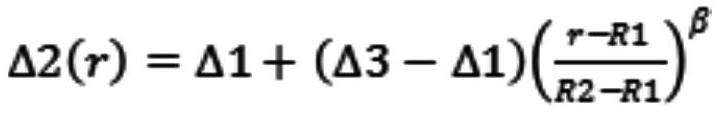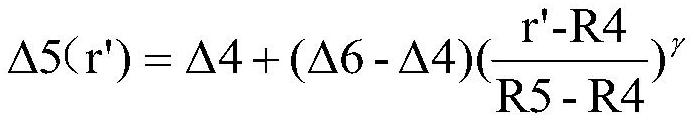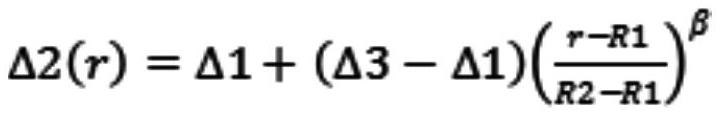A large effective area and low loss single-mode optical fiber
A single-mode fiber, effective area technology, applied in the field of optical communication, can solve the problems of complex doping process, poor fiber strength, difficult concentration control, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing the mode field diameter, reducing stress mutation, and reducing attenuation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0085] The prefabricated inner core rod is prepared by the improved in-tube chemical vapor deposition method MCVD process, and the inner core rod includes: core layer, gradient layer 1, inner cladding layer 1, inner cladding layer 2, gradient layer 2, depression layer, transition layer (the transition layer is doped with F composed of quartz tubes). Use F-doped quartz tube as the deposition substrate tube, SiCl 4 and O 2 for SiO 2 Raw material, SiF 4 , SF 6 、C 2 f 6 or CF 4As a raw material for fluorine doping, GECl 4 As a GE-doped raw material, POCl 3 It is a raw material doped with P; using a hydrogen-oxygen torch moving back and forth as a heat source, by controlling the concentration of each doping element in the tube, the concave layer is sequentially deposited on the inner surface of the substrate tube, and the gradient layer 2, the inner cladding layer 2, the inner cladding layer 1, and the gradient layer 1 and the core layer; then melt the deposition tube to a...
Embodiment 2
[0092] The preparation method is the same as that in Example 1. The improved in-tube chemical vapor deposition method MCVD production process is used to prepare a preform, draw wire, and match the outer tube to obtain an optical fiber. The optical fiber structure includes a core layer, a graded layer 1, an inner cladding layer 1, an inner cladding layer 2, a graded layer 2, a concave layer, a transition layer and an outer cladding layer from the inside to the outside, and the content of doping elements in each layer is shown in Table 1; The layer thicknesses are shown in Table 2.
[0093] Gradient layer 1: Δ2(r)=0.15-0.17×(r-5.8) 0.8 5.8
[0094] Gradient layer 2:
[0095] The performance of the optical fiber obtained in Example 2 was tested, and the results obtained are shown in Table 3.
[0096] As can be seen from Table 2 and Table 3, on the basis of Example 1, the core layer refractive index Δ1 is reduced from 0.20% to 0.15% in Example 2 (the amount of Ge dopin...
Embodiment 3
[0098] The preparation method is the same as that in Example 1. The improved in-tube chemical vapor deposition method MCVD production process is used to prepare a preform, draw wire, and match the outer tube to obtain an optical fiber. The optical fiber structure includes a core layer, a graded layer 1, an inner cladding layer 1, an inner cladding layer 2, a graded layer 2, a concave layer, a transition layer and an outer cladding layer from the inside to the outside, and the content of doping elements in each layer is shown in Table 1; The layer thicknesses are shown in Table 2.
[0099] Gradient Layer 1:
[0100] Gradient layer 2:
[0101] The performance of the optical fiber obtained in Example 3 was tested, and the results obtained are shown in Table 3.
[0102] It can be seen from Table 2 and Table 3 that the core refractive index Δ1 of Example 3 is reduced to 0.12% on the basis of Example 1, the core radius R1 is 6.3 μm, and other structural parameters are basicall...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com