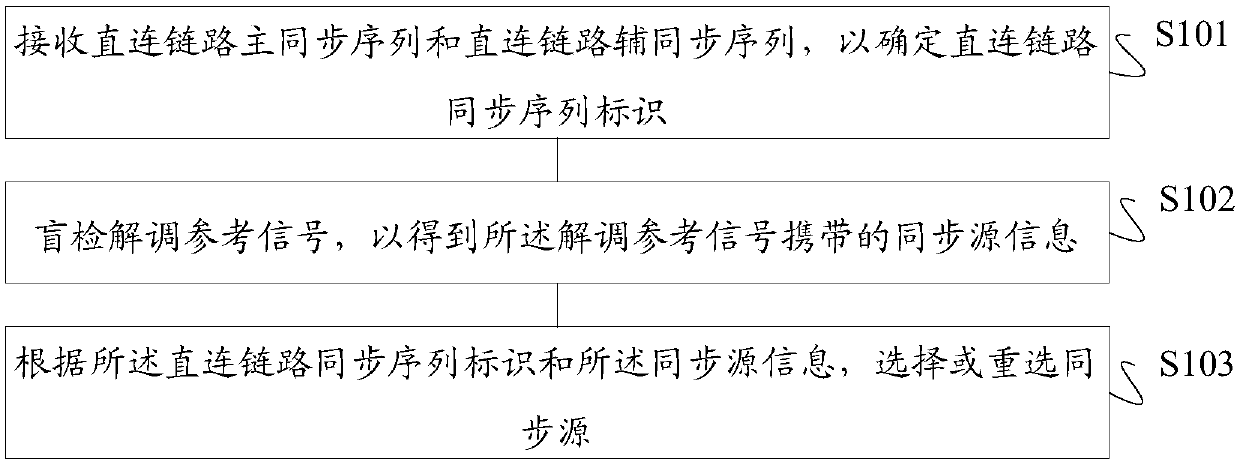
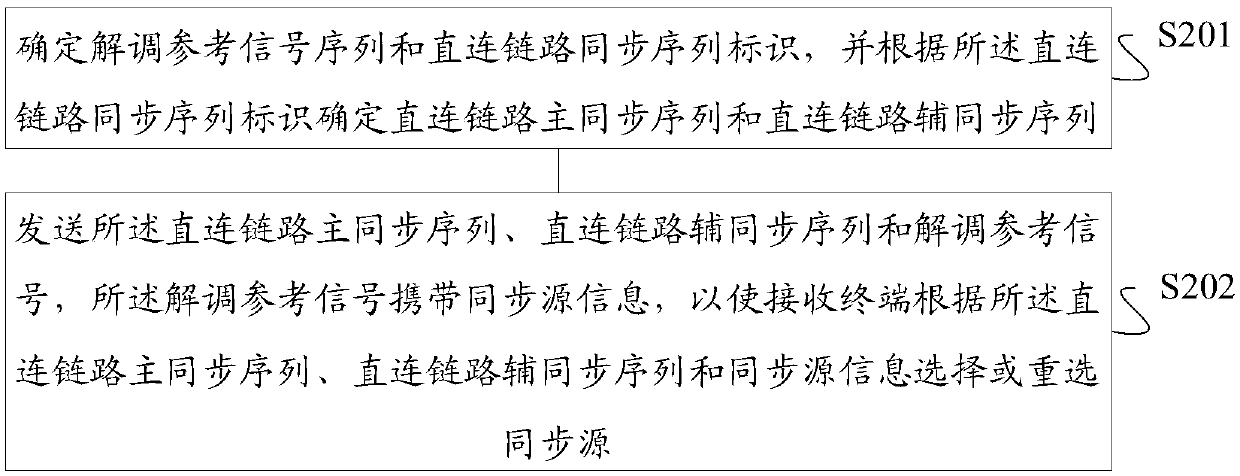
Synchronization source information determination method and device, synchronization source information indication method and device, storage medium and terminal
A technique for determining methods and synchronization sources, applied in synchronization devices, devices dedicated to receivers, wireless communications, etc., can solve problems such as reducing delay and complexity, reduce processing delay, solve PSBCH confusion problems, and reduce Dealing with Complexity Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
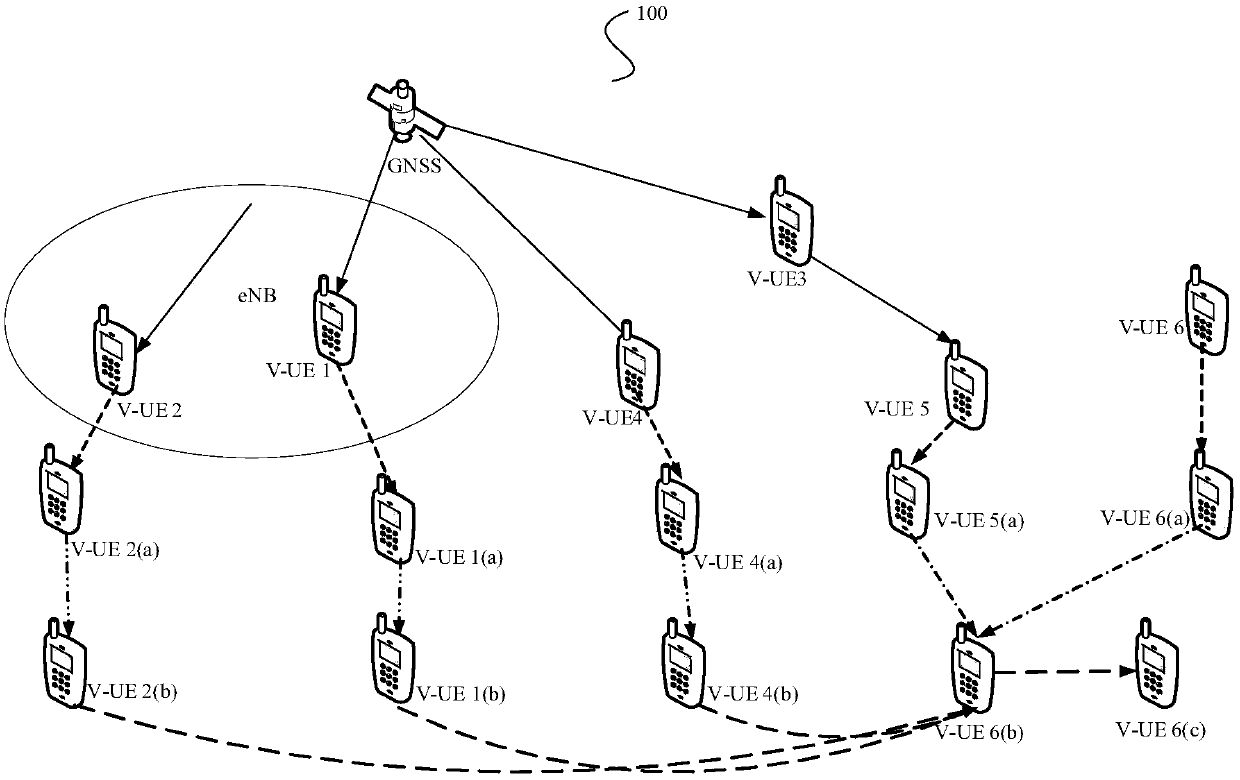
[0099] The synchronization source information carried by the PSBCH DMRS indicates the hop count of the sending terminal.
[0100] The DMRS can carry 3-bit information, as shown in Table 1, each set of bit information corresponds to a DMRS, for example, "000" indicates sequence S0, and "111" indicates sequence S7. Any of these bits can be used to distinguish 1-hop from 2-hop. It is assumed that the lowest bit of the DMRS is used to indicate 1-hop or 2-hop, a bit value of 1 indicates 1-hop, and a bit value of 0 indicates 2-hop. Then, 1-hop can be represented by 001, 011, 101, 111; 2-hop can be represented by 000, 010, 100, 110. Further, the remaining upper two bits of the DMRS may be used to indicate the SSB index, and the SSB index value may be determined according to the actually transmitted S-SSB.
[0101] Table 1
[0102] bit information 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 DMRS sequence S0 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7
[0103] For example, for 1-ho...
specific Embodiment 2
[0114]If the NR V2X design does not identify the hop count information through the SLSSID, then the hop count information can be carried through the DMRS, that is, the hop count information of the sending terminal can be carried through the DMRS. In the specific implementation, it is assumed that the nth hop (denoted as n-hop), the (n+1)th hop (denoted as n+1-hop), and the (n+2)th hop (denoted as n+2-hop) The SLSSIDs of the V-UEs are the same, but the priorities are different, then it is necessary to distinguish the hop count information through an additional indication to determine the priority. At this time, the hop count of the sending terminal may be carried by using the DMRS. If n-hop and n+1-hop need to be distinguished, 1-bit carrying in DMRS may be used. Taking the lowest bit of DMRS as an example, n-hop corresponds to 000, 010, 100 or 110; n+1-hop corresponds to 001, 011, 101 or 111. If more hops need to be distinguished, 2-bit or 3-bit DMRS can be used to carry the...
specific Embodiment 3
[0116] The location of the transmitting terminal synchronized to GNSS can be indicated through the synchronization source information carried by the PSBCH DMRS, that is, the DMRS is used to distinguish whether the V-UE synchronized to GNSS is a GNSS-IC V-UE or a GNSS-OOC V-UE. The DMRS can still carry 3-bit information, and the lowest bit of the DMRS is used to indicate GNSS-IC or GNSS-OOC. When the bit value of the lowest bit is 0, that is, 000, 010, 100 or 110, it indicates that the V-UE is located in GNSS-OOC, and its SL-MIB information is determined by pre-configured parameters; when the bit value of the lowest bit When it is 1, that is, 001, 011, 101 or 111, it indicates that the V-UE is located in the GNSS-IC, and its SL-MIB information is configured by the base station. At this time, the V-UE sending the SLSS as the synchronization source may determine the bit value of the position of the sending terminal synchronized to the GNSS as the bit value of the synchronization ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com