Municipal administration road rainwater reuse facility based on bioretention zone system
A technology of biological retention and municipal roads, applied in the field of rainwater reuse facilities on municipal roads, can solve the problems of affecting the time of rainwater discharge and not fully considering the influence of drainage time of pavement structure, so as to shorten the seepage time, increase the slope, increase the Effect of large seepage area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
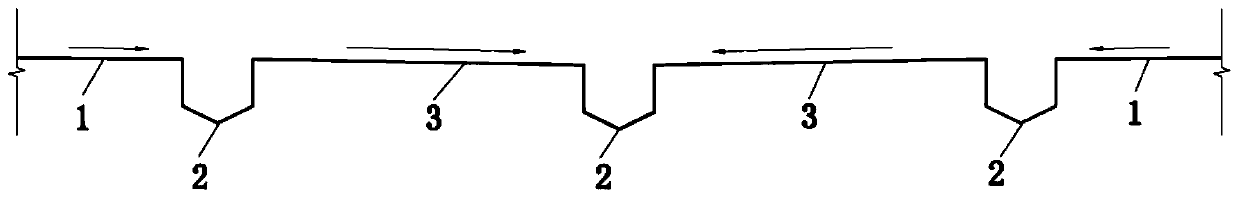
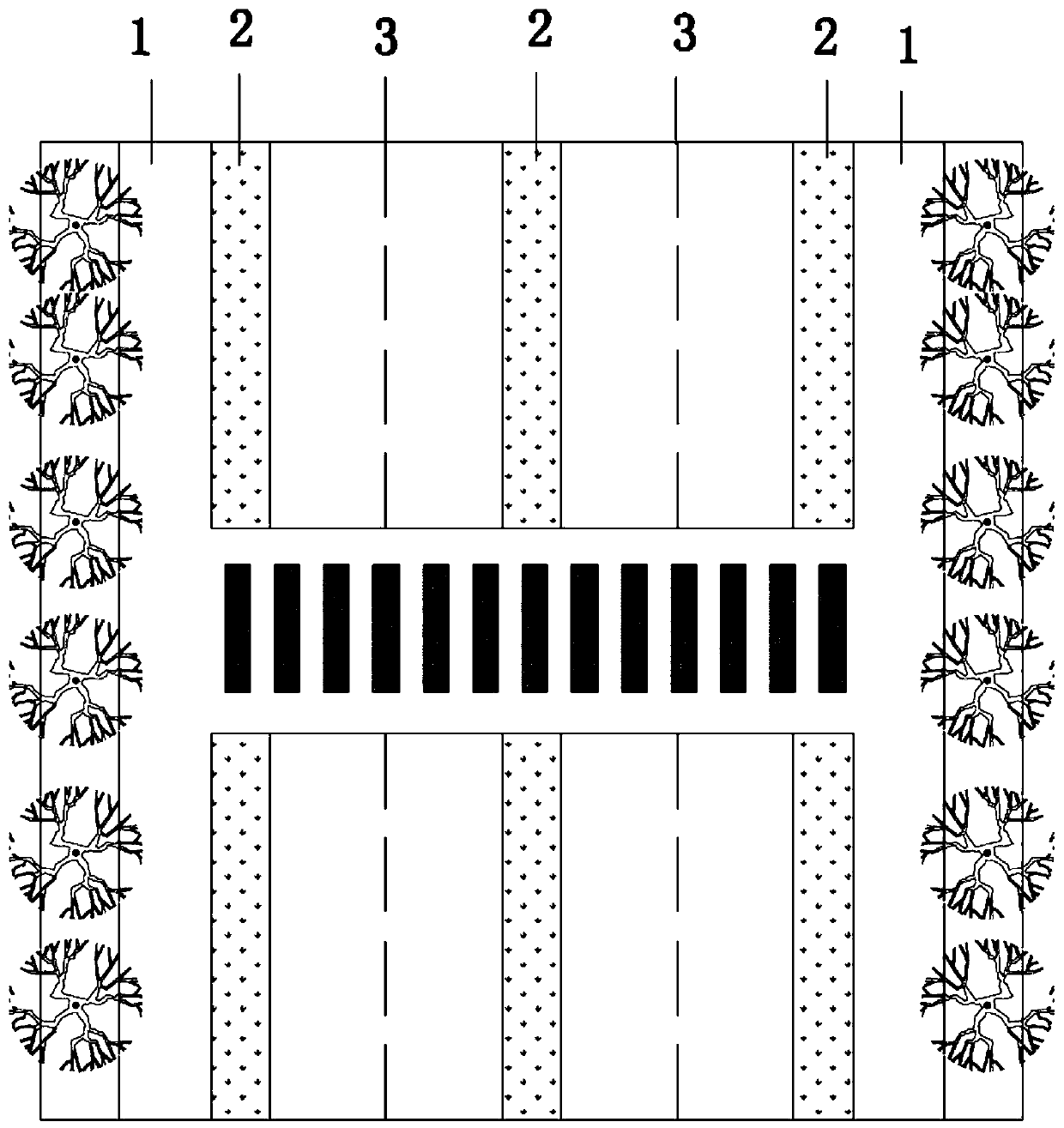
[0029] Embodiment 1: dealing with rainwater runoff when the rainfall is 35mm. The design rainfall is 35mm, the design rainfall return period is 1a, and the rainfall time is 1h. The calculated average rainfall intensity is 35mm·h-1. The rainwater flows to the biological retention zone through the "V"-shaped road, and the measured rainwater runoff discharge Within 1 hour, there will be no water accumulation on the road. After entering the bioretention zone, the runoff rainwater passes through the planting soil layer, artificial packing layer, and gravel layer in sequence, reaches the perforated pipe, and finally enters the storage tank. It is measured that the removal rate of N by the bioretention belt system is above 70%, the removal rate of P is above 85%, and the average removal rate of Cu, Pb, Zn, and Cd is above 60%. Every 100m of the bioretention belt system The water storage capacity is 55m3.
Embodiment 2
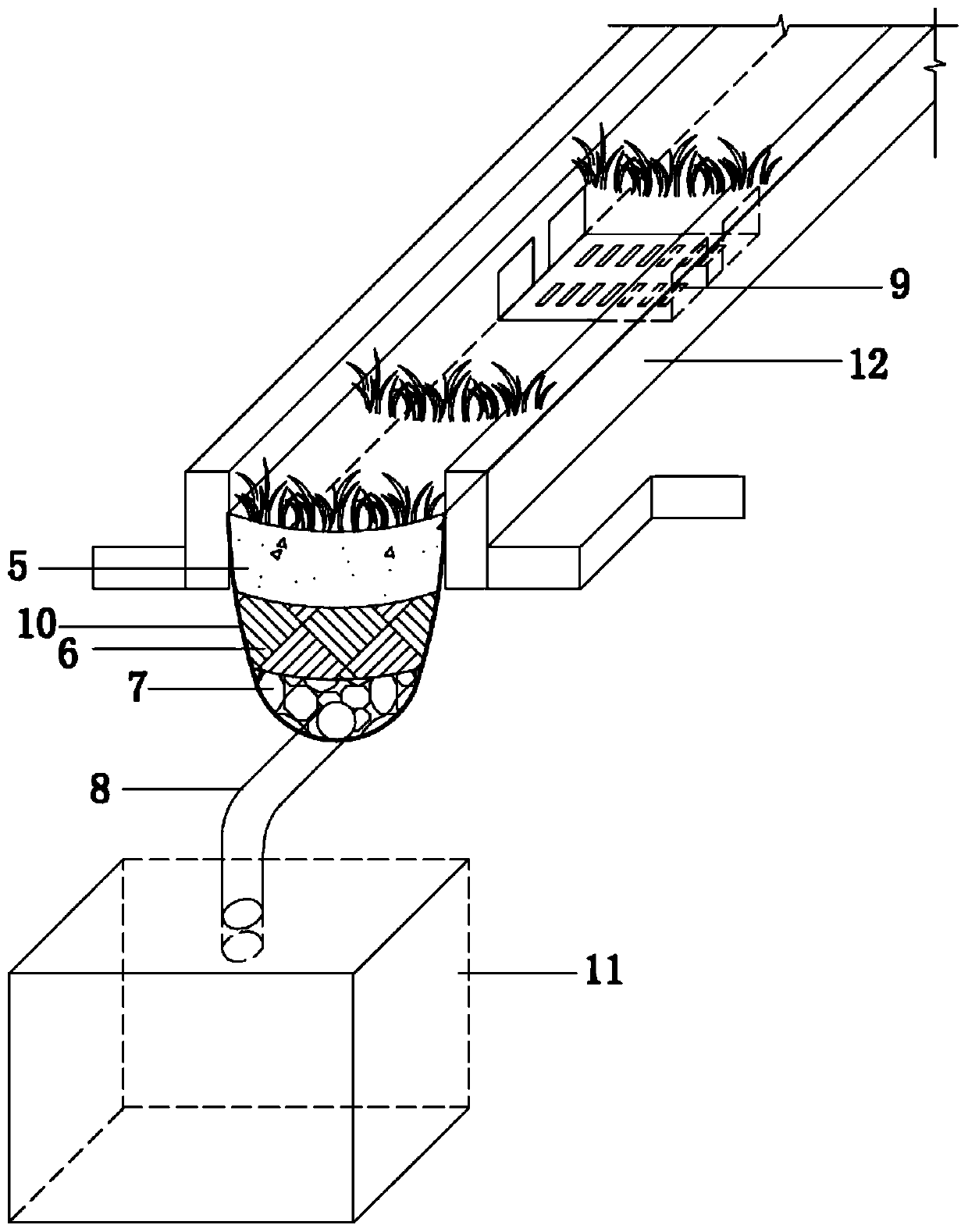
[0030] Embodiment 2: dealing with rainwater runoff when the rainfall is 71 mm. The design rainfall is 35mm, the design rainfall return period is 5a, and the rainfall time is 1h. The calculated average rainfall intensity is 35mm h-1. The rainwater flows to the bioretention zone 2 through the "V"-shaped road, and the rainwater runoff is measured The discharge time is within 1 hour, and there will be no road accumulation. After entering the bioretention zone, the runoff rainwater passes through the planting soil layer 5 , the artificial packing layer 6 , and the gravel layer 7 in sequence, reaches the perforated pipe 8 , and finally enters the reservoir 11 . It is measured that the removal rate of N by the bioretention belt system is above 70%, the removal rate of P is above 85%, and the average removal rate of Cu, Pb, Zn, and Cd is above 60%. Every 100m of the bioretention belt system The water storage capacity is 55m3.
Embodiment 3
[0031]Embodiment 3: dealing with rainwater runoff when the rainfall is 71mm. The design rainfall is 71 mm, the design rainfall return period is 5 years, and the rainfall time is 2 hours. The calculated average rainfall intensity is 71 mm h-1, and the rainwater flows to the bioretention zone 2 through the "V"-shaped road, and the rainwater runoff is measured The discharge time is within 2 hours, and there will be no road accumulation. After entering the bioretention zone, the runoff rainwater passes through the planting soil layer 5 , the artificial packing layer 6 , and the gravel layer 7 in sequence, reaches the perforated pipe 8 , and finally enters the reservoir 11 . It is measured that the removal rate of N by the bioretention belt system is above 70%, the removal rate of P is above 85%, and the average removal rate of Cu, Pb, Zn, and Cd is above 60%. Every 100m of the bioretention belt system The water storage capacity is 100m3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com