Bait feeding method for improving survival rate of loach fries
A technology of bait feeding and survival rate, which is applied in the field of bait feeding to improve the survival rate of loach seedlings, can solve the problems of low survival rate of loach seedlings, and achieve the effects of rapid growth, high economic benefits, and rapid weight gain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
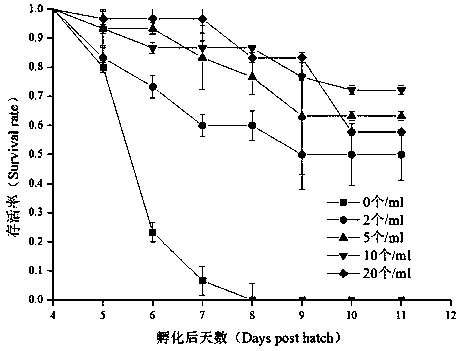
[0026] Embodiment 1 (rotifer feeding density test)
[0027] Cultivation and collection of rotifers: Use a glass aquarium (50cm*40cm*27cm) for indoor cultivation of rotifers, wash the aquarium clean, add an appropriate amount of boiled water, and the water temperature is 25±1°C. The rotifer bait is chlorella pyrenoidosa, and it is fed twice a day, according to the amount of 300,000 cells of chlorella that a rotifer ingests per day, and the amount of bait can be adjusted according to the water color. After each feeding, stir gently to increase the dissolved oxygen in the water. After 3-5 days of cultivation, the density of rotifers reaches 100-200 / mL, which can be collected for future use. Use 80-100 mesh sieves to make small-capacity net cages, fix the net cages with wooden frames, and tie them tightly. Put the net cages on a plastic bucket, use siphon method to suck out the pool water, flow into the net cages for filtration, and carry out wheeling. Worm collection.
[0028]...
Embodiment 2
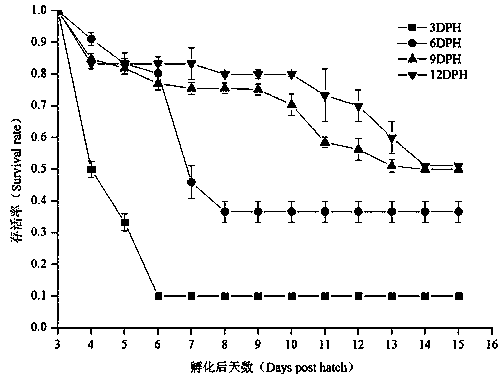
[0034] Example 2 (Live bait optimal time conversion test for larvae)
[0035] The experiment was divided into 5 groups (A~E), each group was set up 3 parallel, and 30 fish were placed in each box. Different conversion time treatment: 3rd, 6th, 9th, 12th day after hatching. The test time was 12 days in total, and the animals were fed once every day at 8: 00-9: 00 and 17: 00-18: 00, and the amount of feeding was slightly surplus. Use the siphon method to suck out the feces, residual bait, dead seedlings and other dirt in the aquarium every afternoon, and change the water at the same time. The amount of water changed each time is about 1 / 4 to 1 / 3 of the total water volume, and the temperature difference of the water does not exceed ±1°C , the survival rate of loach larvae fed Artemia at different post-hatching times is shown in Table 2 and figure 2 shown.
[0036] Such as figure 2As shown, the survival rate of loach larvae in different treatment groups: 3DPH0.05). The 3DPH...
Embodiment 3
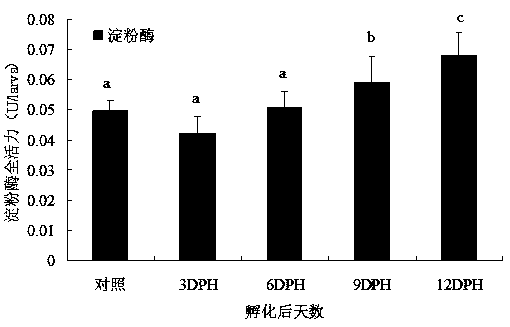
[0041] Example 3 (Test of switching from live bait to compound feed)
[0042] The experiment was divided into 5 groups (A~E), each group was set up 3 parallel, and 30 fish were placed in each box. Different conversion time treatment: 16th, 18th, 20th, 24th, 30th day after hatching. The test time was 34 days in total, and the animals were fed once every day at 8:00-9:00 and 17:00-18:00, and the amount of feeding should be slightly surplus. Use the siphon method to suck out the feces, residual bait, dead seedlings and other dirt in the aquarium every afternoon, and change the water at the same time. The amount of water changed each time is about 1 / 4 to 1 / 3 of the total water volume, and the temperature difference of the water does not exceed ±1°C , the growth and survival rate of loach larvae at different conversion times from live bait to compound feed are shown in Table 3 and Figure 5 shown.
[0043] Table 3 The growth of loach larvae under different conversion times from ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com