Positioning data processing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
A technology for positioning data and processing methods, which is applied in location-based services, power management, electrical components, etc. It can solve problems such as wasting traffic, consuming resources and time, and terminal power consumption, so as to save power consumption and traffic, and reduce The frequency of positioning data collection and the effect of reducing the operation of positioning data collection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
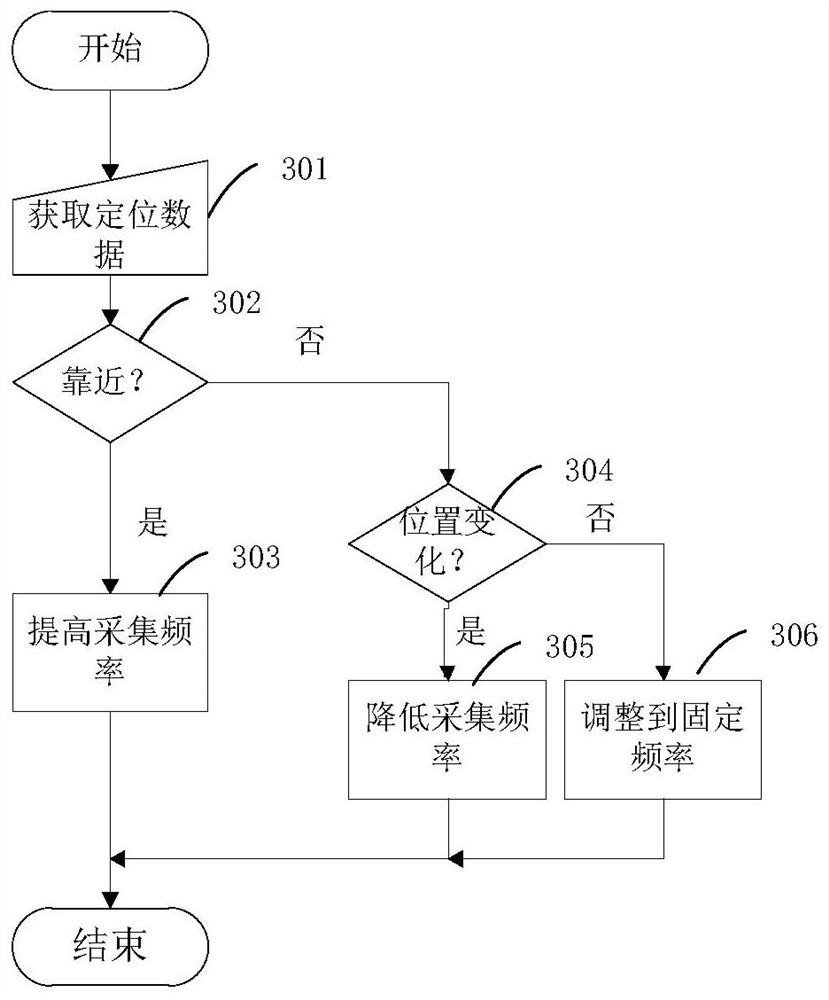
[0098] Method 1: Determine the target acquisition frequency according to the linear relationship between the movement trend and the target frequency. For example, when the movement trend is close to the smart device, the distance between the monitored object and the smart device is determined, and the target collection frequency can be inversely proportional to the distance. In this way, the closer to the smart device, the greater the frequency of target collection.
[0099] Similarly, when the monitored object moves away from the smart device, the distance from the monitored object to the smart device is proportional to the target collection frequency, that is, the farther away from the smart device, the lower the target collection frequency.
[0100] Method 2: In order to adjust the collection frequency to better adapt to actual needs in relation to the context. In the present disclosure, the target acquisition frequency can be determined on the basis of the current acquisition ...
Embodiment approach 1
[0114] Embodiment 1: Determine the target collection frequency according to the following formula (3):
[0115] P n =P (n-1) *[1+(t (n-1) -t n ) / t n ] (3)
[0116] In formula (3), P n Indicates the target acquisition frequency, P (n-1) Indicates the current acquisition frequency (that is, the target acquisition frequency determined last time), t n With t (n-1) The meaning of is the same as in formula (2), namely t n Indicates the time corresponding to the latest position in the historical positioning data, t (n-1) Represents the duration corresponding to the last anchor point of the latest anchor point in the historical positioning data. Among them, if n = 1, then P 0 =A, A is a constant; if the front and rear positions have not changed, the value P can be directly taken n =A (that is, use a fixed frequency for positioning data collection when stationary).
[0117] Among them, in formula (3), (t (n-1) -t n ) The result represents the movement trend, that is, when the result is a nega...
Embodiment approach 2
[0120] Embodiment 2: Determine the target collection frequency according to the following formula (4):
[0121] P n =P (n-1) *[1+(S (n-1) -S n ) / S n ] (4)
[0122] In formula (4), P n Indicates the target acquisition frequency, P (n-1) Indicates the current acquisition frequency (that is, the target acquisition frequency determined last time), S n Indicates the distance from the latest position in the historical positioning data to the smart device, t (n-1) Indicates the distance from the previous positioning point of the latest positioning point in the historical positioning data to the smart device.
[0123] Similar to the principle of formula (3), in formula (4), (S (n-1) -S n ) The result represents the movement trend, that is, when the result is a negative number, it means that the distance from the latest location point to the smart device has increased compared to the last determined distance, that is, the monitored object is far away from the smart device. When it is a positiv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com