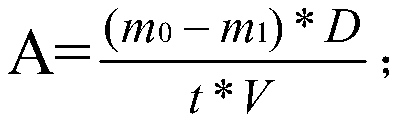Method for reducing starch digestibility and application thereof
A digestibility and starch technology, applied in the field of enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of low production efficiency and low efficiency, and achieve the effect of high production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Example 1: Preparation of different branching enzymes
[0056] Specific steps are as follows:
[0057] Chemical synthesis encodes the glycogen branching enzyme ChlGBE derived from Chlorella kessleri (the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1), and the glycogen branching enzyme HosGBE derived from Homo sapiens (the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1). ID NO: 2), glycogen branching enzyme VvGBE derived from Vibrio vulnificus (amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3), starch branching enzyme derived from cyanobacteria (Cyanothece sp.ATCC 51142) CySBE (amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 4) or the gene of starch branching enzyme RoSBE (amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 5) derived from Rhodothermus obamensis (nucleotide sequence, respectively) (As shown in SEQ ID NO:6, SEQ ID NO:7, SEQ ID NO:8, SEQ ID NO:9, SEQ ID NO:10), and connect the synthesized gene and pET-24a(+) plasmid , Get the recombinant plasmid pET-24a-ChlGBE, pET-24a-HosGBE, pET-24a-...
Embodiment 2
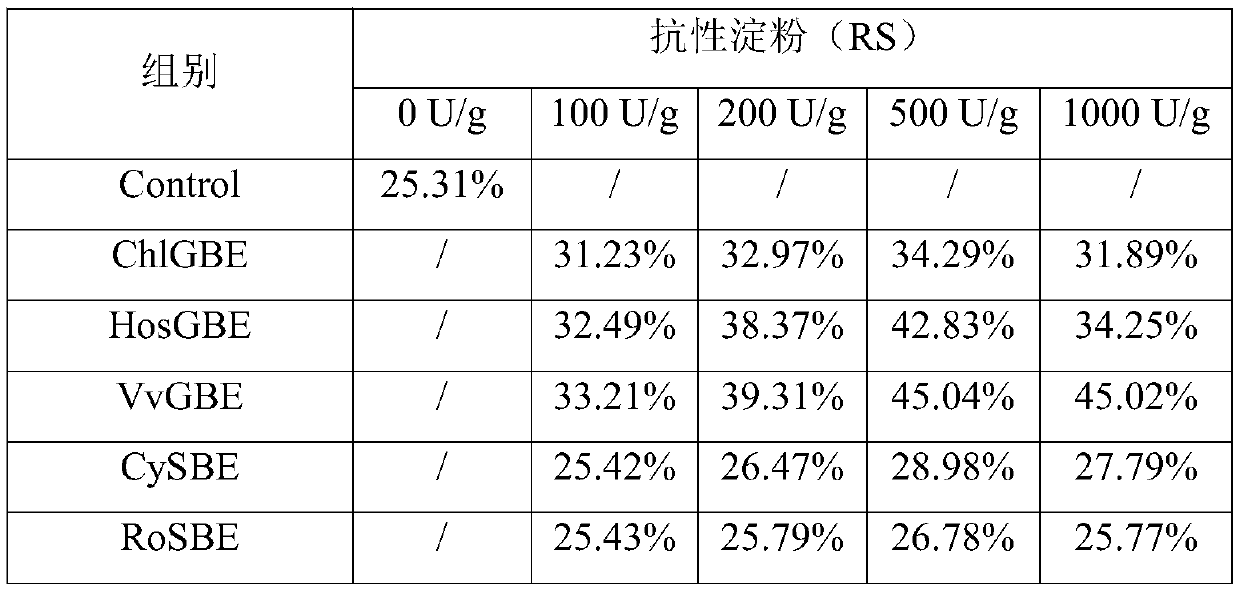
[0059] Example 2: The ability of different branching enzymes to reduce starch digestibility
[0060] Specific steps are as follows:
[0061] Weigh 2.5g of corn starch and add 50mM, pH 7.0 sodium dihydrogen phosphate-disodium hydrogen phosphate buffer to obtain a starch solution; heat and stir the starch solution in a boiling water bath for 30 min. After heating, use a volumetric flask to dilute to 100 mL , Prepared into a 2.5% gelatinized starch solution; place the gelatinized starch solution in a 30°C, 150rpm constant temperature water bath shaker for 10 minutes to obtain an incubation starch solution; add 100, 200, 500, and 1000 U to the incubation starch solution, respectively / g starch of the crude enzyme solution of glycogen branching enzyme ChlGBE, glycogen branching enzyme HosGBE, glycogen branching enzyme VvGBE, branching enzyme CySBE or branching enzyme RoSBE obtained in Example 1, wherein the blank control group (Control) does not add enzymes Make up the solution with bu...
Embodiment 3
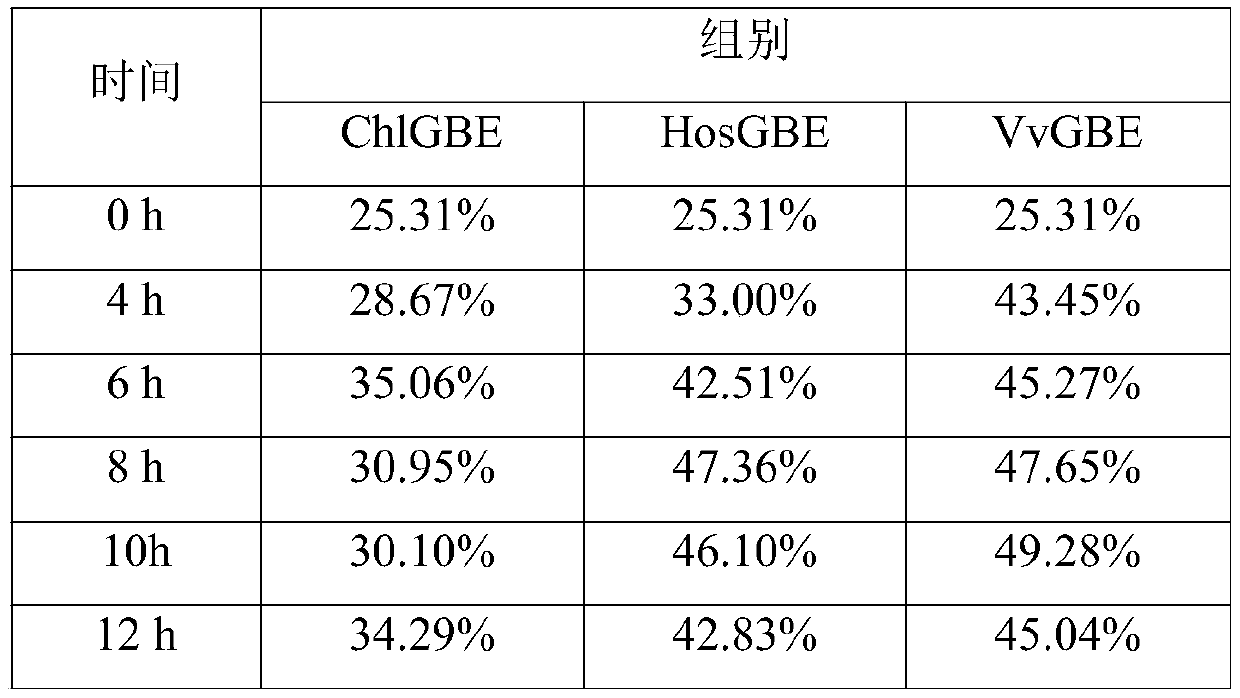
[0066] Example 3: Effect of reaction time on the ability of branching enzymes to reduce starch digestibility
[0067] Weigh 2.5g of corn starch and add 50mM, pH 7.0 sodium dihydrogen phosphate-disodium hydrogen phosphate buffer to obtain a starch solution; heat and stir the starch solution in a boiling water bath for 30 min. After heating, use a volumetric flask to dilute to 100 mL , Prepared into a 2.5% gelatinized starch solution; place the gelatinized starch solution in a constant temperature water bath shaker at 30° C. and 150 rpm for 10 minutes to obtain an incubated starch solution; examples of adding 500 U / g starch to the incubating starch solution 1 The obtained crude enzyme solution of glycogen branching enzyme ChlGBE, glycogen branching enzyme HosGBE or glycogen branching enzyme VvGBE was reacted at 30°C for 0, 4, 8, 10, 12 h, and the reaction was terminated by heating and boiling off the enzyme to obtain The reaction solution. The content of resistant starch (RS) in t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com