Linear frequency modulation signal sparse sampling and reconstruction method based on fractional Fourier transform domain
A technology of linear frequency modulation signal and fractional Fourier, which is applied in the direction of frequency modulation carrier system, code conversion, complex mathematical operations, etc., and can solve problems such as powerlessness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
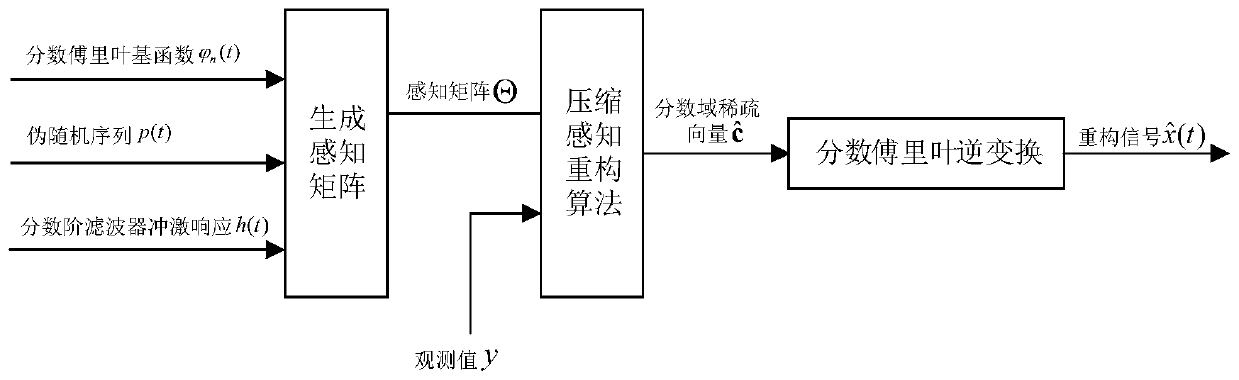
[0072] The invention provides a sparse sampling and reconstruction method of a linear frequency modulation signal based on a fractional Fourier transform domain.
[0073] Step 1: Perform parameter initialization;
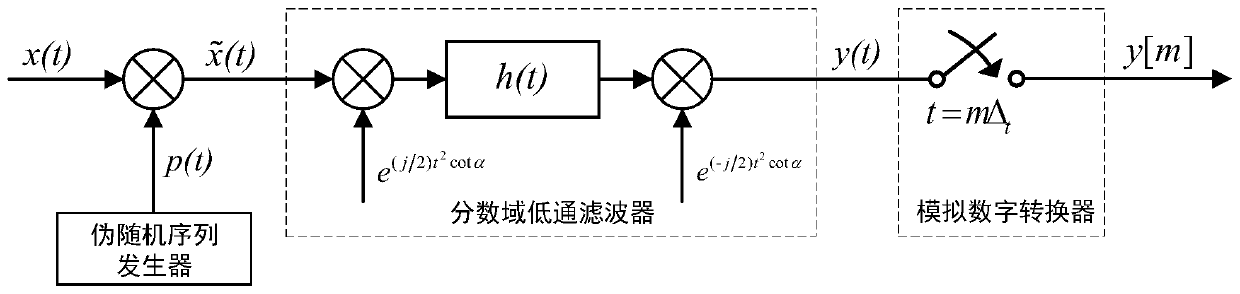
[0074] refer to figure 1 Schematic block diagram of the signal sampling process to construct a sparse representation of an analog chirp signal. For the convenience of analysis, the concept of fractional Fourier transform is introduced first. The fractional Fourier transform of a signal f(t) is defined as
[0075]
[0076] Among them, α is the transformation angle, and the integral kernel K α The expression of (u,t) is
[0077]
[0078] Among them, k is an integer. Correspondingly, the formula of fractional Fourier inverse transform is
[0079]
[0080] Usually, the u-axis is called the fractional Fourier transform domain, and the corresponding variable u is called the fractional order frequency. In particular, when α=π / 2, the fractional Fourier trans...
specific Embodiment 2
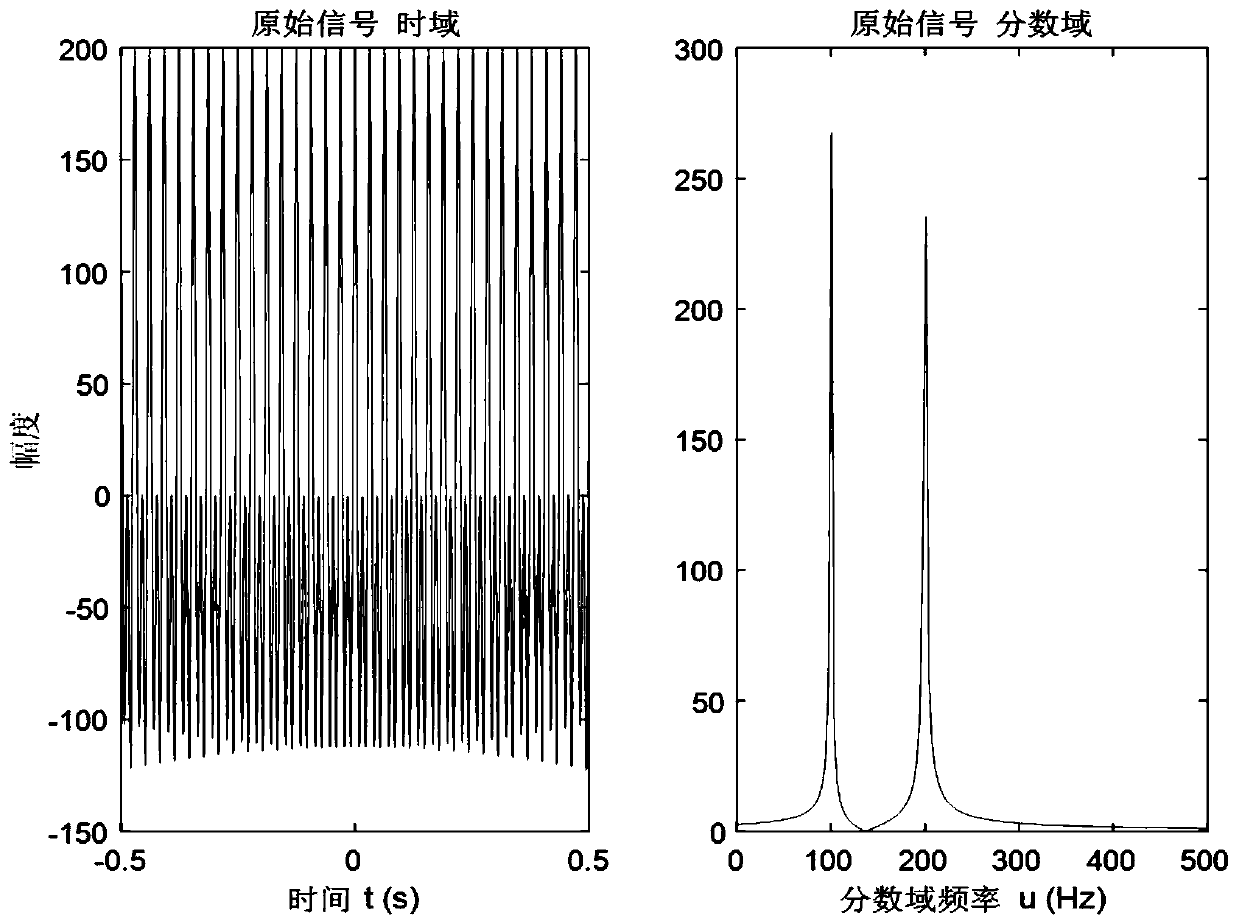
[0146] according to Figure 2 to Figure 6 As shown, this example uses two chirp signals as input signals, where the amplitude of the chirp signals is B=100, and the modulation frequencies are both The central angular frequencies ω are 200Hz and 400Hz, respectively. From the above derivation, it can be seen that the energy of the signal is best gathered in the fractional domain where the rotation angle is α=π / 6, and it is an impulse function at u=ωsinα=100Hz and 200Hz, which is consistent with the simulation results in .
[0147] The chirp signal x(t) is then multiplied by the pseudo-random code c(t). The pseudo-random sequence c(t) in this example is the m-sequence generated by the longest linear shift register, and the period of the pseudo-random sequence is NT c =1, so the interval of spectral lines in the frequency domain is ω 0 =2π / NT c = 2π. As shown, the multiplied signal Its fractional spectrum is moved to every equally spaced frequency point. Consistent with f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com