Active suspension system based on stack type self-coding and working method thereof
A stacked self-encoding and active suspension technology, applied in the field of automotive active suspension system control, can solve the problems of wasting energy and failing to achieve optimal performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
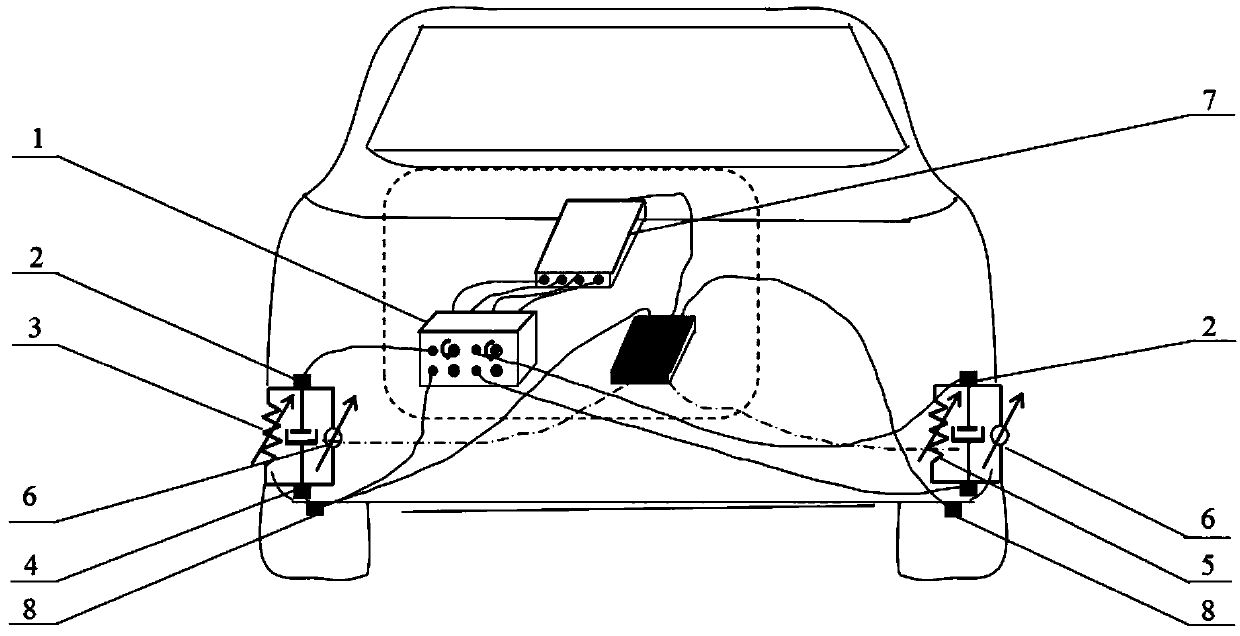
[0117] Such as Figure 1-2 shown.
[0118] An active suspension system based on stacked self-encoding, including a control unit and signal acquisition units respectively arranged on four wheels; the signal acquisition unit includes a vehicle body acceleration sensor 2, a wheel acceleration sensor 4, and a wheel speed sensor 8 , an air spring 5 and a magneto-rheological shock absorber 6; the control unit is connected with four signal acquisition units.
[0119] The wheel acceleration sensor measures the vertical acceleration of the unsprung mass, that is, the vertical acceleration of the wheel under the suspension; the body acceleration sensor measures the vertical acceleration of the sprung mass, that is, the vertical acceleration of the vehicle body above the suspension; the wheel speed sensor measures the wheel speed;
[0120] The signal acquisition unit is connected to the control unit through the charge amplifier 1 and the data acquisition instrument 7 in sequence.
[01...
Embodiment 2
[0126] Such as image 3 , 9 shown.
[0127] A working method of the active suspension system as described in embodiment 1, comprising steps as follows:
[0128] 1) Construct a stacked self-encoder neural network;
[0129] 1.1) training the first hidden layer; under different road conditions, the signals collected by four signal acquisition units are used as input signals to train the stacked autoencoder; the stacked autoencoder learns to obtain the first-order feature of the input signal;
[0130] 1.2) Train the second hidden layer; take the first-order feature of the input signal as input, and train the stacked autoencoder to obtain the second-order feature;
[0131] 1.3) using the second-order feature as the input of the softmax classifier layer, training a model that can map the second-order feature to a digital label;
[0132] Stacked autoencoder network for pattern recognition of active suspension systems;
[0133] 2) Pattern recognition of the active suspension syst...
Embodiment 3
[0212] As the working method of the active suspension system described in embodiment 2, further, in the step 2), the definition method of the comfort mode and the safety mode is to use the carsim software to carry out the simulation working condition setting; as Figure 6-8 shown.
[0213] ①Double lane shifting simulation working condition with a vehicle speed of 10km / h-100km / h, the speed interval is 1km / h, the control mode is the safe mode when the speed is ≥30km / h, and the comfort mode is the control mode when the speed is <30km / h;
[0214] ②Simulation working condition of expressway with vehicle speed of 10km / h-100km / h, the speed interval is 1km / h, and the control mode is comfort mode at this time;
[0215] ③In the fishhook simulation working condition with a vehicle speed of 10km / h-100km / h, the speed interval is 1km / h, when the speed is ≥30km / h, the control mode is the safe mode, and when the speed is <30km / h, the control mode is the comfort mode;
[0216] In the follow-u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com