Cloud manufacturing multi-task scheduling optimization method based on game theory
An optimization method and cloud manufacturing technology, applied in manufacturing computing systems, instruments, computing models, etc., can solve problems such as poor population diversity and premature convergence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
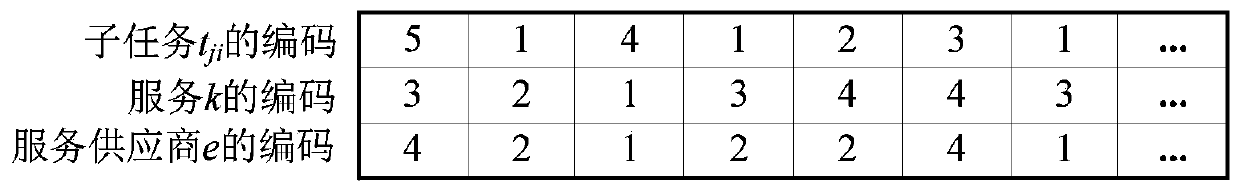
[0112] Such as figure 2 As shown, the value of each element in the first row of the matrix represents the code of the task. For example, the value of the second element is 1, which means the first task, and the number of times the same element value appears is the code of the subtask, for example, the fourth element The value is also 1, and this is the second occurrence of 1, so this 1 represents the second subtask of the first task; the second row of the matrix represents the code of the service, and the third row represents the code of the service provider. Taking the fourth column {1,3,2} as an example, this means that the second subtask of the first task (ie, t 21 ) Is performed by the third service provided by the second supplier (ie, s 32 ).
[0113] This representation method expresses the three decision variables intuitively and clearly, and the independence and correlation between the decision variables is maintained, which is convenient for subsequent migration operatio...
Embodiment 2
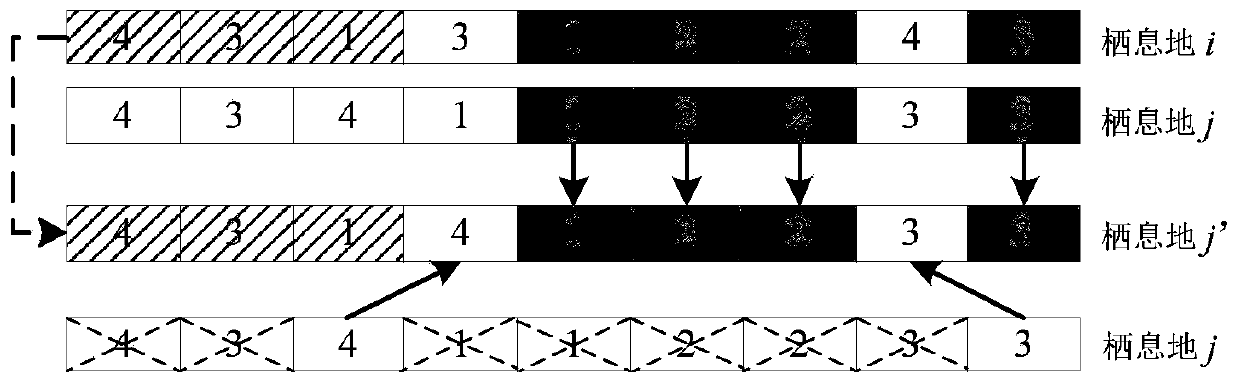
[0132] Such as image 3 As shown, habitat i is the emigration habitat, habitat j is the emigration habitat, and habitat j’ is the emigration habitat improved after the migration operation. image 3 Get the first line of habitat i and habitat j to perform the task sequence migration operation.
[0133] Compare the number of tasks in the corresponding slots of habitat i and j. The slots with the same task number in habitat j remain unchanged, while the slots with different task numbers are changed. The tasks in the four gray slots of habitat j in the figure are The number is the same as the task number in the gray slot corresponding to habitat i, so the task number of the corresponding slot in the improved habitat j'remains unchanged. The other slots are changed as follows: first, randomly select about half of the total number of different task numbers in habitat i (that is, the three diagonal grooves in the figure), and place them in the corresponding slots of improved habitat j'in...
Embodiment 3
[0148] Such as Figure 5 As shown, it is the first row in the habitat to be mutated. Two SIVs in the first row are randomly selected and inserted into the first and second slots of the habitat in turn. Then, the remaining SIVs move their positions backward in turn.
[0149] Such as Image 6 Shown are the second and third rows of the habitat to be mutated. Two SIVs are randomly selected and inserted into the first and second slots of the habitat in turn. Then, the remaining SIVs move their positions backward in turn.
[0150] Performing mutation operations on the task sequence and service sequence separately can further enhance the diversity of the population and help obtain the optimal solution.
[0151] It should be noted that, in order to avoid destroying the habitat with the highest HSI value during each iteration, when calculating the mutation rate of the population, the mutation rate of the optimal solution obtained after the migration operation in step 2.3 is set to zero.
[01...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com