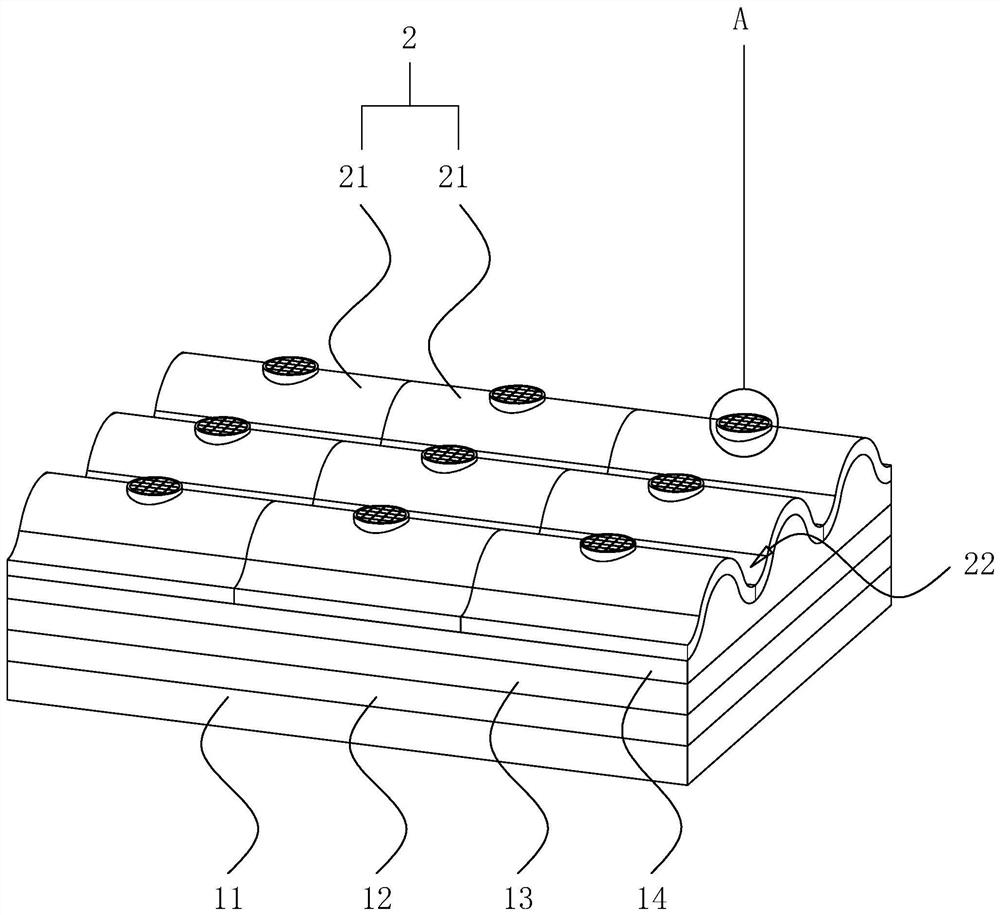
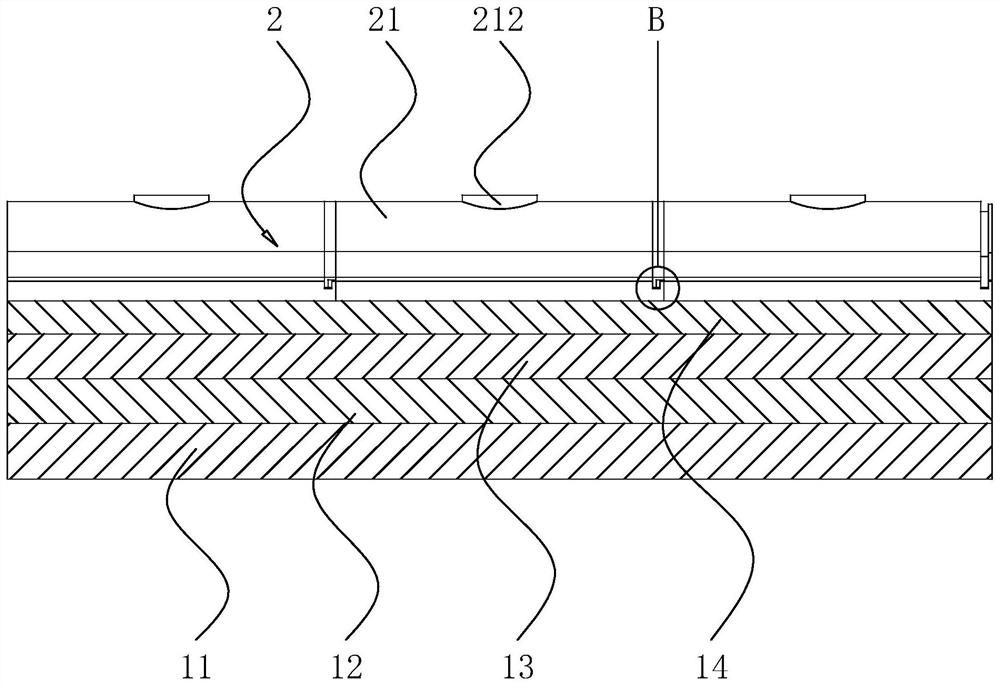
[0041] refer to figure 1 , the present embodiment proposes an anti-seepage structure for an artificial lake, including a rammed earth layer 11 , a clay layer 12 , a planting soil layer 14 and a water-resistant layer 2 . The rammed earth layer 11 needs to be dug out from the bottom of the artificial lake, and then the large rocks in the soil are screened out, and then the screened soil is backfilled. The degree of compaction of the rammed earth layer 11 is greater than 0.85, and preferably not greater than 0.95, so that the rammed earth layer 11 has a certain water permeability function while maintaining the support force. After the rammed earth layer 11 is compacted, the upper surface thereof shall ensure that the flatness per square meter shall not exceed 20mm, and there shall be no obvious holes.
[0042] The clay layer 12 is laid on the upper surface of the rammed earth layer 11, and the inside of the clay layer 12 is clay or commercial montmorillonite with a clay content ...
Embodiment 2
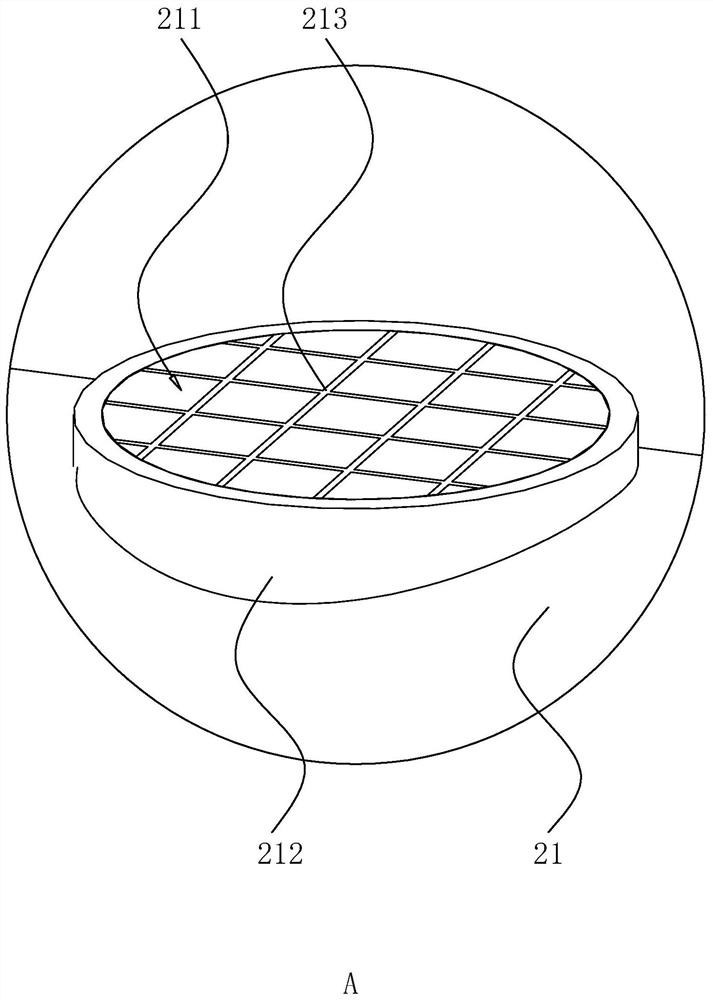
[0055] refer to image 3 and Figure 4 , this embodiment proposes an artificial lake anti-seepage structure, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the two ends of the water-proof tile 21 in the length direction are respectively provided with a first block 214 and a second block 215, wherein the first A block 214 is arranged on the upper end of the water-insulating tile 21 , and a second block 215 is arranged on the lower end of the water-insulating tile 21 . The first clamping block 214 and the second clamping block 215 on two adjacent water-proof tiles 21 in the length direction are clamped with each other, and after the clamping of the first clamping block 214 and the second clamping block 215 is completed, the middle is formed There is a gap, and clay slurry 216 is applied in the gap.
[0056] refer to Figure 5 and Image 6 , the width direction of the water-proof tile 21 is respectively provided with a third block 217 and a fourth block 218, wherein the third block...
Embodiment 3
[0060] refer to Figure 7 , This embodiment proposes an artificial lake anti-seepage structure. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that it also includes a revetment 3, which can be made of reinforced concrete, or it can be made of stones and filled with cement mortar. The bottom of the revetment 3 is inserted into the rammed earth layer 11, and the side of the revetment 3 close to the center of the lake is provided with a first step 32, a second step 33 and a third step 34 in sequence from low to high, and the revetment 3 is at the first step 32 The thickness at the third step 34 decreases successively.
[0061] When laying the rammed earth layer 11 , the upper end surface of the first step 32 is flush with the upper end surface of the rammed earth layer 11 , and the side surfaces of the first step 32 are pressed against the end surface of the rammed earth layer 11 . When laying the clay layer 12 , the upper end surface of the second step 33 is flush with the upper end surfa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com