Ubiquitous power Internet of Things monitoring method
A technology of power Internet of things and prediction models, which is applied in measurement devices, electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve problems that are difficult to meet the requirements of accuracy and adaptability, the connection between virtual and physical spaces is not close enough, and the complexity of power grid systems increases. Degradation function failure and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] In order to better understand the essence of the present invention, the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific embodiments and accompanying drawings.
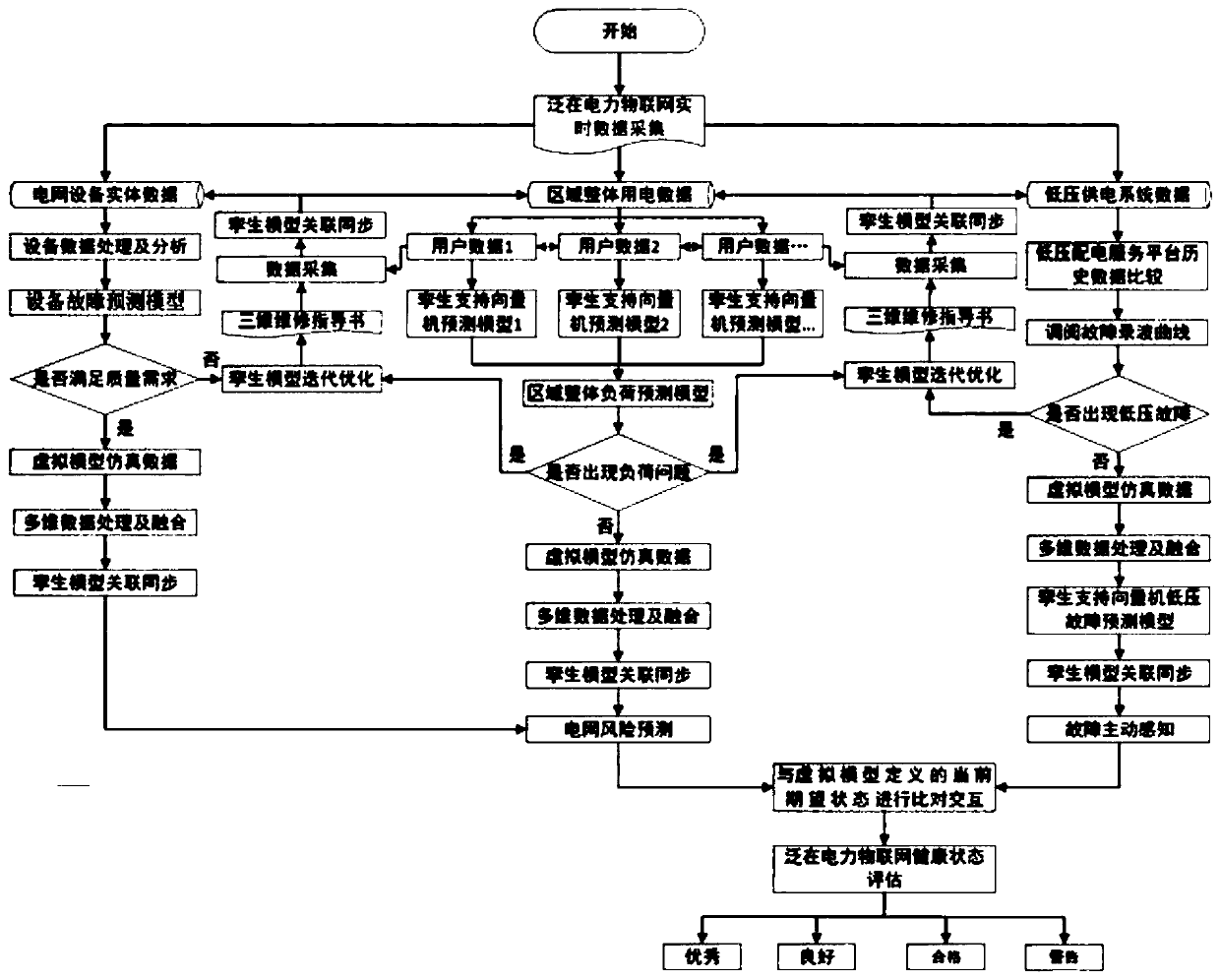
[0027] The invention discloses a monitoring method for the ubiquitous power Internet of things, the specific steps are as follows figure 1 Shown:
[0028] Step 1: Use data acquisition equipment to collect real-time data from each unit in the ubiquitous power Internet of Things. The collected real-time data is stored and managed for the life cycle data of ubiquitous power Internet of Things through distributed cloud server storage technology. data acquisition equipment such as Figure 4 As shown, it includes physical feature measurement and control equipment, protection measurement and control equipment, temperature monitoring equipment and operating environment monitoring equipment, etc. The collected data types include electrical parameters and non-electric parameters.
[0029...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com