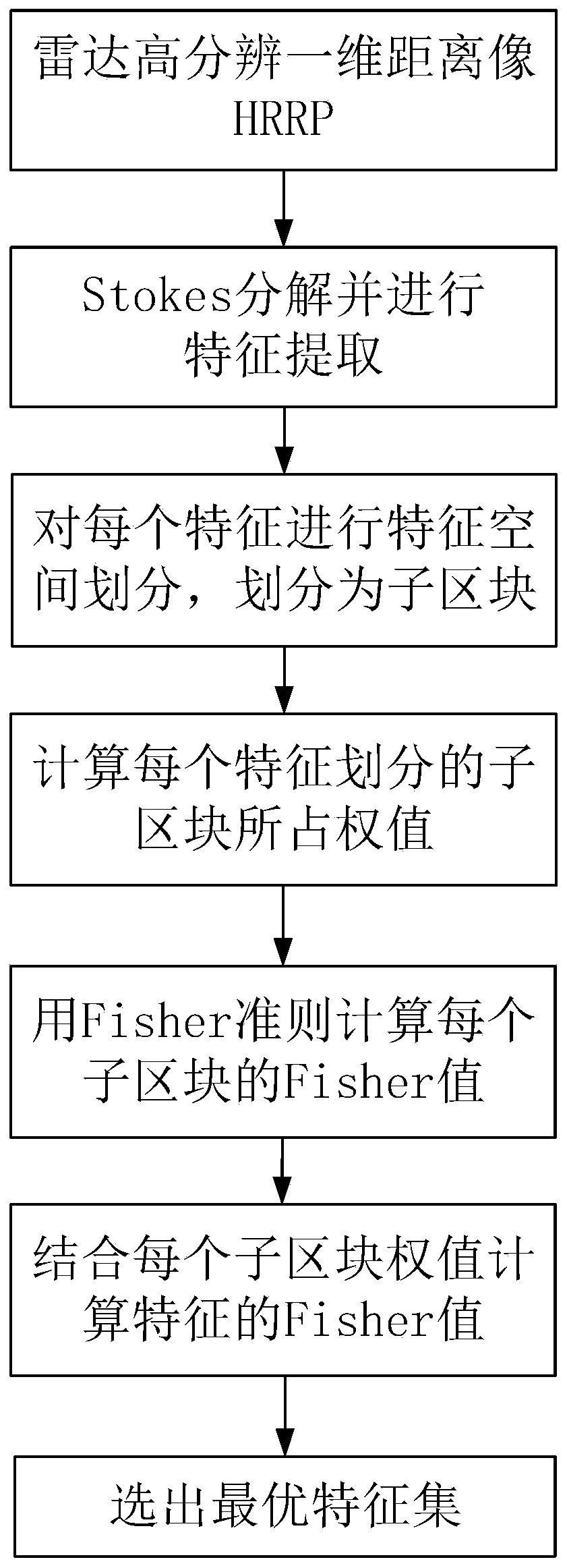
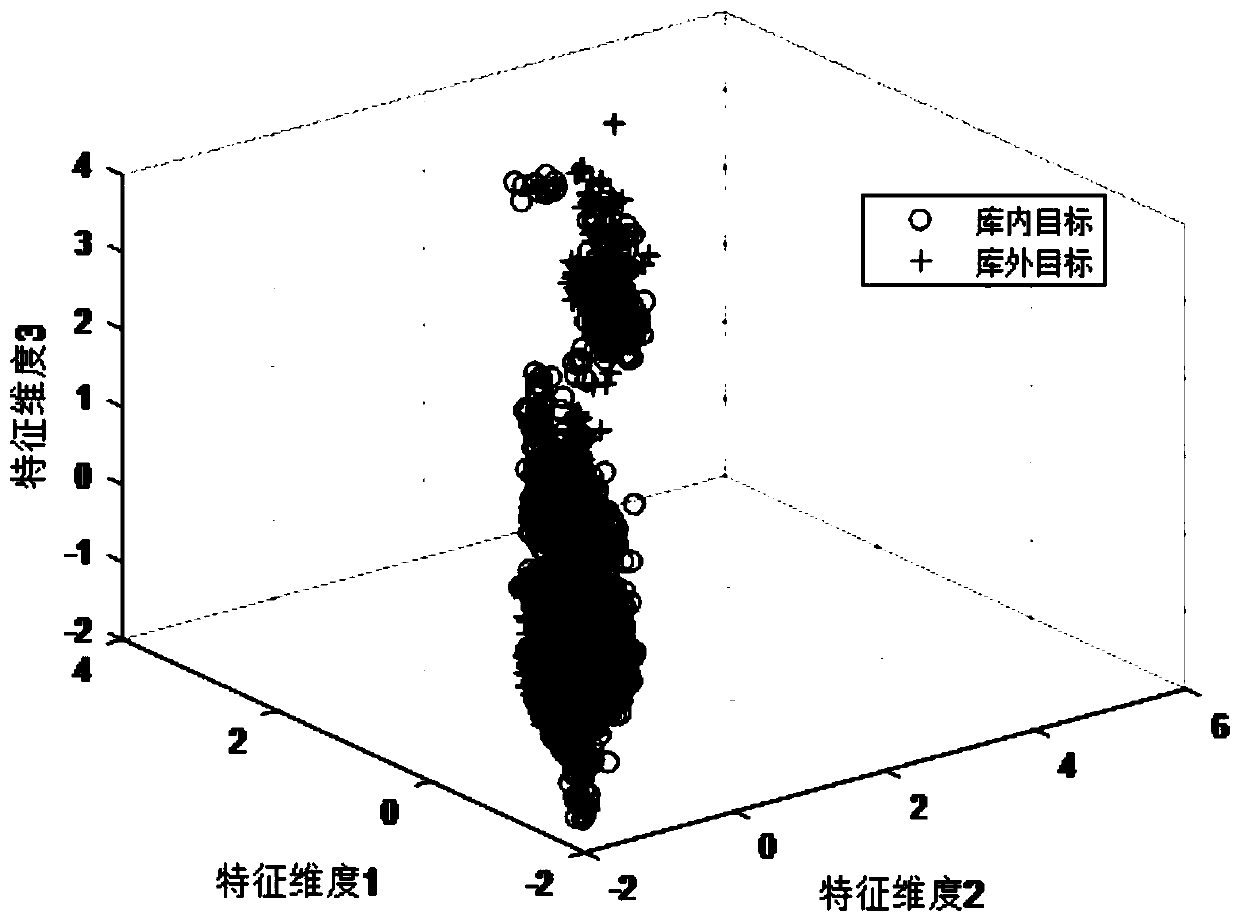
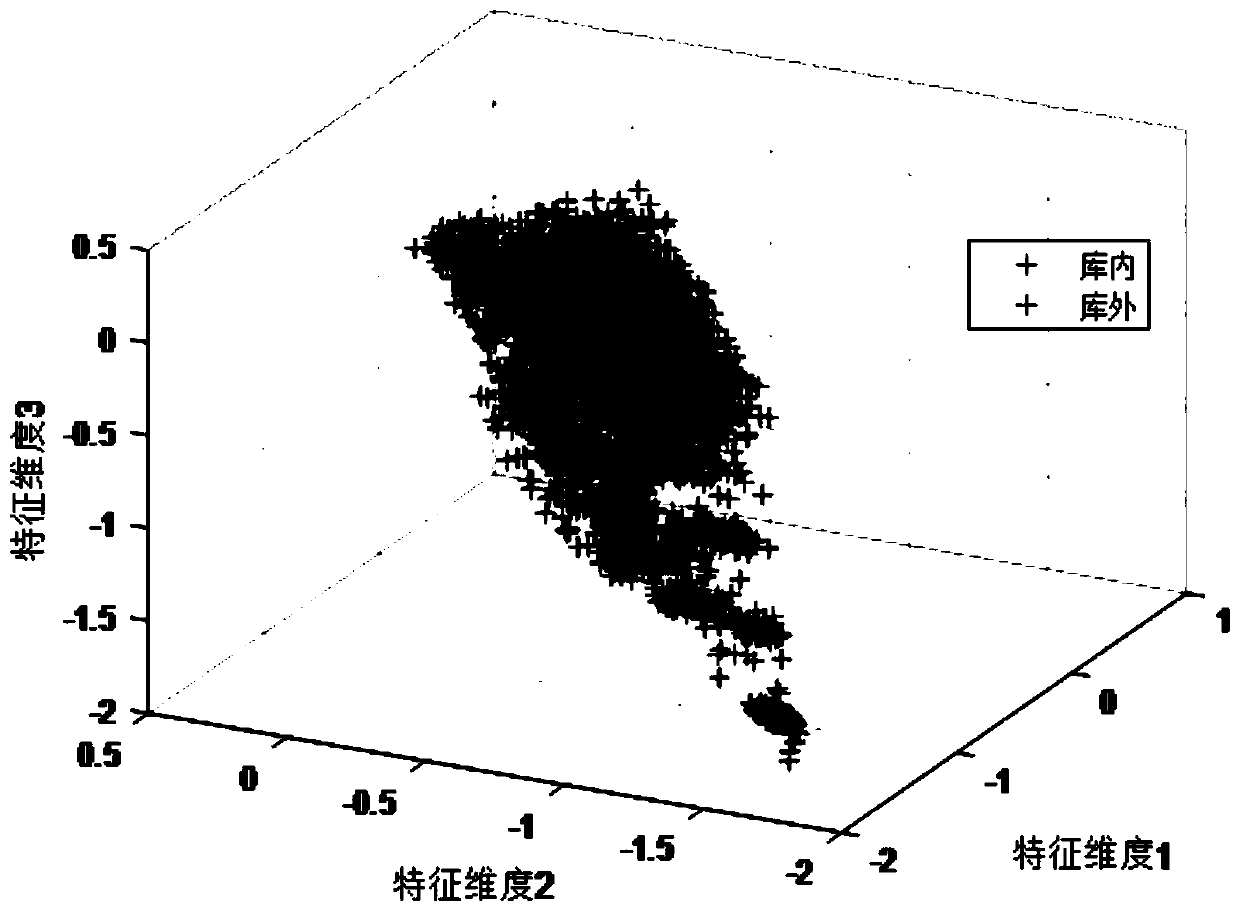
Fisher feature selection method based on feature space distribution
A feature selection method and feature space technology, applied in the field of radar, can solve the problems of poor separability, inability to fully reflect the separability of feature component categories, small separability values, etc., and achieve target identification probability improvement , Improve the probability of target recognition and the effect of improving the identification rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Since its birth, radar has focused on detection and has made outstanding contributions in different fields. With the increasingly complex radar detection environment and the continuous development of modern technology, target recognition has become an important technology in the development of modern radar. Radar Automatic Target Recognition (RATR) technology is based on radar echo signals, extracts target features, and realizes automatic determination of target attributes, categories or types. Selecting features with good separability will greatly improve the probability of target recognition . At present, the commonly used feature selection is the Fisher criterion based on the distance within and between classes in the Filter algorithm, which is more intuitive and easy to operate. However, the calculation error of the separability of non-uniform multi-region aggregation distribution features is relatively large, and it is easy to misjudge features with good separabili...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The Fisher feature selection method based on feature space distribution is the same as embodiment 1, and the construction training template library original feature set X described in step 1 comprises the following steps:
[0037] 1a) Acquisition of target data: Collect N sets of high-resolution one-dimensional range images of targets measured by dual-polarization radars, which are co-polarization high-resolution one-dimensional range images S LL , cross-polarized high-resolution one-dimensional range image S RL .
[0038] 1b) m-δ decomposition: perform m-δ decomposition on the obtained high-resolution one-dimensional range image, and obtain the secondary scattering component V of the target respectively d , volume scattering component V v and the surface scattering component V s ; m-δ decomposition can be calculated according to Stokes vector:
[0039]
[0040] where S LL , S RL are the amplitudes of the co-polarization and cross-polarization channels respecti...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment 3: The Fisher feature selection method based on feature space distribution is the same as that of Embodiment 1-2. In step 2 of the present invention, each feature in the original feature set X is divided into regions, specifically including: generating K m K in a feature subspace region m Computed from the minimum sum of squared errors MSSE, denote the qth subspace region of the mth feature as F m,q =(θ m,q , η m,q ,ψ m,q ), where θ m,q Indicates the number of target features in the qth subspace region of the mth feature, η m,q Represents the target feature set of the qth subspace region of the mth feature, ψ m,q ={1,2} indicates the category of the sample in the subspace region q of the mth feature, 1 is the target in the library, 2 is the target outside the library, i=1,2...θ m,q , q=1,2...K m , the subspace region in the present invention is also the sub-block; the minimum MSSE formula is as follows:
[0052]
[0053] in, j=1,2...K m , K m T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com