Multi-channel tissue scaffold, and preparation method and application thereof
A tissue scaffold and multi-channel technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, methods of supporting/immobilizing microorganisms, tissue culture, etc., can solve the problem that organ donation cannot meet the needs of clinical patients, poor mechanical properties of three-dimensional cell culture, and unsuitable Long-term large-scale cultivation and other issues to achieve good biocompatibility, rapid manufacturing, and high through-hole porosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] Example 1 Polyglutamic acid multi-channel tissue scaffold
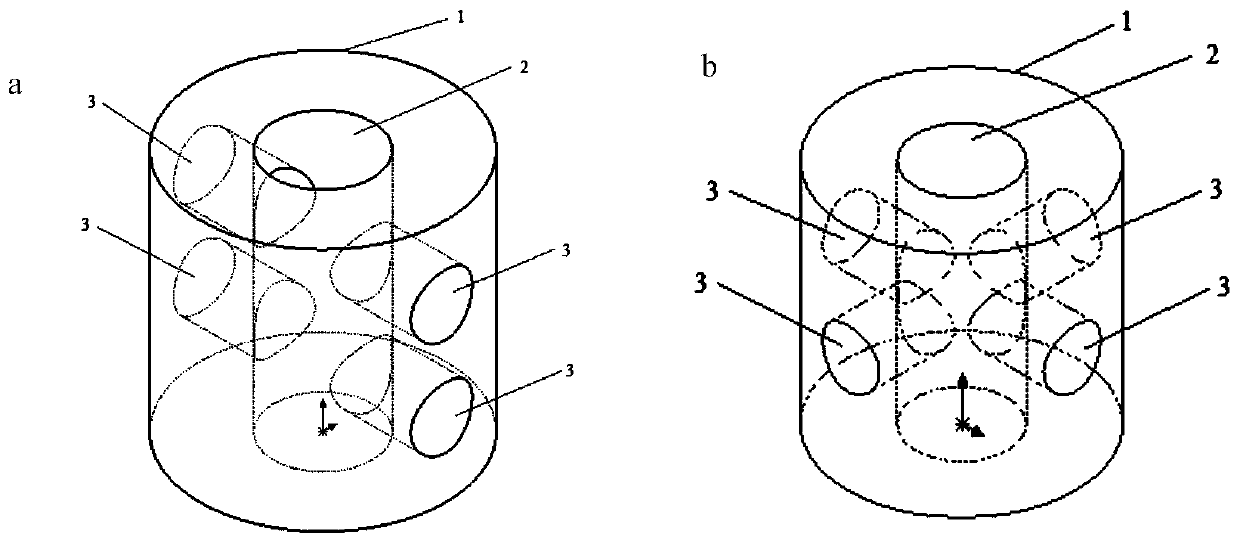
[0074] This embodiment provides a multi-channel tissue support, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a tissue support body 1, the top of the body 1 has a hollow first channel 2, and the side of the body also has at least one hollow second channel 3, and the first channel 2 is connected to the first channel 2. Two channels 3 are vertical; the body 1 is a porous structure; the material of the body 1 is polyglutamic acid (PGA, the molecular weight is about 150,000). The number of the second channels is 4, parallel to each other. . The diameter (outer diameter) of the multi-channel tissue scaffold described in this embodiment is 1100 μm, and the height is 1000 μm; the diameter of the first channel is about 300 μm, and the diameter of the second channel is about 250 μm. The porosity is 60%.
[0075] The polyglutamic acid (PGA) is tested for cell adhesion, cytotoxicity and mechanical properties, and it is found...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Example 2 polycaprolactone multi-channel tissue scaffold
[0093] Compared with Example 1, the only difference is that the material of the tissue support body is polycaprolactone (PCL).
[0094] Experiments have found that using PCL as the main implementation material also has good biodegradability and biocompatibility, and can be widely used in products such as controlled-release drug carriers, cells, tissue culture scaffolds, and surgical sutures.
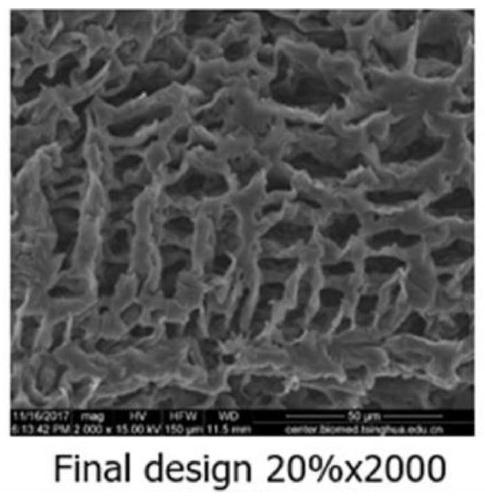
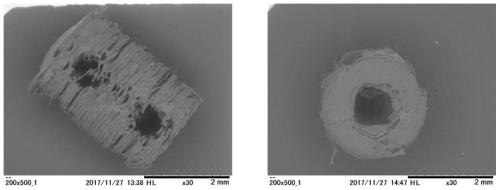
[0095] The internal structure of the tissue scaffold prepared in this embodiment is as follows: image 3 shown. image 3 The through holes inside the bracket can be clearly observed in the figure.
Embodiment 3
[0096] Example 3 Poly-L-lactic acid multi-channel tissue scaffold
[0097] This embodiment provides a tissue support, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a tissue support body 1, the top of the body 1 has a hollow first channel 2, and the side of the body also has at least one hollow second channel 3, and the first channel 2 is connected to the first channel 2. The two channels 3 are vertical; the body 1 is a porous structure; the material of the body is poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA for short). The number of the second channels is 4. The porosity of the body is around 93.5%. The diameter (outer diameter) of the stent is 2000 μm, and the height is 2000 μm; the diameter of the first channel is about 800 μm, and the diameter of the second channel is about 600 μm. The porosity of the tissue scaffold body is 93.5%.
[0098] This embodiment also provides a preparation method for the above-mentioned tissue scaffold, comprising the following steps:
[0099] 1) Build a three-dimens...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com