Rotor Pole Segmented Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor and Its Electromagnetic Vibration Weakening Method
A technology for permanent magnet synchronous motors and rotor poles, applied to synchronous motors with stationary armatures and rotating magnets, synchronous machines, and parts of synchronous machines, which can solve the problem of weakening the cogging torque and torque ripple of permanent magnet motors Electromagnetic vibration, unfavorable motor high-precision control occasions, increased difficulty and cost of industrial manufacturing, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing electromagnetic vibration, reducing processing costs, and low processing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
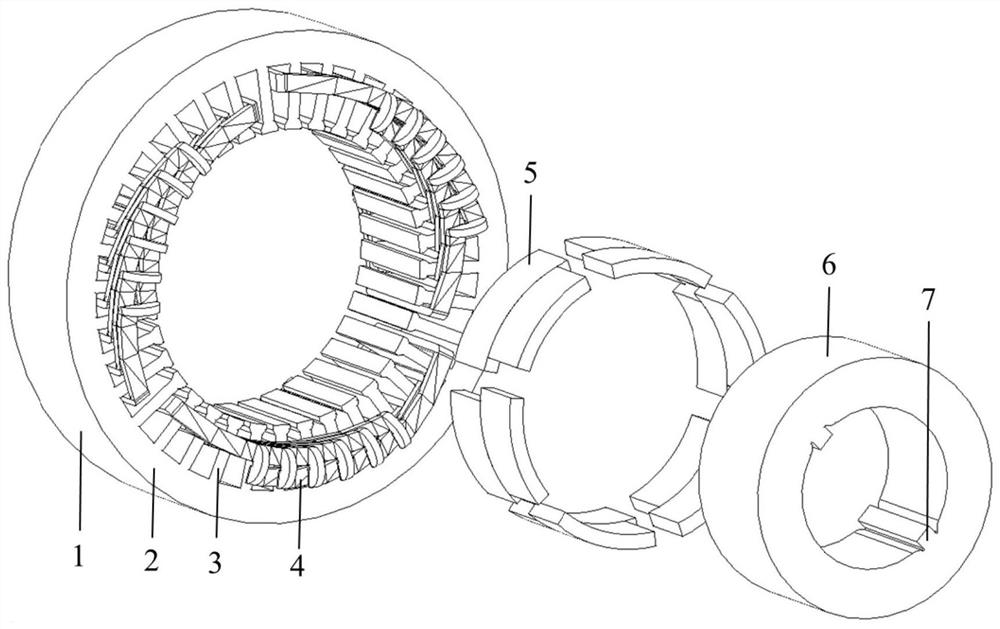
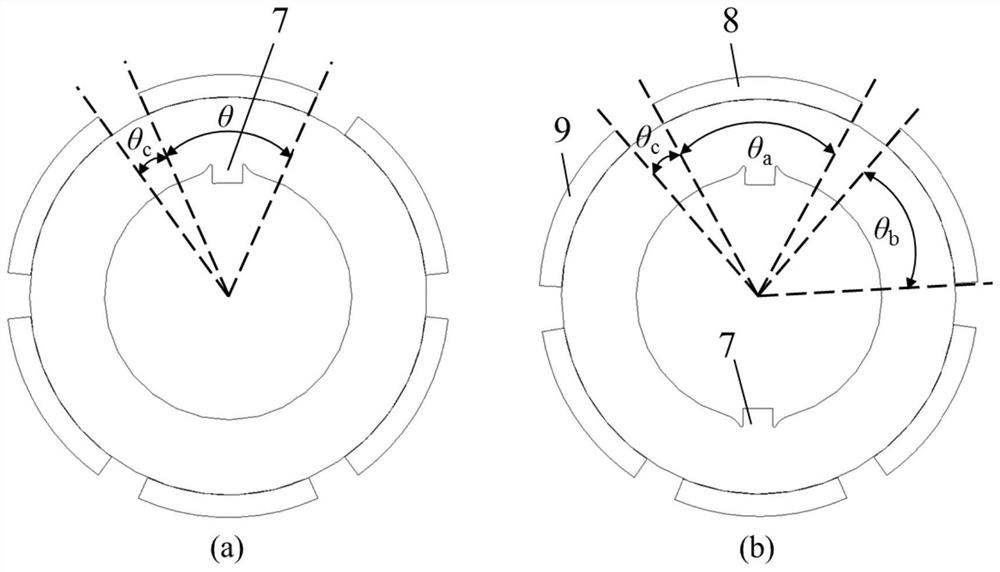
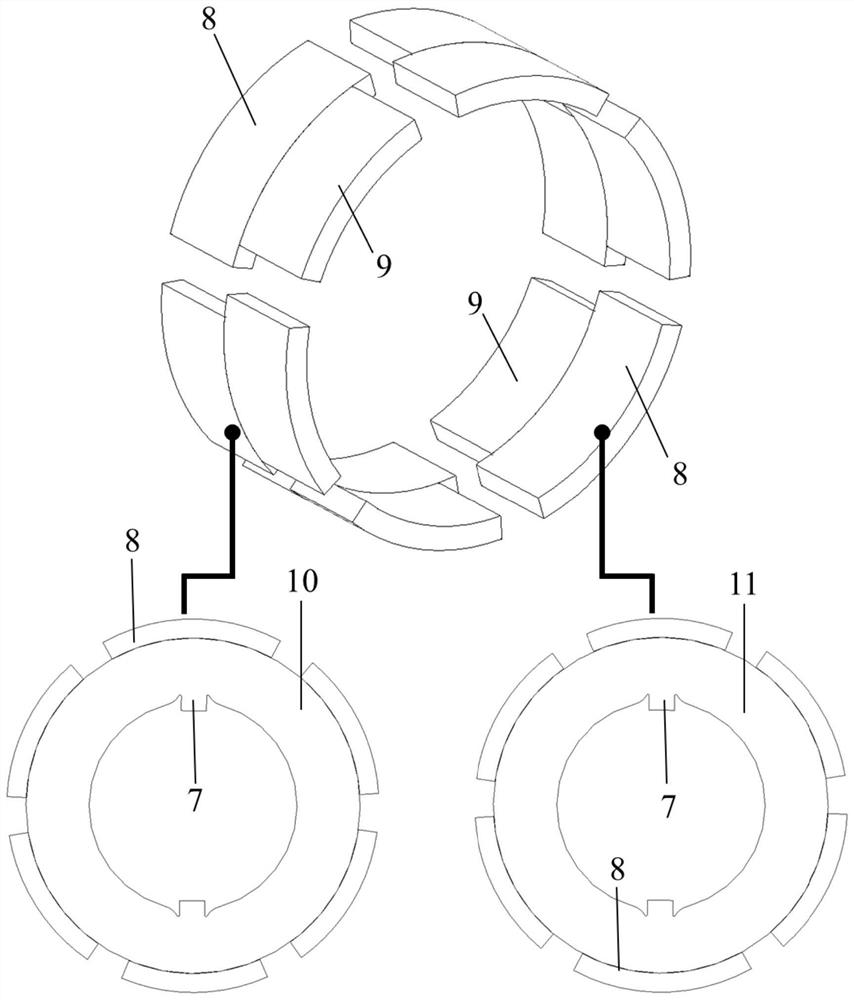
[0078] like Figure 1-Figure 8 As shown, the number of motor poles in this embodiment is 6, and the number of stator slots is 36. This embodiment includes a stator 1, permanent magnet rotors 10 and 11, and armature windings 4. The permanent magnet rotors 10 and 11 include a rotor core 6 and permanent magnet 5, the stator 1 is provided with a stator slot, the armature winding 4 is placed in the stator slot, the permanent magnet rotors 10 and 11 are arranged concentrically with the stator 1, and the permanent magnet rotor is divided into two parts along the axial direction. The two sections 10 and 11 have six permanent magnets 5 placed on the rotor surface of each section, and the pole arc width corresponding to one permanent magnet 8 in the six permanent magnets 5 is different from the pole arc width corresponding to the other permanent magnets 9 In this embodiment, the pole arc width corresponding to the permanent magnet 8 is greater than the pole arc width corresponding to th...
Embodiment 2
[0086] like Figure 9-Figure 16 As shown, the number of motor poles in this embodiment is 6, and the number of stator slots is 36. This embodiment includes a stator 1, permanent magnet rotors 10 and 11, and armature windings 4. The permanent magnet rotors 10 and 11 include a rotor core 6 and permanent magnet 5, the stator 1 is provided with a stator slot, the armature winding 4 is placed in the stator slot, the permanent magnet rotors 10 and 11 are arranged concentrically with the stator 1, and the permanent magnet rotor is divided into two parts along the axial direction. There are two sections 10 and 11, and six permanent magnets 5 are placed on the rotor surface of each section.
[0087] Among the six permanent magnets 5 , the pole arc width corresponding to one permanent magnet 8 is different from the pole arc width corresponding to the other permanent magnets 9 . In this embodiment, the pole arc width corresponding to the permanent magnet 8 is smaller than the pole arc w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com