Methods for treating netosis and neutrophil activation
A technology of neutrophils and cells, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, extracellular fluid diseases, etc., can solve problems such as tissue damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0423] The preparation of such modified nucleic acids, backbones and nucleobases is well known in the art.
[0424] Another modification of the inhibitory nucleic acid featured in the invention involves chemically linking to the inhibitory nucleic acid one or more ligands, moieties or conjugates that enhance the cellular uptake, activity of the iRNA , cellular distribution or pharmacokinetic properties. Such moieties include, but are not limited to: lipid moieties, such as cholesterol moieties (Letsinger et al., Proc. Natl. Acid. Sci. USA, 1989, 86:6553-6556); Let., 1994, 4:1053-1060); thioethers, such as beryl-S-trityl mercaptan (Manoharan et al., Ann.N.Y.Acad.Sci., 1992, 660:306-309; Manoharan et al., Biorg Med.Chem.Let., 1993, 3:2765-2770); Thiocholesterol (Oberhauser et al., Nucl.Acids Res., 1992, 20:533-538); Fatty chains, such as dodecanediol or deca -Alkyl residues (Saison-Behmoaras et al., EMBO J, 1991, 10:1111-1118; Kabanov et al., FEBS Lett., 1990, 259:327-330; Svi...
Embodiment 1
[0581] Example 1: Anti-DEspR therapy in maladaptive neutrophil hyperactivity-mediated pathology
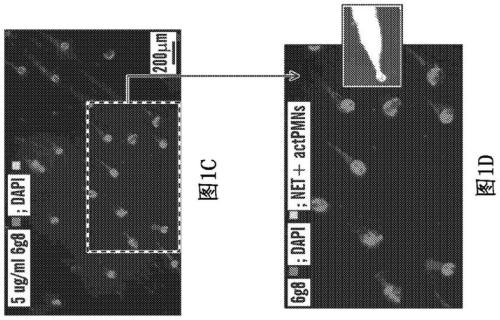
[0582] The present invention relates to anti-DEspR technology that inhibits or abrogates (abrogate) the prolonged survival mechanism in activated neutrophils (IC 50 <8nM), thereby inhibiting all activated neutrophil activity that drives and interacts with other cellular players towards maladaptive pathogenic cascades. The actPMN-driven pathogenicity cascade results in a rapid feed-forward interaction that tends toward disease progression and subsequent debilitating sequelae or death.
[0583] The present invention further relates to compositions comprising DEspR inhibitory compounds and methods of using these DEspR inhibitory compounds for the treatment of disorders or diseases involving induction by activated neutrophils (actPMN) and / or by NETosis , driven and / or propagated pathogenicity cascade.
[0584] Neutrophils are polymorphonuclear cells (PMCs) with 2-5 lobes in their nu...
Embodiment 2
[0659] Example 2: Anti-DEspR mAb Therapy [hu-6g8]: Efficacy-Safety Advantages
[0660] Stabilized S228P IgG4 backbone: efficacy based on receptor blockade rather than ADCC or CDC
[0661] Overview of the rationale and mode of action of anti-DEspR in combination with immunotherapy:
[0662] Complementary mode of action: Inhibition of CSC survival / self-renewal, tumor cell invasiveness, and angiogenesis by anti-DEspR (hu-6g8 or ABT-468) collectively causes a decrease in metastatic dissemination and progression cycles, which complements Immunotherapy immunosurveillance to eliminate tumor cells. This can be seen in the fact that anti-DEspR was more effective in tumor regression in spontaneous mammary tumors in immunocompetent rats than in xenografted pancreatic tumors and glioblastomas in which tumor growth rate was suppressed without regression. Strong ( Figure 16 ) 74 .
[0663] Depletion of activated neutrophils (tumor-associated neutrophils or TAN and circulating neutroph...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com