A method for ultra-broadband optical absorption enhancement using composite microstructures
A composite microstructure and light absorption technology, which is applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large depth of microstructure, increased difficulty, and many film logarithms, and achieve high absorption efficiency and excellent broadband light absorption performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1: Visible light to near-infrared band ultra-broadband absorber designed with composite microstructure
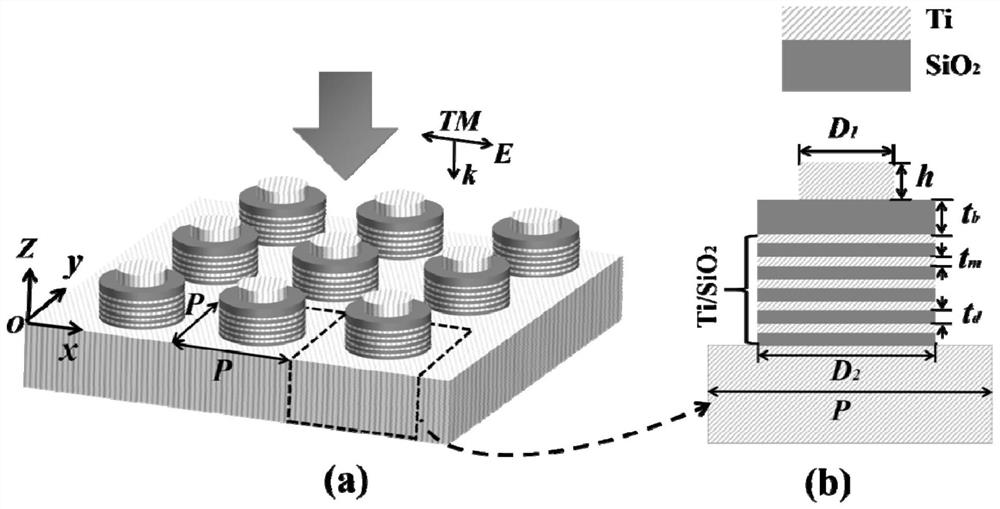
[0025] 11. The composite microstructure is used to design the ultra-broadband absorber in the visible light to near-infrared band. The schematic diagram of its structure is shown in figure 1 shown. The selected metal and dielectric materials are titanium (Ti) and silicon dioxide (SiO 2 ), since the structure is a periodic structure, for a cell, it consists of a Ti cylinder and Ti / SiO 2 Multilayer film cylinders are cascaded, and the diameter of the Ti cylinders is smaller than that of Ti / SiO 2 The diameter of the multilayered cylinder with SiO between the Ti cylinder and the multilayered cylinder 2 Medium buffer layer. The height and diameter of the Ti cylinder are h and D respectively 1 , the thickness and diameter of the buffer layer are t b and D 2 , Ti and SiO in a multilayer film cylinder 2 The thickness is t m and t d , the diameter of the mul...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2: Electric field localization and energy flow distribution of composite microstructures
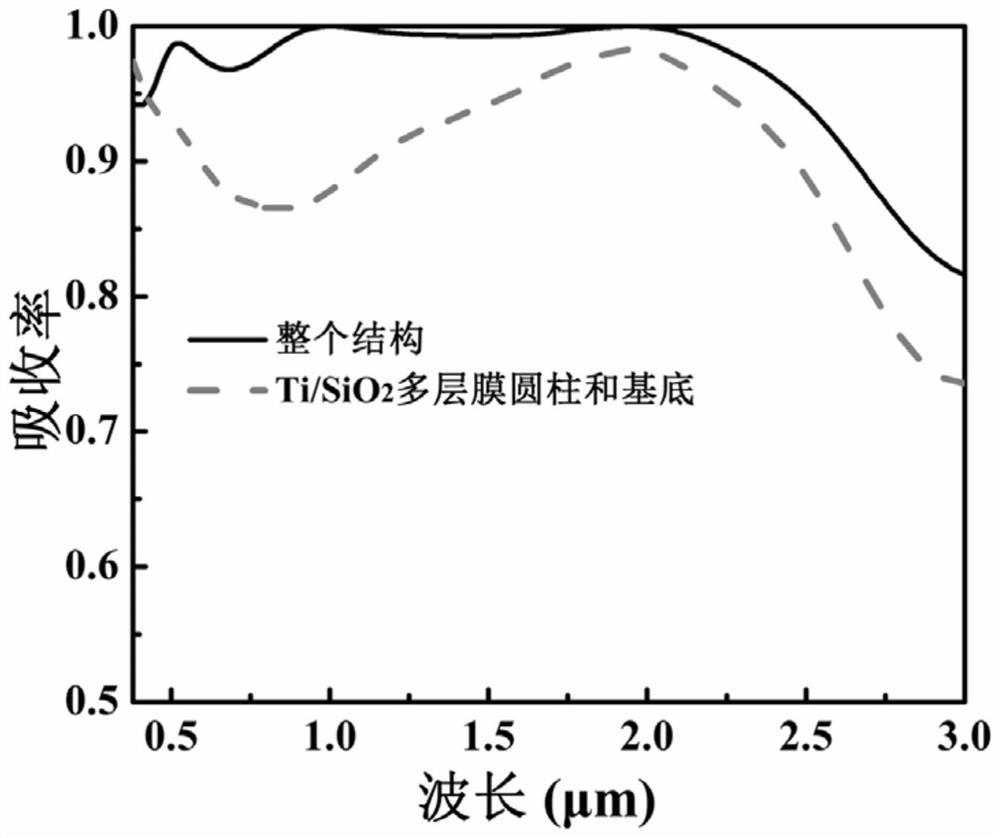
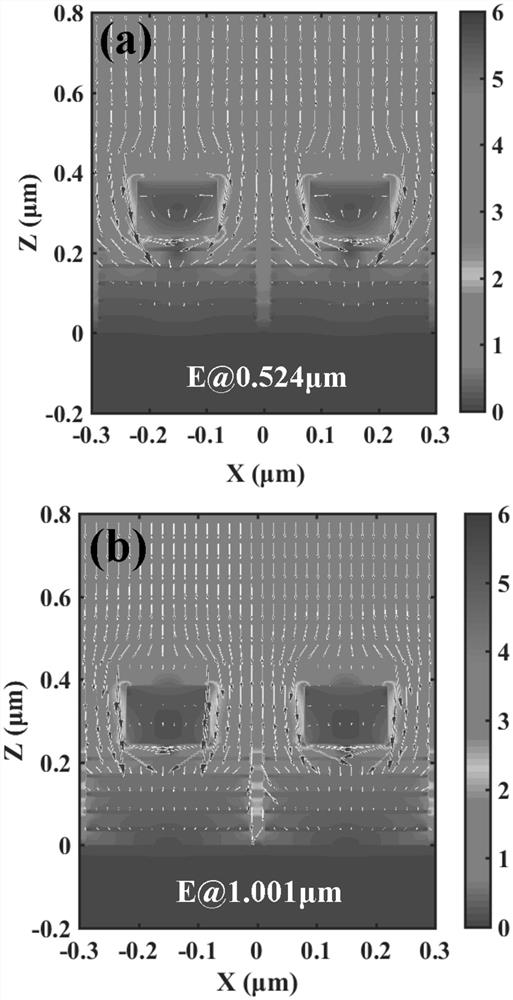
[0029] Based on the calculation results of Example 1, in order to better understand the ultra-broadband strong light absorption mechanism of the structure, the electric field and energy flow distribution at the three resonant absorption peaks were studied. Other parameters of the structure are the same as in Example 1, and the corresponding wavelengths are respectively 524nm, 1001nm, 1952nm, such as image 3 shown.
[0030] from image 3 It can be seen that at short wavelengths (524nm), the electric field is mainly localized around the Ti cylinder and produces significant enhancement, showing a surface plasmon resonance mode, and the incident light field circulates along the surface of the Ti cylinder, thereby causing surface plasmons Enhanced bulk resonance absorption. At the long wavelength (1952nm), the electric field is mainly localized in the cavity between the mul...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3: Effect of Ti cylinder size change on broadband absorption characteristics
[0032] Based on the composite microstructure ultra-broadband absorber of Example 1, under the parameter conditions of Example 1, for the case of normal incidence, the Ti cylinder height h and the Ti cylinder height diameter D are calculated using the finite time domain difference method 1 The absorption spectrum of the absorber when the change occurs, we get Figure 4 .
[0033] like Figure 4 As shown in (a), when there is no Ti cylinder (h = 0), the broadband high absorption performance of the structure is poor. The introduction of Ti cylinders can improve the light absorption efficiency in a wide range of wavelengths, but with the increase of the height of Ti cylinders, the absorption performance tends to be saturated. When the height of the Ti column exceeds 140 nm, the light absorption rate decreases. Therefore, when the height of Ti cylinders is 140 nm, the structure has exc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com