Computer simulation method for self-adaptive particle fluid
A particle fluid and simulation method technology, applied in computer-aided design, calculation, design optimization/simulation, etc., to achieve the effect of improving simulation efficiency, high efficiency, and increasing calculation speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0039] The solution in Embodiment 1 will be further introduced below in combination with specific examples and calculation formulas. For details, see the following description:
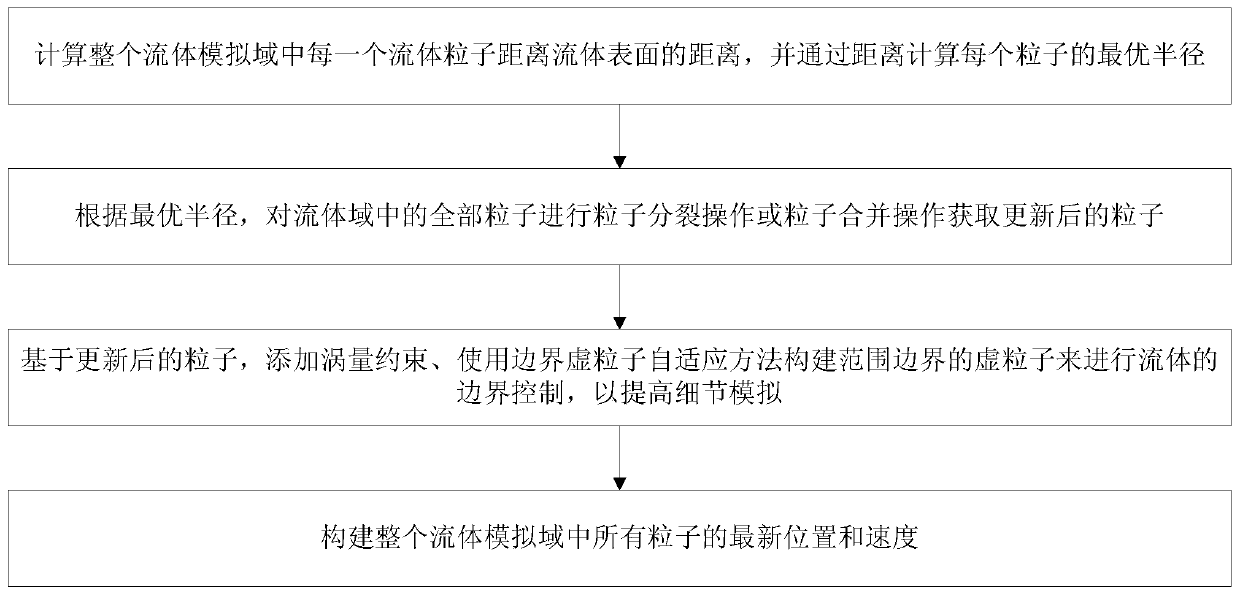
[0040] Step S0101: Use the particle level set method to estimate the distance of each fluid particle i from the fluid surface, as shown in formula (1), formula (2), formula (3), and formula (4).
[0041]
[0042]
[0043]
[0044]
[0045] Where x j And r j Are the position and radius of particle j, Is the average position of fluid particles in the neighborhood of particle i, Is the average radius in the neighborhood, Is an initial value for calculating the distance level set function, h represents the range of the neighborhood h, W ij Is the coefficient, and W is the kernel function in the SPH method.
[0046] Step S0102: Calculate the initial estimated value of the distance between the particles close to the surface and the fluid surface by the step length As shown in formula (5).
[0047]
[0048] amon...
Embodiment 3
[0093] The feasibility verification of the schemes in Examples 1 and 2 is carried out below in conjunction with specific experiments, as detailed in the following description:
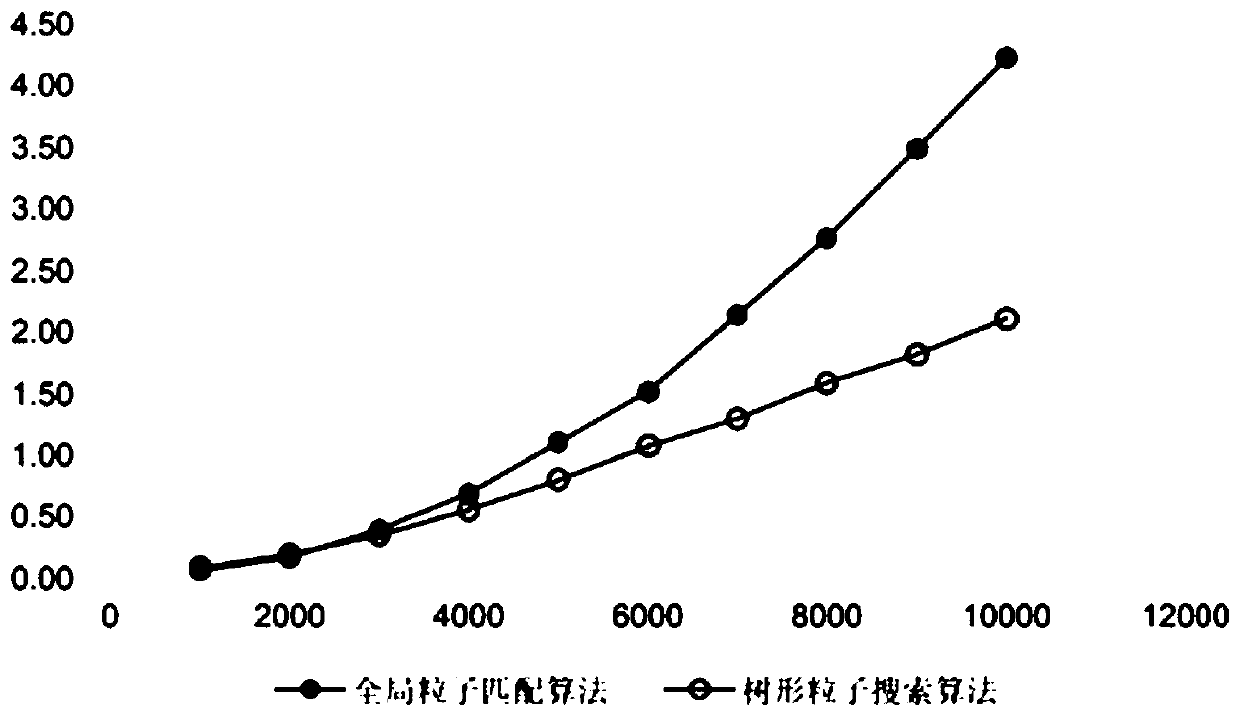
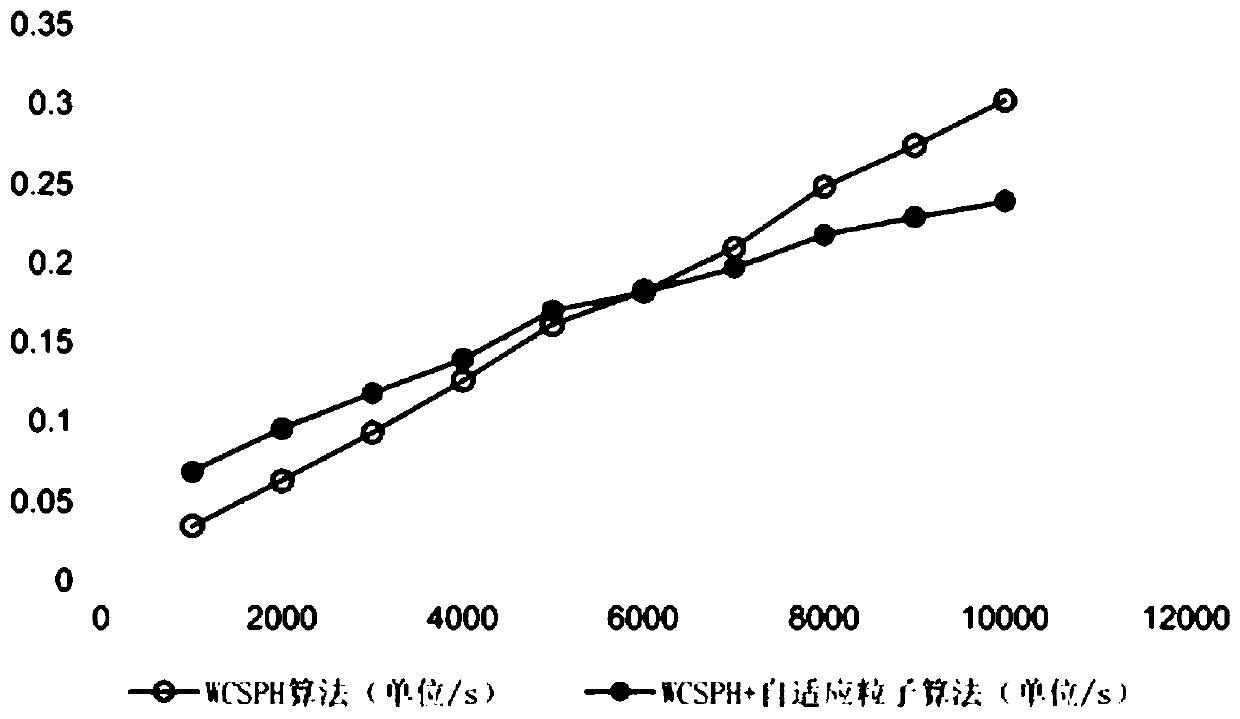
[0094] in figure 2 As can be seen from Table 1, as the number of particles increases, the search time of the tree search algorithm is significantly better than that of the global matching search algorithm. In terms of memory consumption, using the global matching search algorithm saves more memory, while using the tree search algorithm takes up slightly more memory.
[0095] Table 1 Search algorithm memory usage table
[0096]
[0097] In summary, if you want to simulate a fluid domain simulation with a smaller number of fluid particles, the efficiency of the global matching particle search algorithm may be better, but if the number of simulated particles is large, most of the time, the present invention must at least simulate There are tens of thousands of particles, so the tree search algorithm is a more ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com