Method for treating oxytetracycline fungi residues
A treatment method and technology of oxytetracycline, applied in the fields of organic fertilizer, climate change adaptation, waste fuel, etc., can solve the problems of secondary environmental pollution, long treatment period, large floor space, etc., to prevent pollution, eliminate toxicity, To achieve harmless effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
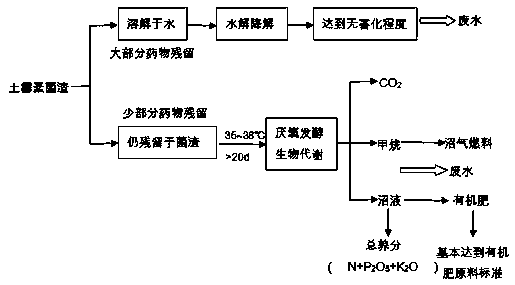
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, adopt the following method to process oxytetracycline bacteria residue:
[0033] (1) Use the alkali-hydrothermal method to pretreat the bacterial residue, inject a certain amount of water into the bacterial residue and stir evenly, adjust the moisture content to about 98%, and filter out the insoluble coarse residue, add 0.08-0.12 to the filtrate g / gTS NaOH solution, heat at 80-120°C for 2 hours, and discharge the supernatant after solid-liquid separation.
[0034] (2) Anaerobic digestion treatment of oxytetracycline bacteria residue, the solid residue after the treatment in step (1) was added to the single-stage UASB anaerobic reactor, which was pre-filled with 20.8g / L anaerobic activated sludge, and the load 1.5 kgVS / m3·d, stirred and fermented at 35-38°C for 20-30 days, and part of the biogas and biogas slurry produced by the fermentation was backfilled into the UASB reactor for cyclic fermentation.
Embodiment 2
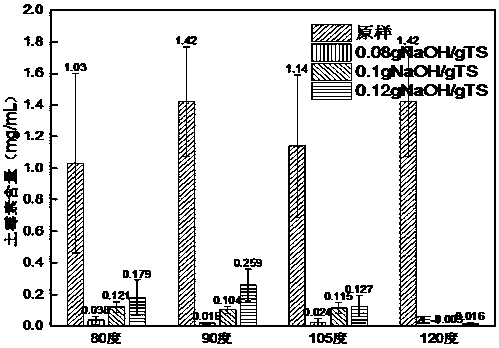
[0036] The effects of different temperatures and NaOH dosages on the removal rate of oxytetracycline in oxytetracycline residue in step (1) of Example 1 were determined. In order to avoid chance and make the research results more convincing, no less than 10 repeated experiments were carried out for each reaction condition, and the results of each group were averaged, and the corresponding graphs were drawn.
[0037] Experimental results such as figure 2 , image 3 shown. figure 2 It is the change of oxytetracycline content in bacterial residue before and after alkali-hydrothermal treatment at different temperatures and NaOH dosages. Before treatment, oxytetracycline content was >1mg / mL, and after treatment, the reduction effect was obvious. image 3 It is the reduction rate of oxytetracycline in bacterial residues before and after alkali-hydrothermal treatment at different temperatures and NaOH dosages. The higher the temperature is, the higher the reduction rate is, while...
Embodiment 3
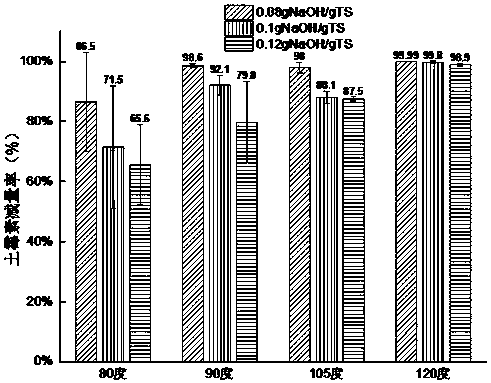
[0039] The effects of different temperatures and NaOH dosages on TS in oxytetracycline residue in step (1) of Example 1 were determined. In order to avoid chance and make the research results more convincing, no less than 10 repeated experiments were carried out for each reaction condition, and the results of each group were averaged, and the corresponding graphs were drawn.
[0040] Experimental results such as Figure 4 , Figure 5 shown. Figure 4 is the change of TS content in the fungal residue before and after alkali-hydrothermal treatment at different temperatures and NaOH dosages, Figure 5is the reduction rate of TS in the fungal residue before and after alkali-hydrothermal treatment at different temperatures and NaOH dosages. It can be seen from the figure that the TS before treatment is about 18000~20000mg / L, and after treatment, it all decreases, and the lowest reduction rate is 5 %about. As the reaction temperature increases, the TS reduction rate basically sh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com