RFID label number estimation system and method based on virtual vector Aloha protocol
An RFID tag, virtual vector technology, applied in electromagnetic radiation induction, short-distance communication services, electrical components and other directions, can solve the problems of slow query speed, high time complexity, high computational resource overhead, etc., to improve the estimation accuracy, The effect of low time complexity and low computational overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
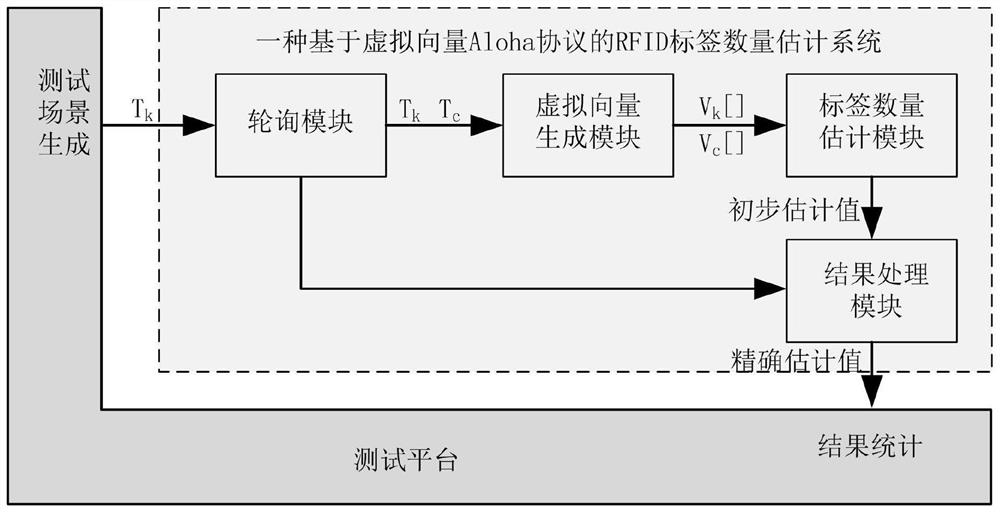
[0032] Specific embodiment one: present embodiment is based on the RFID label quantity estimation system of virtual vector Aloha agreement and comprises:
[0033] The composition of the RFID tag quantity estimation system based on the virtual vector Aloha protocol is as follows: figure 2 As shown, the functions of each module are as follows:
[0034] Virtual vector generation module, vector analysis and probability estimation execution module, single reader polling module, result processing module and testing module based on Aloha protocol;
[0035] The virtual vector generation module based on the Aloha protocol is used to generate the expected vector V of the target label set k [ ] and collect the response vector V that gets the response c [·];
[0036] The vector analysis and probability estimation execution module is used for the expected vector V k [ ] with the response vector V c [·] Perform comparison and analysis to obtain an estimate of the number of target tags...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0041] Specific embodiment two: the specific process of the method for estimating the number of RFID tags based on the virtual vector Aloha protocol in this embodiment is as follows
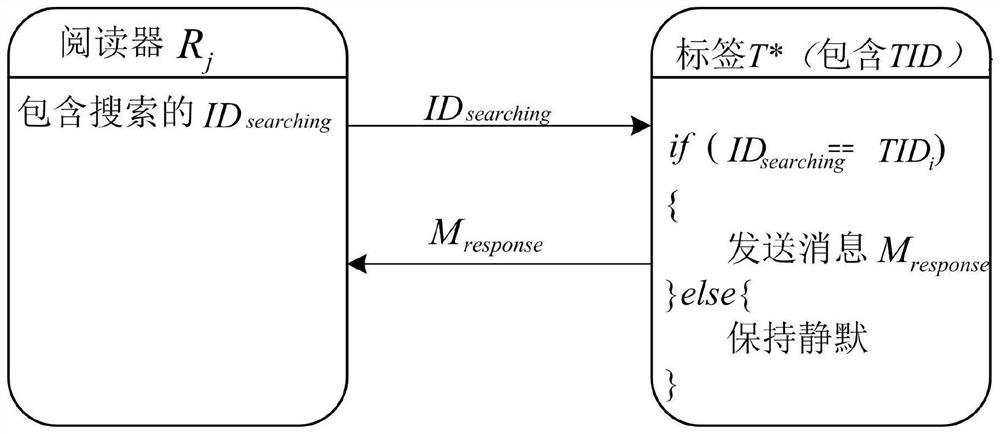
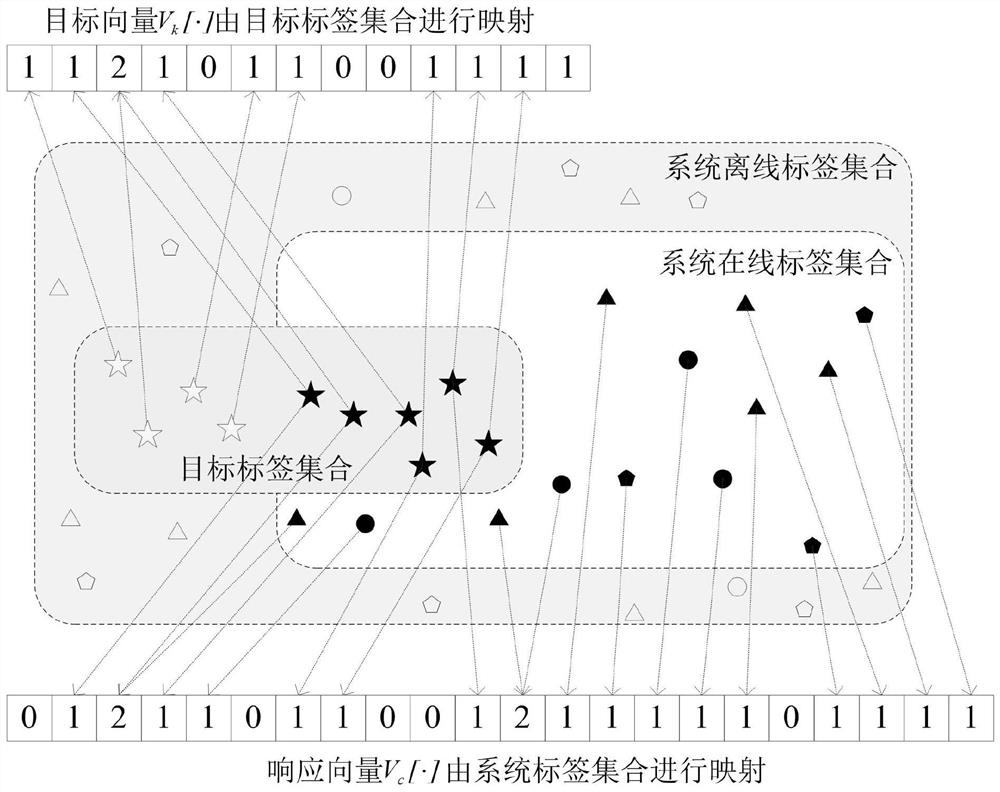
[0042] The estimation of the number of RFID tags is in a given RFID system, for the known target tag set A={t 1 ,t 2 ,...,t n}, in the current RFID system C={...,t i ,...,t j ,...,t k ,...} to obtain the quantity ||T|| of target set T=A∩C, that is to obtain the quantity of online target labels in the system. There are many types of tags within the effective range of the reader, and each tag is divided into online status and offline status according to whether it is in the current system.
[0043] Aiming at the problem of estimating the number of target tags in a low-cost RFID system, it is necessary to meet the problem of high estimation efficiency and estimation accuracy at the same time. set and expected vector V k [ ], and calculate the response vector V of all tags in the system c [·]...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0057] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment two is that: the virtual vector generation module based on the Aloha protocol in the step two is used for the reader according to the known target tag set T k information, using a uniformly distributed hash function H(TID,f c ,f s ) to map, fill and generate the desired vector V k [·]; the specific process is:
[0058] Define the hash function H(TID,f c ,f s )for:
[0059] rest V k [·]=0;
[0060] Among them, TID represents the tag ID, r represents the random number generated by the reader; V k [ ] is the expected vector; % is the operation of "remainder", is an "exclusive or" operation;
[0061] where N×f c determines the size of the desired vector, f s =512 is the frame length;
[0062] According to H(TID,f c ,f s ) function fills the desired vector V k [·];
[0063] filled with not V k [·]=0;
[0064] Other steps and parameters are the same as in the secon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com