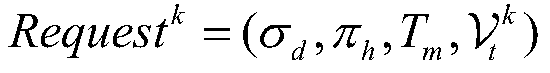Distributed multi-agent task cooperation method based on linear sequential logic
A linear sequential logic, multi-agent technology, applied in data processing applications, instruments, computing, etc., can solve problems such as multi-agent task decoupling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The following describes the robot as an example.
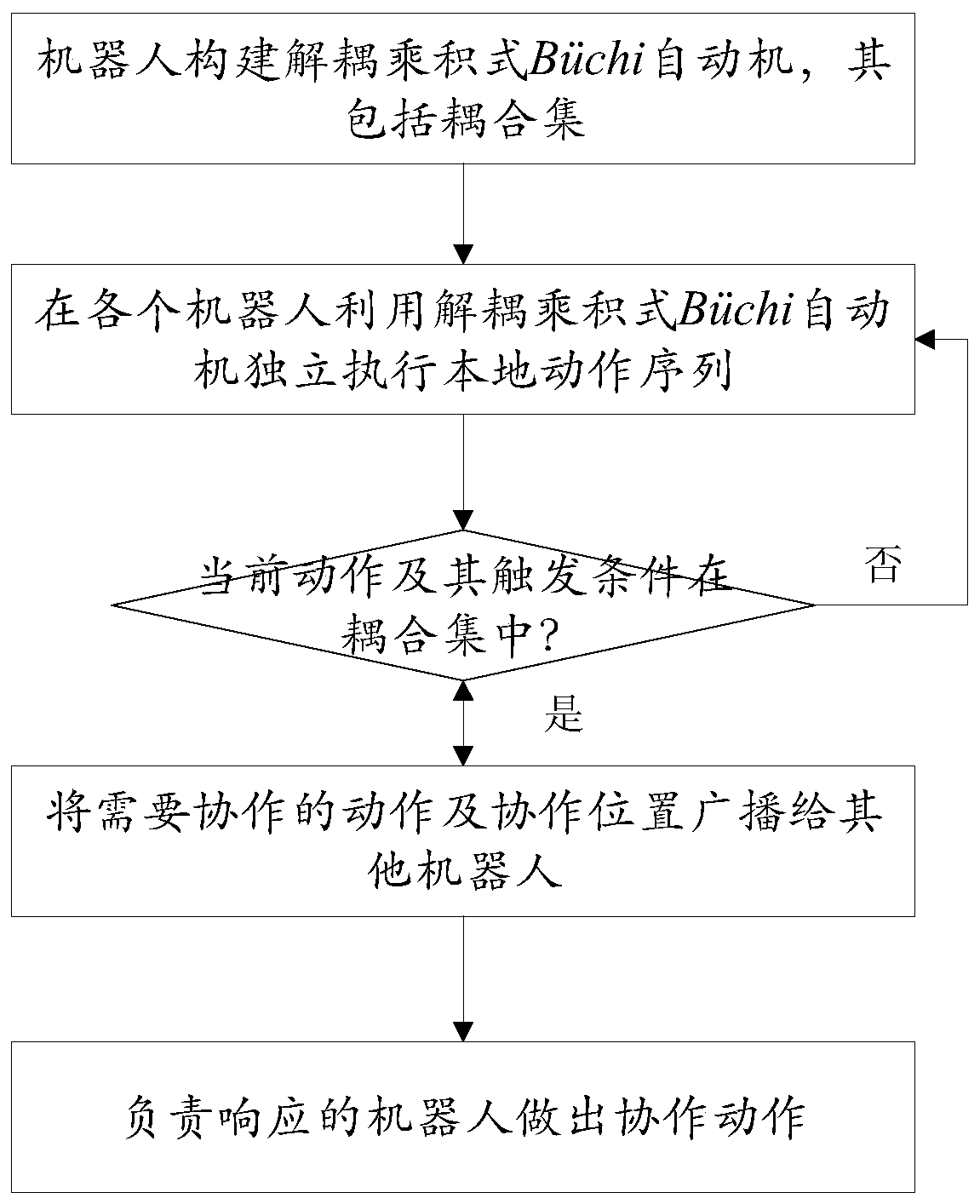
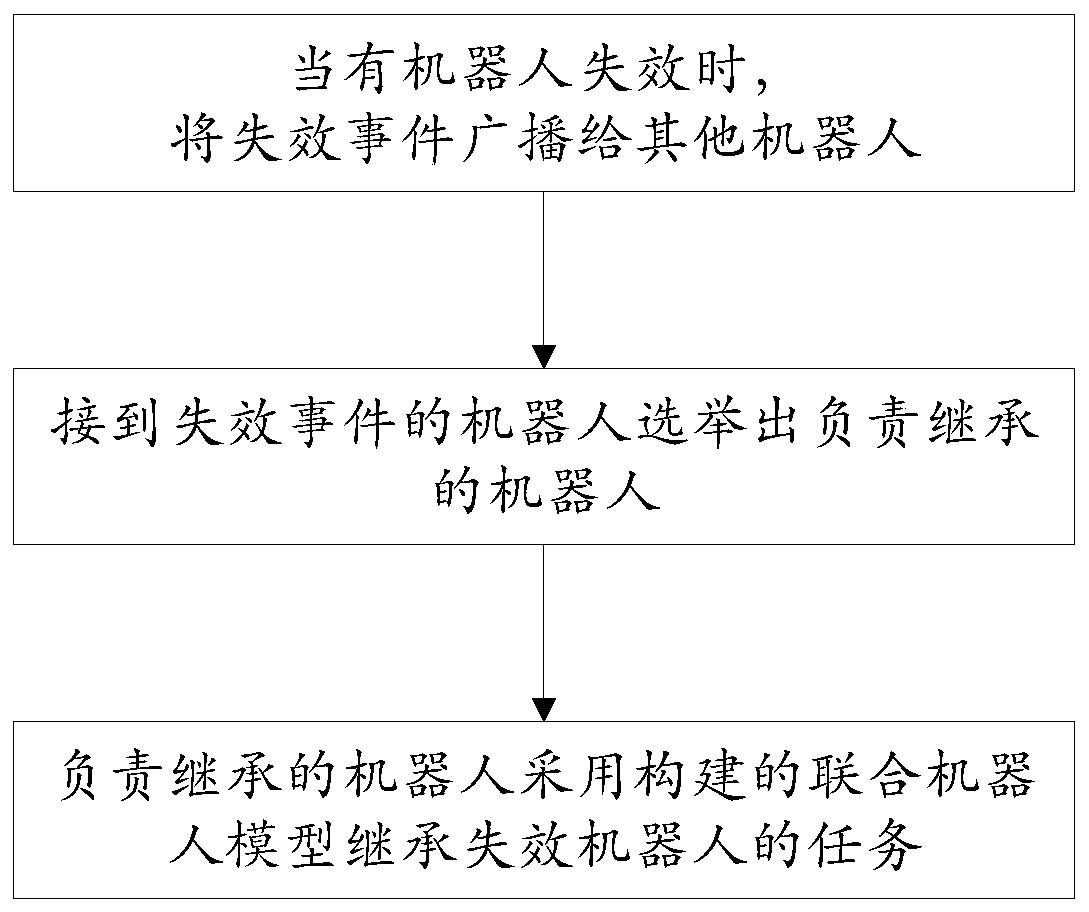
[0044] see figure 1 and figure 2 , the present invention's distributed multi-robot task collaboration method based on linear sequential logic comprises the following steps:
[0045] ●Under normal working conditions, each robot independently constructs its own decoupled product Büchi automaton, and constructs its own action sequence through this automaton. The decoupled product Büchi automata here is the result of adding coupled sets to the product Büchi automata. Coupling edges and their trigger conditions are recorded in the coupling set, and the endpoints of the coupling edges correspond to the actions that need to be coordinated.
[0046] ●When each robot independently executes the local action sequence by using the decoupled product Büchi automaton, judge whether the currently executed action and its corresponding trigger condition are in the coupling set, and if so, the currently executed action is an action th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com