Application of tea saponin in killing of aquatic harmful organisms in Apostichopus japonicus breeding
A technology for predatory organisms and tea saponin, applied in the field of aquaculture, can solve the problems of adverse effects on the ecological environment and product safety, cumbersome processing technology, little progress, etc. High killing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Qingdao National Marine Science Research Center Aquatic Seedling Industrialization Base Experiment
[0044] (1) The experimental container is a 60L sorting box. Each box is put into a corrugated basket with 50 glass ascidians and 30 ginseng seedlings. Oxygenation, water temperature 21.2 ℃, salinity 33.
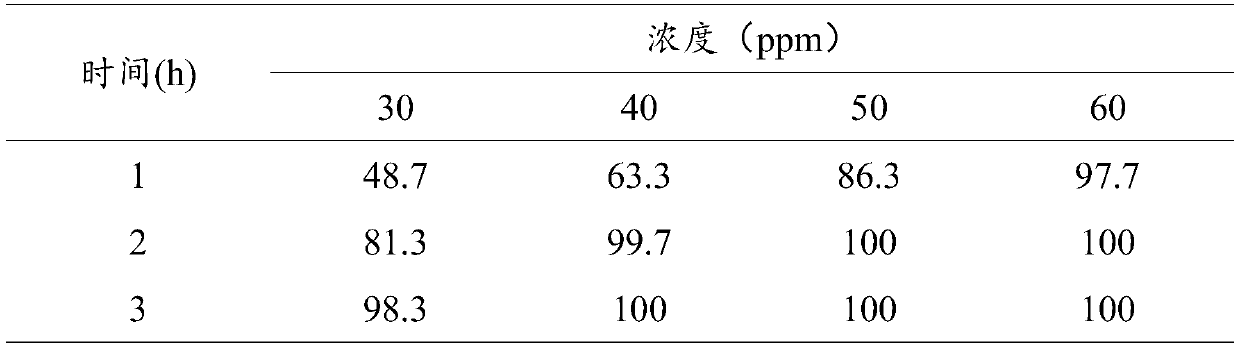
[0045] (2) Set up four tea saponin concentration groups of 30ppm, 40ppm, 50ppm, and 60ppm respectively, and set up three parallel groups for each group.
[0046] (3) The ginseng seedlings were adapted to the medicated bath for 48 hours, stopped eating 1 day before the medicated bath, and stopped oxygenation during the medicated bath.
[0047] (4) After the medicated bath, the water outlet holes of the Ciona opened, and after death, the rucksack was wrinkled, inelastic, unresponsive to artificial stimulation, or attached to the board or fell off to the bottom of the box. The vitality of the ginseng seedlings in each group was normal, the spines did not shrink, and the ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Experiment of a sea cucumber breeding company in Hongdao
[0053] (1) The implementation site is 3 cement cultivation ponds, and the size of the cement pond is 15m 3 / pond, the size of the ginseng seedlings cultured in the pond is 5g / head to 25g / head, and the diameter of the epiphytic Ciona is mostly greater than 5mm. Oxygenation is performed for 24 hours, the water temperature is 23.4°C, and the salinity is 32.
[0054] (2) Set three tea saponin concentrations of 40ppm, 50ppm and 60ppm respectively.
[0055] (3) Dissolve the tea saponin powder in seawater 2-3 days before use, filter it through a 200-mesh sieve, and put it in the refrigerator for later use.
[0056] (4) Splash the whole pool at 7 o'clock in the morning on the day of the medicinal bath, and pour the pool after 2 hours of stopping gas. The killing rates of Ciona in the three cultivation pools were 98%, 100%, and 100%, respectively.
[0057] (5) After changing the water and pouring the pool, sprinkle the ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Experiment of a sea cucumber breeding company in Penglai
[0060] (1) The test site is 3 cement cultivation ponds, and the size of the cement pond is 20m 3 / pool, the size of japonicus seedlings in the pool is 1g / head to 20g / head, and the diameter of the epiphytic Ciona is mostly less than 5mm. Oxygenation is carried out for 24 hours. The water temperature is 22.8°C and the salinity is 33.
[0061] (2) Set three tea saponin concentrations of 30ppm, 40ppm and 50ppm respectively.
[0062] (3) Dissolve the tea saponin powder in seawater 2-3 days before use, filter it through a 200-mesh sieve, and put it in the refrigerator for later use.
[0063] (4) Splash the whole pond at 9 o'clock in the morning on the day of the medicinal bath, and pour the pond after stopping the gas for 3 hours. The killing rates of Ciona in the three cultivation ponds were 99%, 100%, and 100% respectively.
[0064] (5) After changing the water and pouring the pool, sprinkle the ginseng seedlings...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com