Ecological cultivation method for grapes
A cultivation method and grape technology, applied in the field of viticulture, can solve the problems of plant burns, poor soil air permeability, drying and death, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing effective time, reducing use, and reducing pests and diseases.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: Heat 500 parts of distilled water to 80-95 ° C, adjust the pH of the aqueous solution to 4-5, dissolve 0.5-1 part of matrine, 5-8 parts of polyvinyl alcohol and 1-2 parts of chitosan according to the amount Spray-dry in distilled water to prepare a composite insecticide with a particle size of 5-10 μm.
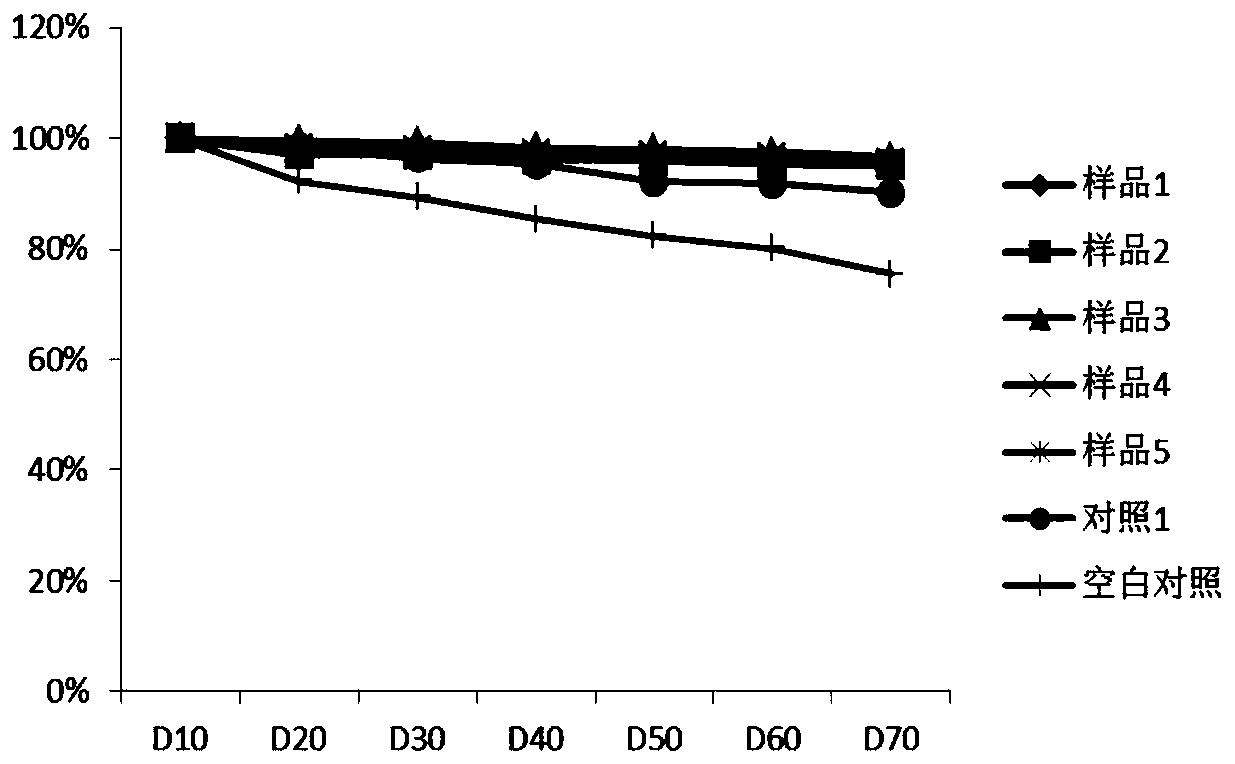
[0038] Table 1 Investigation of insect control effect of compound insecticides
[0039] components sample 1 sample 2 sample 3 Sample 4 Sample 5 Matrine 3 5 4 4.5 3.5 polyvinyl alcohol 5 8 6 6 8 Chitosan 1 2 1.5 1.2 1
[0040] Take 0.3% matrine water as control 1, dilute 0.3% matrine water 800 times, focus on spraying on the middle and upper young leaves of grape plants, and the active ingredients of matrine applied in the remaining samples 1-5 and Contrast 1 is the same, distilled water is used as blank control, investigates the morbidity rate of grape plant from flowering stage to ripe stage, the results...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2: During the leaf spreading period, the difference between the daytime temperature in the shed and the nighttime temperature in the shed affects the quality of the grapes. The blank control is the grapes grown at natural temperature. The rest of the treatment conditions are the same, and the chlorophyll content of the grape plants after entering the expansion period is measured. , the survey results of different varieties of grapes are shown in Table 2. From the results in Table 2, it can be seen that the stress resistance of grapes can be significantly improved, the growth of grape plants can be increased, and the grape Chlorophyll content in leaves.
[0043] Table 2 Effect of low temperature stimulation on grape growth
[0044]
Embodiment 3
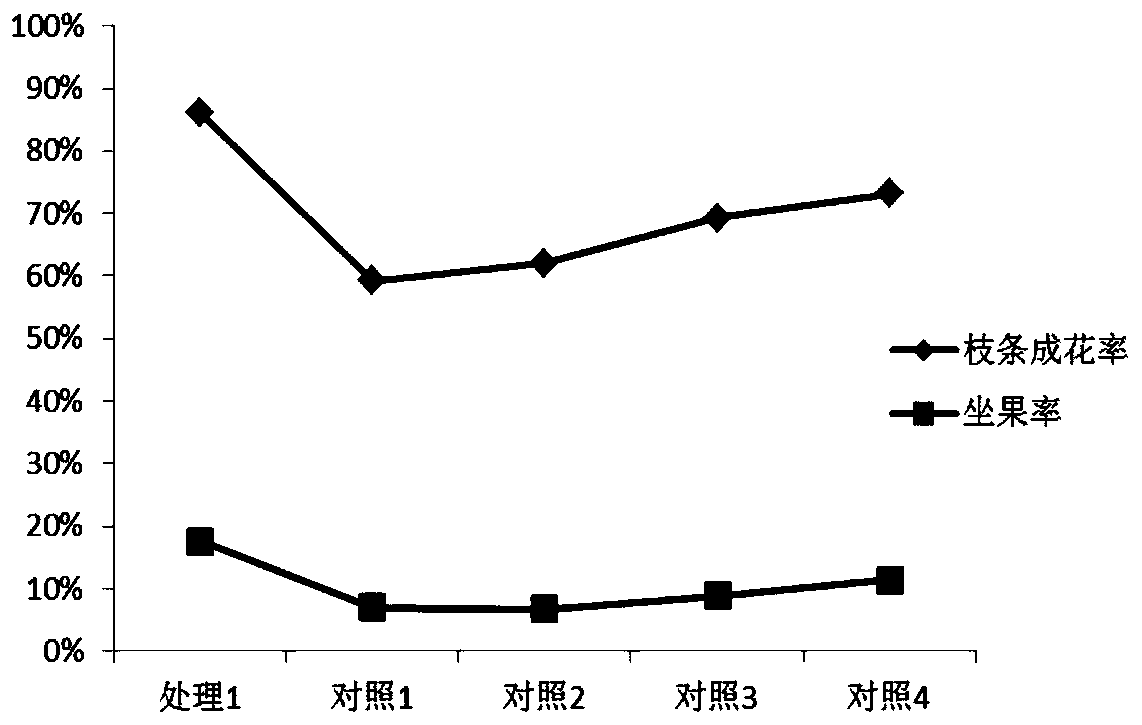
[0045] Embodiment 3: the microbial bacterial fertilizer and calcium superphosphate are mixed in a mass ratio of 2:1, the microbial bacterial fertilizer is 10kg / mu, and the amount of calcium phosphate is 5kg / mu; At the bottom of the hole, spread urea on the upper layer of microbial fertilizer. The mass ratio of urea and microbial fertilizer is 1:1. Each grape is 20g of microbial agent, and urea is 20g / plant; the control is the amount of calcium phosphate used alone 5kg / mu, 10kg / mu, 15kg / mu, 20kg / mu and the rest are the same. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0046] Table 3 Effects of different fertilizer spraying at the budding stage on flowering and fruit setting rate of Sunshine Rose branches
[0047]
[0048]
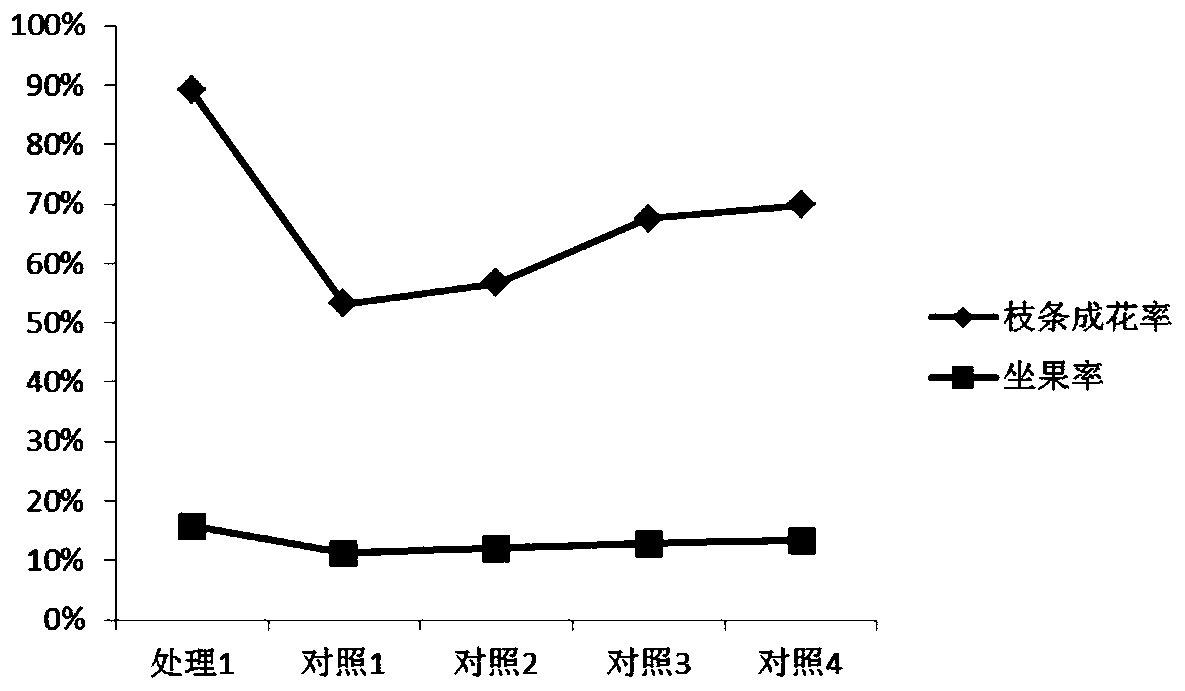
[0049] Table 4 Effects of different fertilizer spraying at the germination stage on the flowering and fruit setting rate of Xiahei branches
[0050]
[0051] As can be seen from the results of Table 3 and Table 4, in the present invention, when calcium ph...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com