A time-dependent de-redundancy method for temperature-aware data
A time-dependent, data-sensing technology, applied in other database retrieval, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems of increasing sensor computing energy consumption, unresearched, large data fluctuations, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing transmission energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061]In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention clearer, the following further describes the present invention in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, but not to limit the present invention.
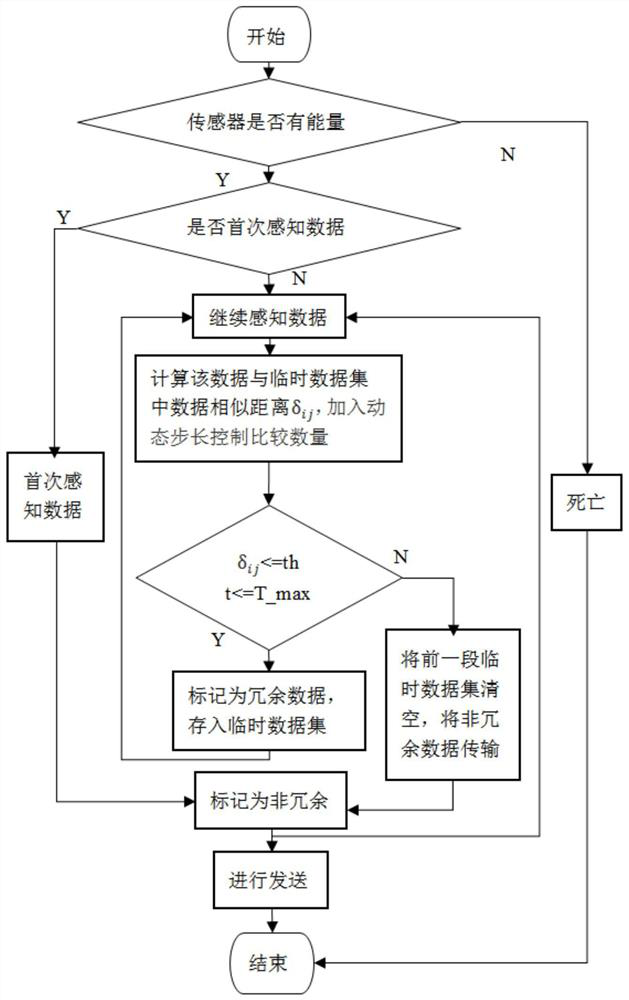
[0062]The time-correlation de-redundancy method for temperature sensing data in the embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
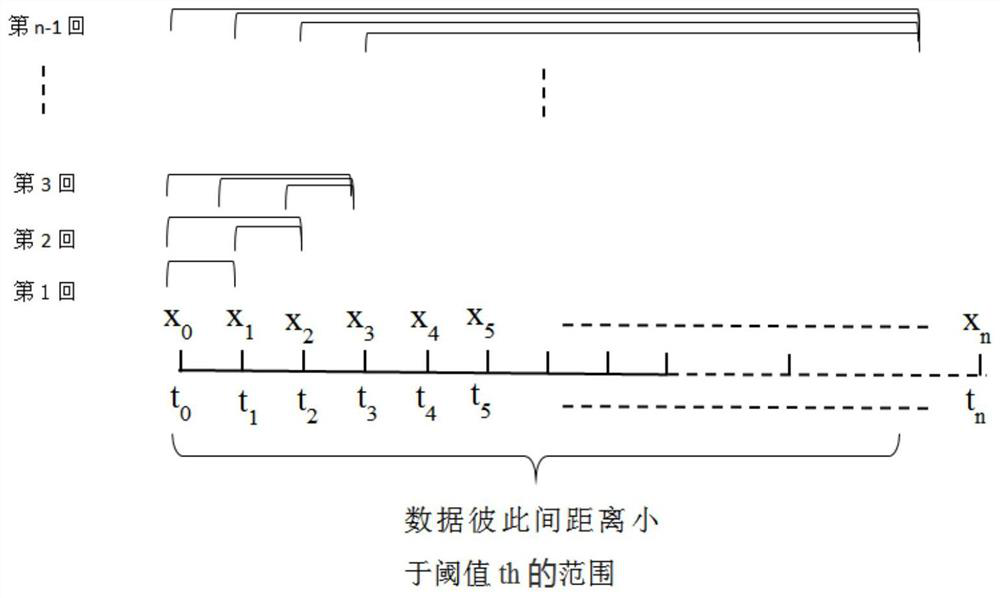
[0063]Step 1: Obtain the temperature sensing data collected by multiple temperature sensors, and perform preliminary processing on it, build a temperature sensing data de-redundancy model based on the time series correlation of dynamically changing steps, and there is a lot of redundant information in the data To process
[0064]Step 2: Determine whether the temperature sensing data currently collected by the temperature sensor is the first sensing data. If ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com