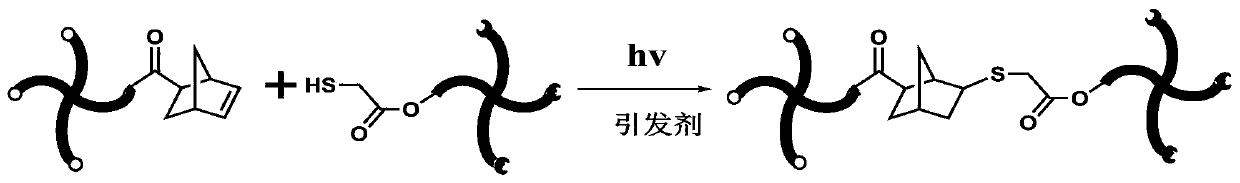
Methods for preparing biodegradable body temperature induction material and degradable body temperature induction memory bioscaffold for 4D printing
A technology of sensing materials and bio-stents, which is applied in additive processing, medical science, surgery, etc., to achieve fast molding speed, narrow thermal transition peak width, and reduce the pain of patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0050] A method for preparing a biodegradable body temperature sensing material, by using a biodegradable polymer terminal with a hydroxyl group (ie, a hydroxyl-terminated biodegradable polymer) as the basic main raw material to prepare a material that can be degraded at a physiological temperature and has a sulfhydryl group terminal. or norbornene-based multicomponent biodegradable polymers, that is, multicomponent biodegradable polymers terminated by mercapto or norbornene groups. The material is applied to the field of 4D printing. It is a multi-component biodegradable polymer terminated by a mercapto or norbornene group and a corresponding two-arm or multi-arm norbornene or mercapto-terminated degradable macromolecule. Next, photocatalytic norbornene-sulfhydryl click chemistry reaction occurred. The biostents prepared by this reaction, such as vascular stents, have the advantages of fast recovery of shape and structure, more accurate recovery temperature and controllable d...
Embodiment 1
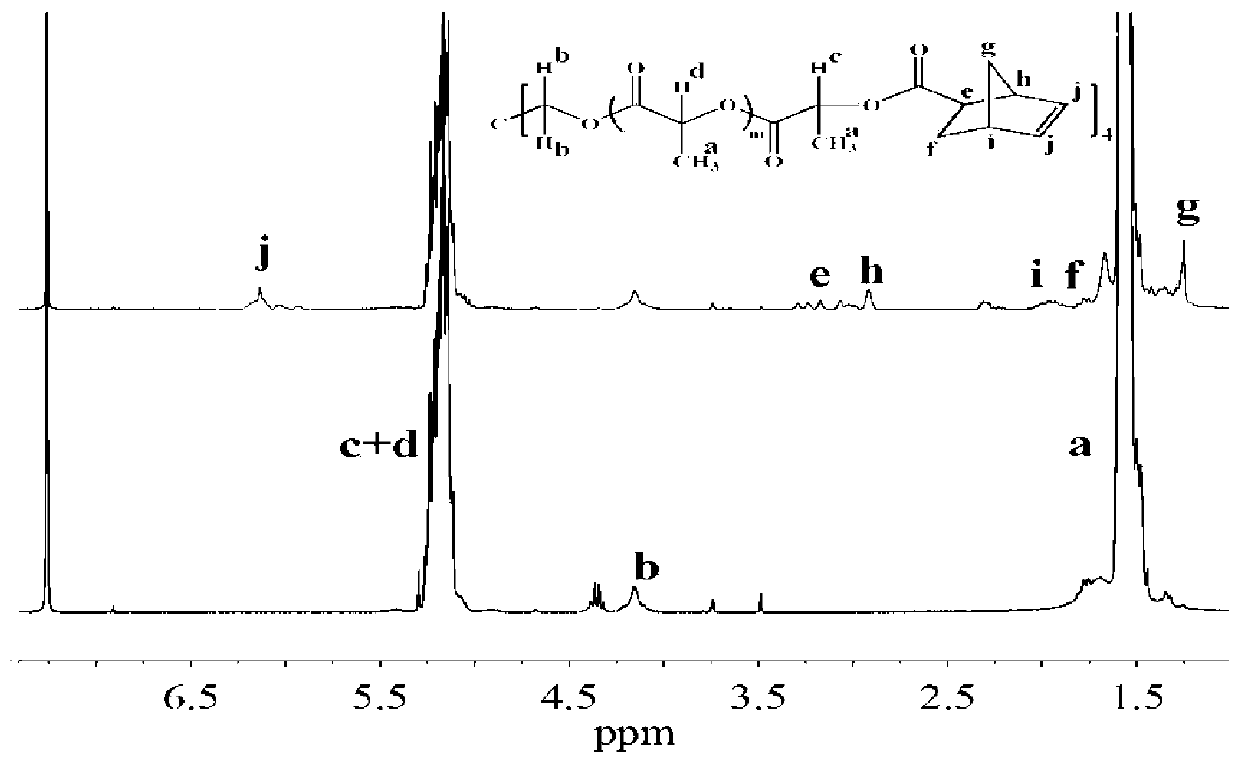
[0071] Add 0.076mmol of stannous octoate, 69.6mmol of trimethylene carbonate, 309.6mmol of D, L-lactide and 50mmol of pentaerythritol into an anhydrous and oxygen-free reaction flask, vacuumize and blow nitrogen, repeat three times. After the reaction system was sealed, it was reacted in an oil bath at 130°C for 24 hours. After the reaction was completed, the reaction system was cooled to room temperature, and an appropriate amount of chloroform was added to dissolve the product. Slowly add the reaction mixture dropwise into cold methanol for precipitation, where the volume of methanol is 5-10 times the volume of the chloroform solution of the reactant, and then dissolve and precipitate again after filtration to obtain the hydroxyl-terminated four-arm poly D,L-lactate Ester-co-trimethylene carbonate copolymer (M n =1568; M w =1770;T g =34~36℃), such as Figure 9 Tan δ–temperature curves of the shown hydroxyl-terminated four-armed poly-D,L-lactide-co-trimethylene carbonate ...
Embodiment 2
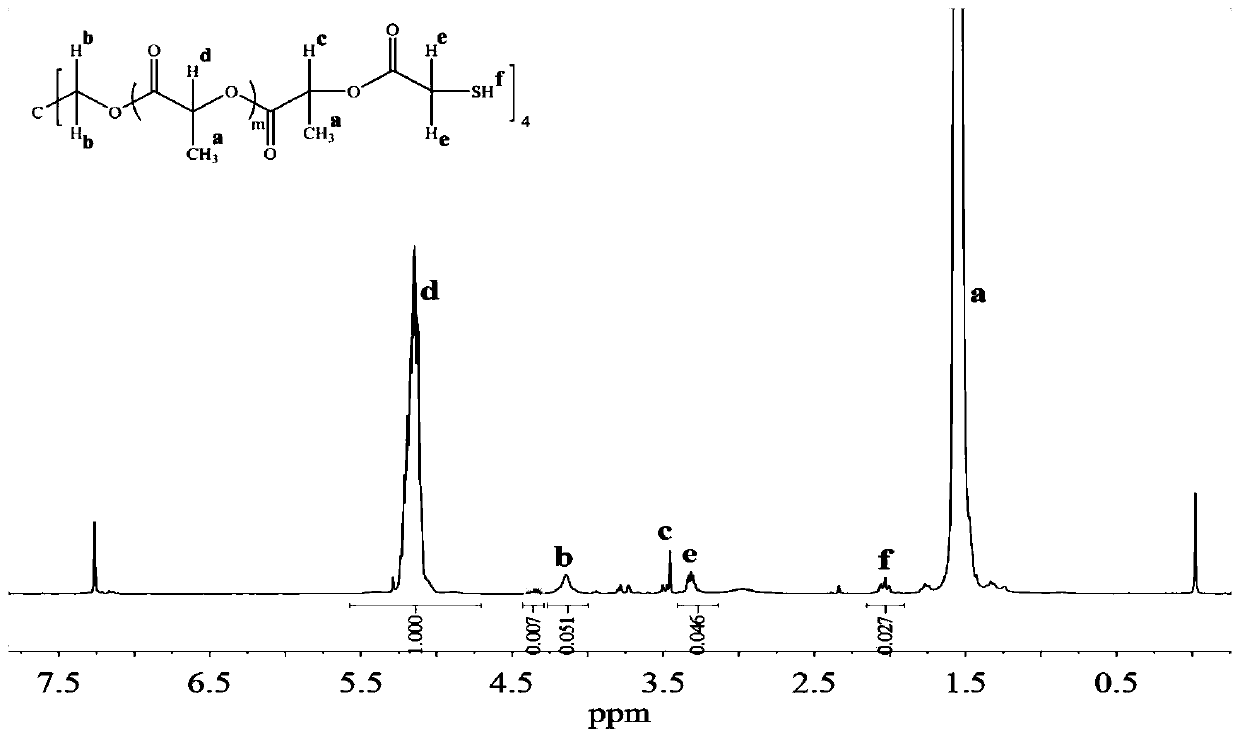
[0075] Compared with Embodiment 1, this embodiment is the same except for the following differences. The only difference is that tetrakis(3-mercaptopropionate) pentaerythritol is replaced by trimethylolpropane tris(3-mercaptopropionate).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com