A strain of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis and its application in the preparation of soybean milk
A technology of Lactococcus lactis and lactic acid subspecies, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of less research on the flavor quality of sour milk, and achieve the effects of improving quality characteristics, increasing content, and reducing content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: Method for isolation and identification of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactic acid CCFM 1092 strain
[0036] (1) Prepare appropriate sample dilution gradient and culture
[0037] The Yunnan Dali milk glycerol samples stored in the -80°C refrigerator were taken out and thawed on ice. After shaking and mixing, take 0.5mL sample and add it to 4.5mL sterile normal saline to complete a 10-fold dilution to 10 -1 , shake and mix well, then take out 0.5mL of the diluent and add it to 4.5mL of sterile saline to complete the second 10-fold dilution to 10 -2 , and so on, until diluted to 10 -6 , draw 100 μL from each gradient dilution, evenly spread it on the MRS solid medium plate, invert it, place it under anaerobic culture at 37°C for 36-48 hours, and observe it in time.
[0038] (2) Line separation and purification
[0039] After taking out the plate with colony growth, select the gradient plate with obvious single colony, pick the colonies with different colony f...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2: Growth characteristics of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactic acid CCFM 1092 in soybean milk
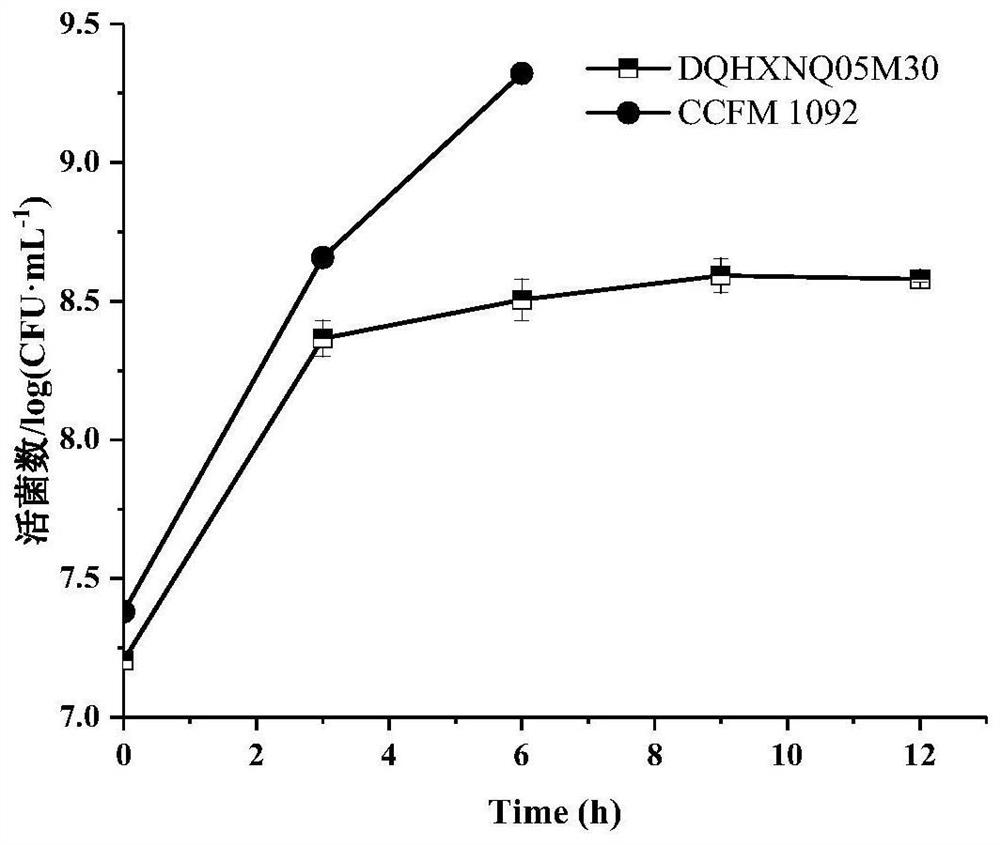
[0059] Inoculate Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis CCFM 1092 of the present invention stored at -80°C in liquid MRS medium, and after culturing at 30°C for 24 hours, inoculate it into fresh liquid MRS medium at an inoculum size of 2% (v / v) Medium, carry out subculture, subculture 2 to 3 times, to 10 8 ~10 9 cfu / mL. Take out the activated bacterial solution in MRS and inoculate it in soybean milk at a volume ratio of 2% to 4%, so that the number of viable bacteria in the system reaches 10 6 ~10 7 cfu / mL. Put the inoculated samples into an incubator at 37°C for fermentation, take samples every 3 hours, and detect the changes in the number of viable bacteria during the fermentation process. The results are as follows: image 3 shown. Depend on image 3 It can be seen that the number of live bacteria of the strain CCFM 1092 increased by 1.94 orders of magnitude after...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3 Acid-producing properties of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactic acid CCFM 1092 in soybean milk
[0061] Inoculate Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactic acid CCFM 1092 of the present invention stored at -80°C in MRS medium, culture at 30°C for 24 hours, and subculture 2 to 3 times until 10 8 ~10 9 cfu / mL. Take out the activated bacterial solution in the MRS and inoculate it in soybean milk at a volume ratio of 2% to 4%, so that the number of viable bacteria in the system reaches 10 7 cfu / g. Put the inoculated sample into an incubator at 37°C for fermentation, and take samples every 3 hours to detect the change of pH during the fermentation process. The experimental results are as follows: Figure 4 As shown, the pH of strain CCFM1092 dropped to 4.64 after 6 hours of fermentation, reaching the end of fermentation (soymilk fermentation reached the end of fermentation when the pH was 4.5-4.7), so the strain CCFM 1092 had a faster acid production rate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com