Method for converting source codes into numeric identifiers and comparison against data sets
An identifier and code technology, applied in the field of code processing and data technology, to simplify database search and reduce data occupied space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
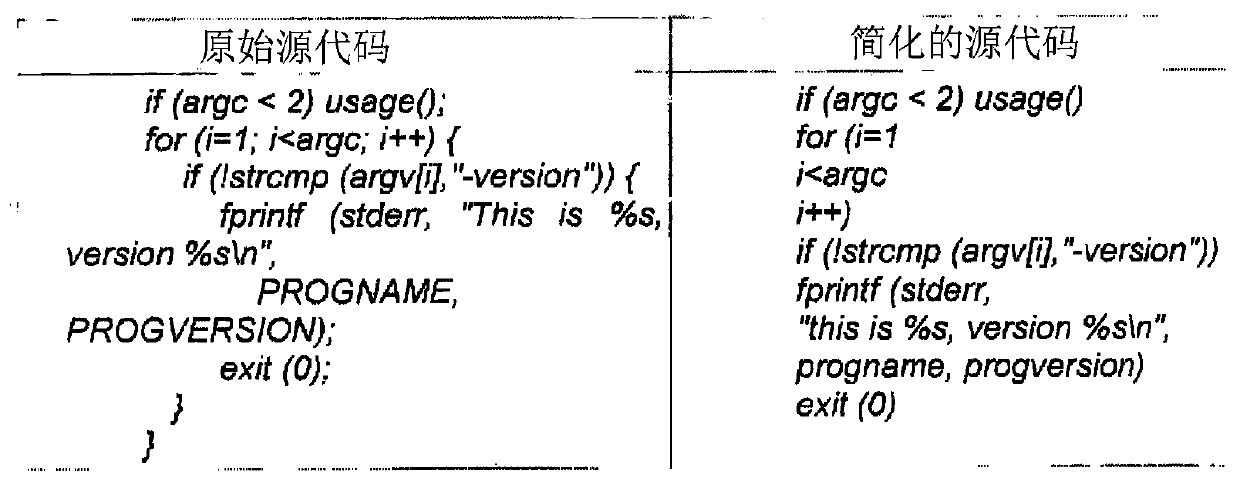
[0014] Embodiments described herein allow source code to be compared to datasets without requiring a copy of the original source code for those datasets. These implementations also allow row ID generation and database searching to be separated at different locations. Thus, the individual performing the database search does not need access to the code being compared, only the generated row ID. This logical isolation allows database searches to be done without access to the original code or the original source code for comparison.
[0015] Additionally, due to the fact that searches are performed against a fixed-length balanced index, the embodiments described herein allow for a reduced storage footprint by saving only code snippet IDs (not source code) from large datasets, as well as reduced processing time and faster Search responses, which are a result of the uniform data distribution nature provided by cryptographic hashing algorithms.
[0016] The term "large dataset" is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com