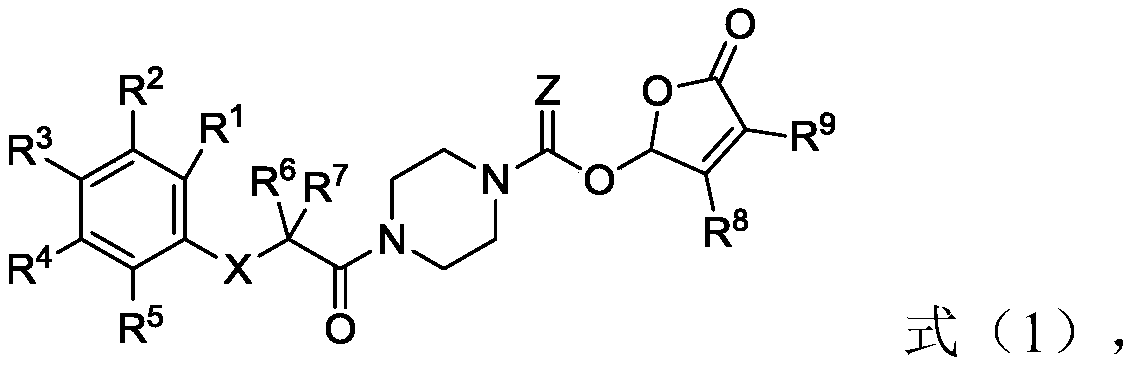
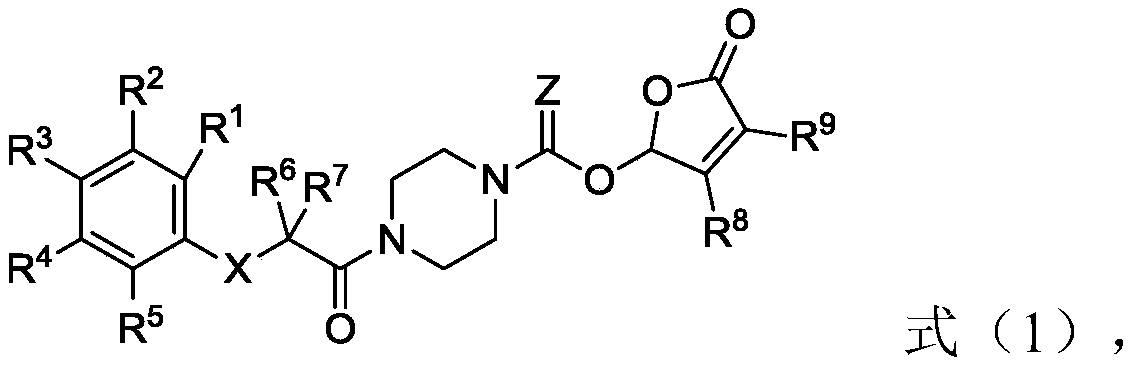
Piperazine amide derivative and preparation method thereof, root parasitic weed seed germination accelerator and method for preventing and controlling root parasitic weeds
A technology of piperazinamide and derivatives, applied in the field of pesticide chemistry, can solve problems such as ineffective prevention and control of root parasitic weeds, and achieve the effects of being favorable for commercialization, low in preparation cost, and promoting germination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
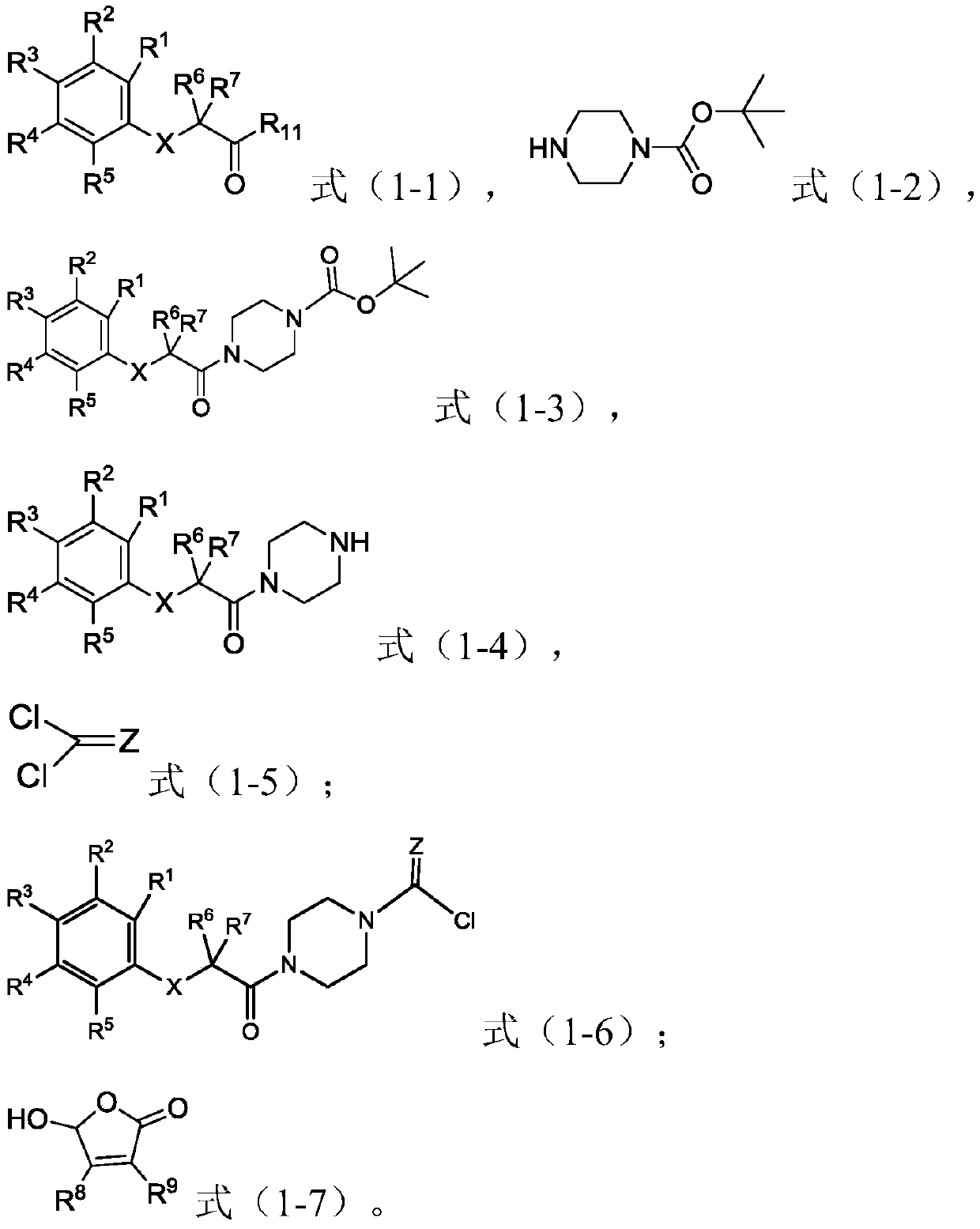
[0055] The second aspect of the present invention provides the preparation method of the piperazine amide derivative of the present invention, the method comprises the following steps:
[0056] (1) In the first solvent, carry out condensation reaction with raw material A shown in formula (1-1), raw material B shown in formula (1-2), coupling agent and condensing agent, obtain formula (1-3 ) intermediate C shown in );
[0057] (2) In the second solvent, the intermediate C is subjected to a deprotection reaction with a deprotecting agent to obtain an intermediate D represented by formula (1-4);
[0058] (3) In the third solvent, the acid chlorination reaction of the intermediate D, the acyl chloride agent represented by the formula (1-5) and the first base occurs to obtain the intermediate E represented by the formula (1-6) ;
[0059] (4) In the fourth solvent, the intermediate E, the raw material F represented by the formula (1-7) and the second base undergo an esterification...
Embodiment 1
[0124] Embodiment 1---the synthesis of compound 52
[0125] (1) the raw material A (R) shown in the formula (1-1) of 15mmol 1 ~R 7 , X is selected as shown in compound 52 of Table 1, R 11 = H), 15 mmol of raw material B (tert-butoxycarbonyl piperazine) shown in formula (1-2), 19.5 mmol of coupling agent (2-(7-benzotriazole oxide)-N,N, N', N'-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate) and 150 mL of the first solvent (dichloromethane) were added to the reaction flask, and 43.5 mmol of condensing agent (N, N '-diisopropylethylamine, DIPEA) and continued to react at room temperature for 8 hours. After the reaction was completed, 100 mL of water was added to the system and vigorously stirred for 15 min. Separate the organic layer, wash the water layer with 50mL of the first solvent, combine the organic layers, wash the organic layer with water and saturated brine successively, dry with anhydrous sodium sulfate, and remove the organic solvent under reduced pressure to obtain the fo...
Embodiment 2
[0136] Embodiment 2 --- the synthesis of compound 46
[0137] With reference to the method of Example 1, the difference is that the raw materials used are different to prepare the compound 46 in Table 1, in the specific raw materials R 1 ~R 9 , X and Z are selected as shown in compound 46 in Table 1, R 11 =H.
[0138] The yield is 90%.
[0139] The proton spectrum data of gained compound is: 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ6.94–6.74(m,5H),4.70(s,2H),3.85–3.32(m,8H),2.23(s,3H),1.99(s,3H).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com