SPCP infrared weak and small target detection method based on 3DATV constraints
A technology of weak and small targets and detection methods, applied in image data processing, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve problems such as poor adaptability, weak edge suppression, and low noise robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
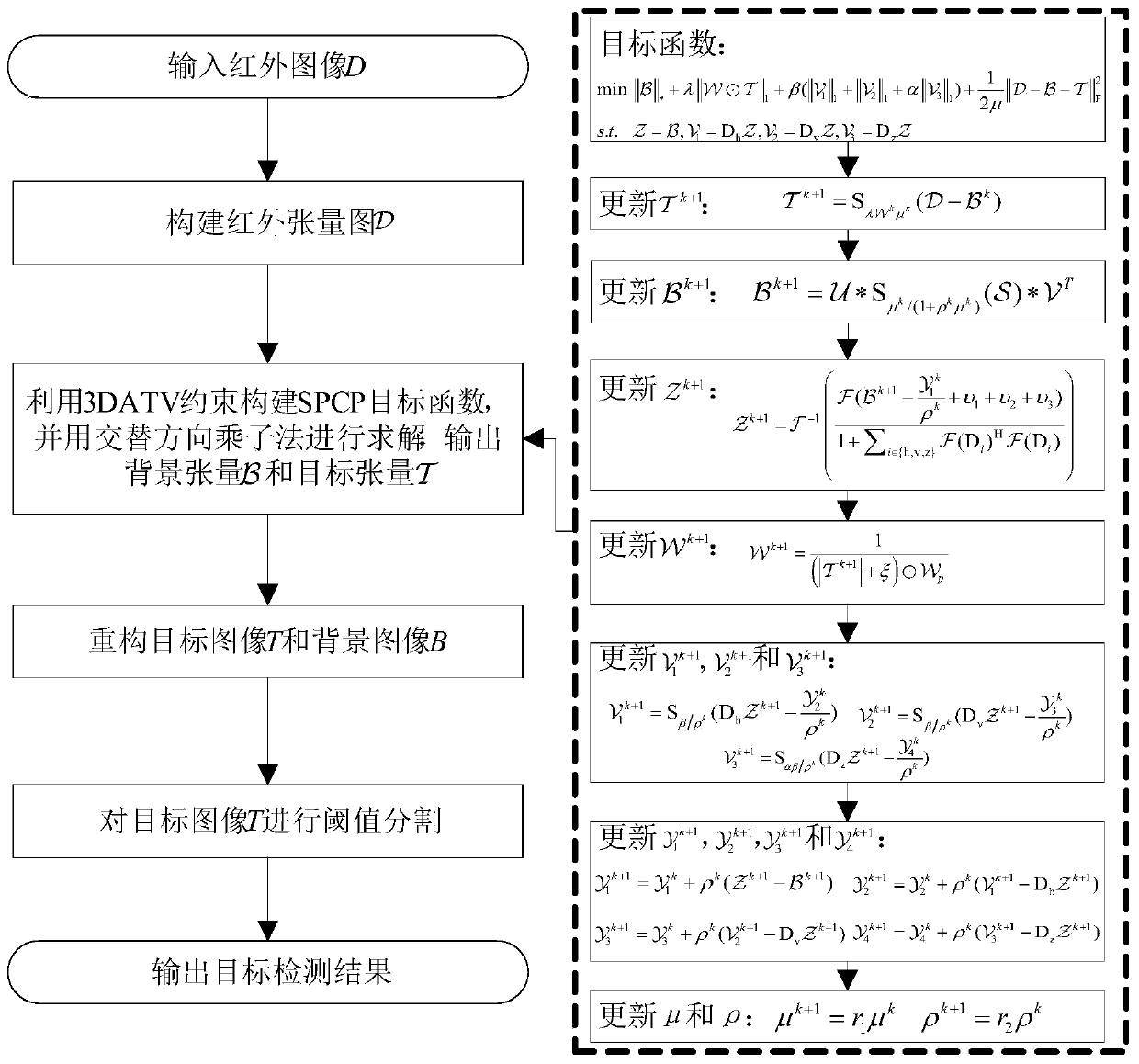
[0126] Such as Figure 1-11 As shown, the SPCP infrared faint target detection method based on 3DATV constraints includes the following steps:
[0127] Step 1: Construct the third-order tensor of the original image D
[0128] Step 2: Extract the prior information of the original image D and construct the prior weight tensor
[0129] Step 3: Use Tensor Kernel Function||·|| * and tensor l 1 Norm, combined with three-dimensional anisotropic total variation (3DATV) constraints, constructs an objective function, transforms the original target detection problem into a stable principal component tracking (Stable Principle Component Pursuit, SPCP) problem, and uses ADMM Solve the objective function to obtain the background tensor and the target tensor
[0130] Step 4: According to the background tensor and the target tensor Reconstruct the background image B and the target image T;
[0131] Step 5: Carry out adaptive threshold segmentation on the target image T to det...
Embodiment 2
[0135] Based on Embodiment 1, the steps of this application are refined, and the technical means adopted to solve technical problems are recorded in detail: using tensor kernel function||·|| * and tensor l 1 Norm, combined with three-dimensional anisotropic total variation (3D Anisotropic TotalVariation, 3DATV) constraints, construct the objective function, transform the original target detection problem into a stable principal component tracking (Stable Principle Component Pursuit, SPCP) problem, and use ADMM Solve the objective function to obtain the background tensor and the target tensor.
[0136] Step 1 includes the following steps:
[0137] Step 1.1: Acquire the infrared image to be processed (raw image) The size is 140×220;
[0138] Step 1.2: Use a sliding window w with a size of 40×40 to traverse the original image D with a step size of 40, and use the matrix with a size of 40×40 in each sliding window w as a frontal slice;
[0139] Step 1.3: Repeat step 1.2 accor...
Embodiment 3
[0203] Based on embodiment 1, this embodiment refines step 2, extracts the prior information of the original image, constructs the prior information weight tensor, and utilizes the prior information related to the background and the target to ensure that the target is not distorted, which speeds up the algorithm. The convergence speed also improves the robustness of the algorithm.
[0204] Step 2 includes the following steps:
[0205] Step 2.1: Define the structure tensor of the original image D J ρ It is defined as follows:
[0206]
[0207] Among them, K ρ Indicates the Gaussian kernel function with variance 2, * indicates the convolution operation, D σ Indicates that the Gaussian smoothing filter with a variance of 9 is performed on the original image, represents the Kronecker product, Indicates the gradient, means D σ the gradient along the x direction, means D σ Gradient along the y direction, J 11 replace J 12 Substitute K ρ *I x I y , J 21 Subs...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com