Method for point-to-point matching between non-rigid three-dimensional models
A three-dimensional model, non-rigid technology, applied in 3D modeling, character and pattern recognition, details involving 3D image data, etc., can solve problems affecting the accuracy of final matching, achieve superior computing efficiency and stability, and compact structure , matching the exact effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
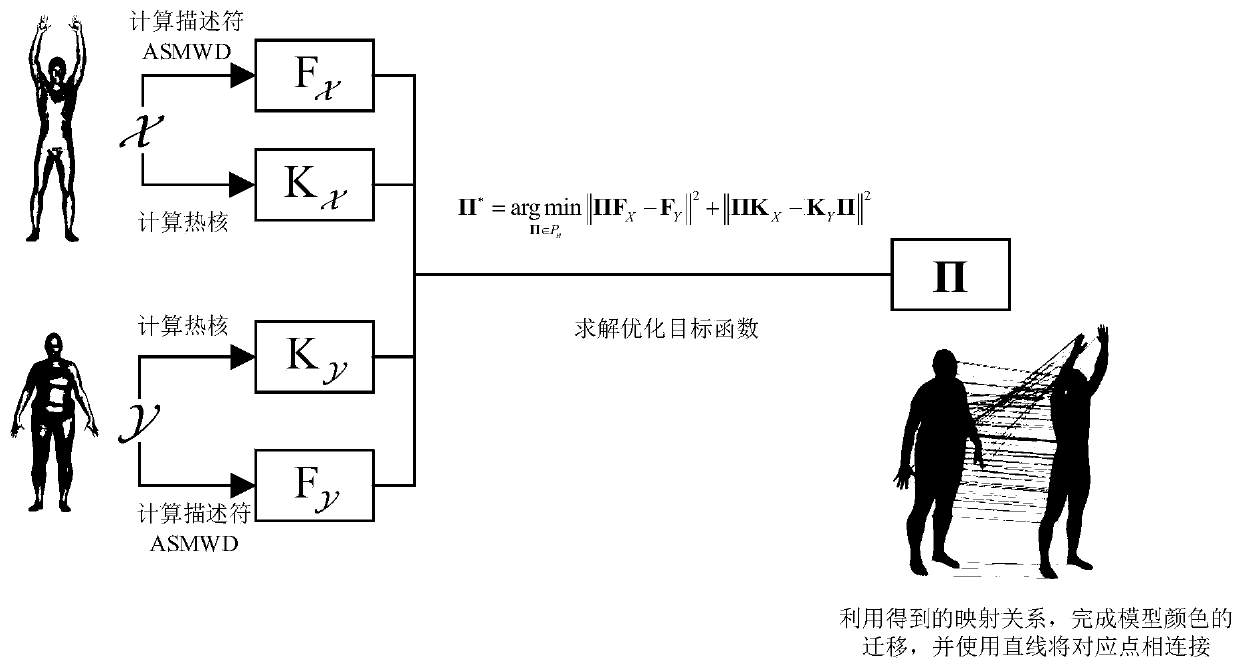
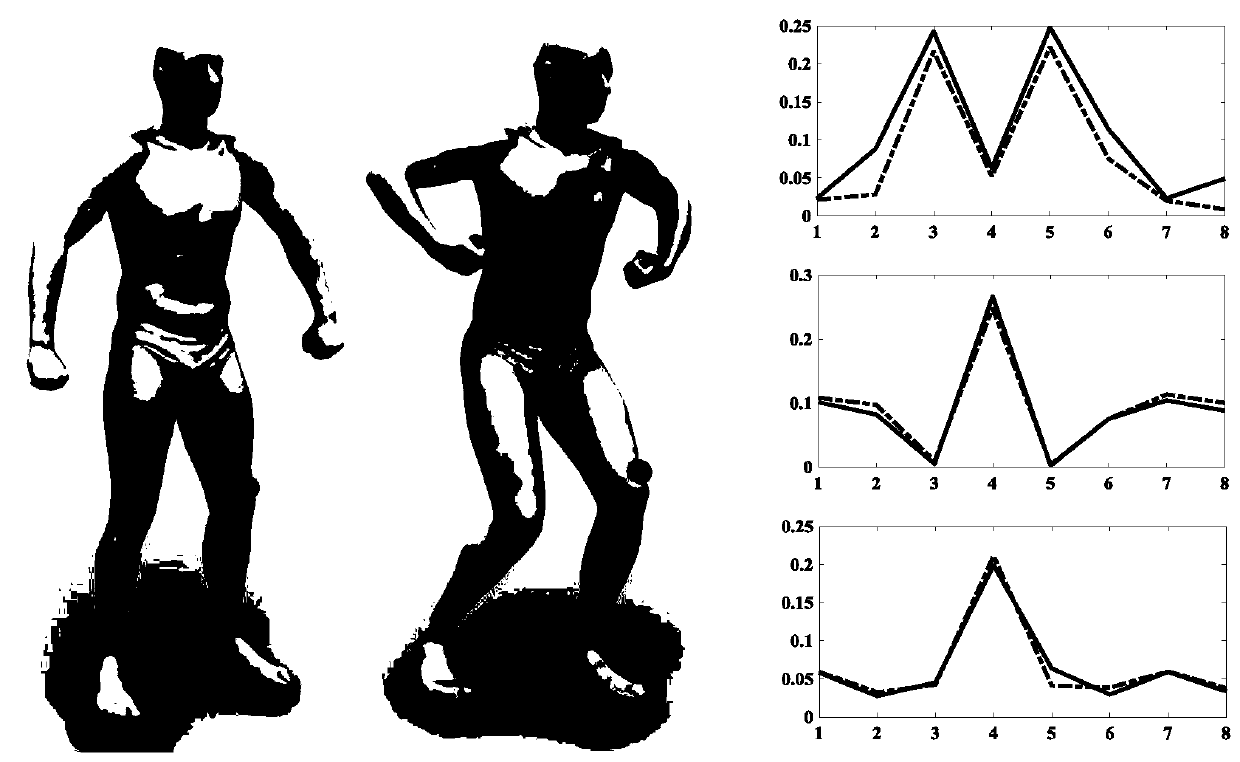
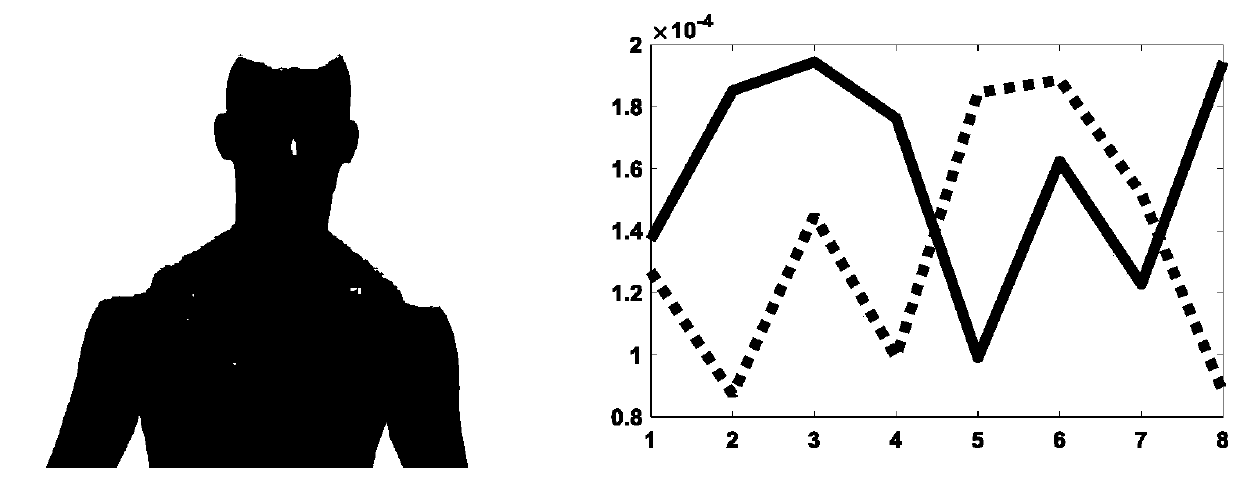
[0039] The high-performance 3D model matching method disclosed in this embodiment is called ASMWD-PMF (product manifold spatial filtering based on anisotropic spectral manifold wavelet descriptor). The matching between models with approximately isometric deformation can be realized very accurately, the calculation efficiency of the method is high, and the performance is far superior to the existing matching method, which can provide important technical guarantee for the subsequent application of the three-dimensional model.
[0040] Such as figure 1 As shown, in specific implementation, the detailed calculation steps are:
[0041] 1. Establish anisotropic spectral manifold wavelet descriptor.
[0042] The algorithm of the descriptor can be divided into the following three steps:
[0043] 1.1 Calculate the anisotropic Laplace-Belthem matrix and its eigendecomposition of the model;
[0044] First calculate the anisotropic Laplacian-Belter Mi operator, and generally express th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com