High-resolution minimum variance ultrasonic imaging method based on frequency domain segmentation
An ultrasonic imaging method and a technique of minimum variance, applied in the analysis of fluids using sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves, the analysis of solids using sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves, and the use of sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves for material analysis, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
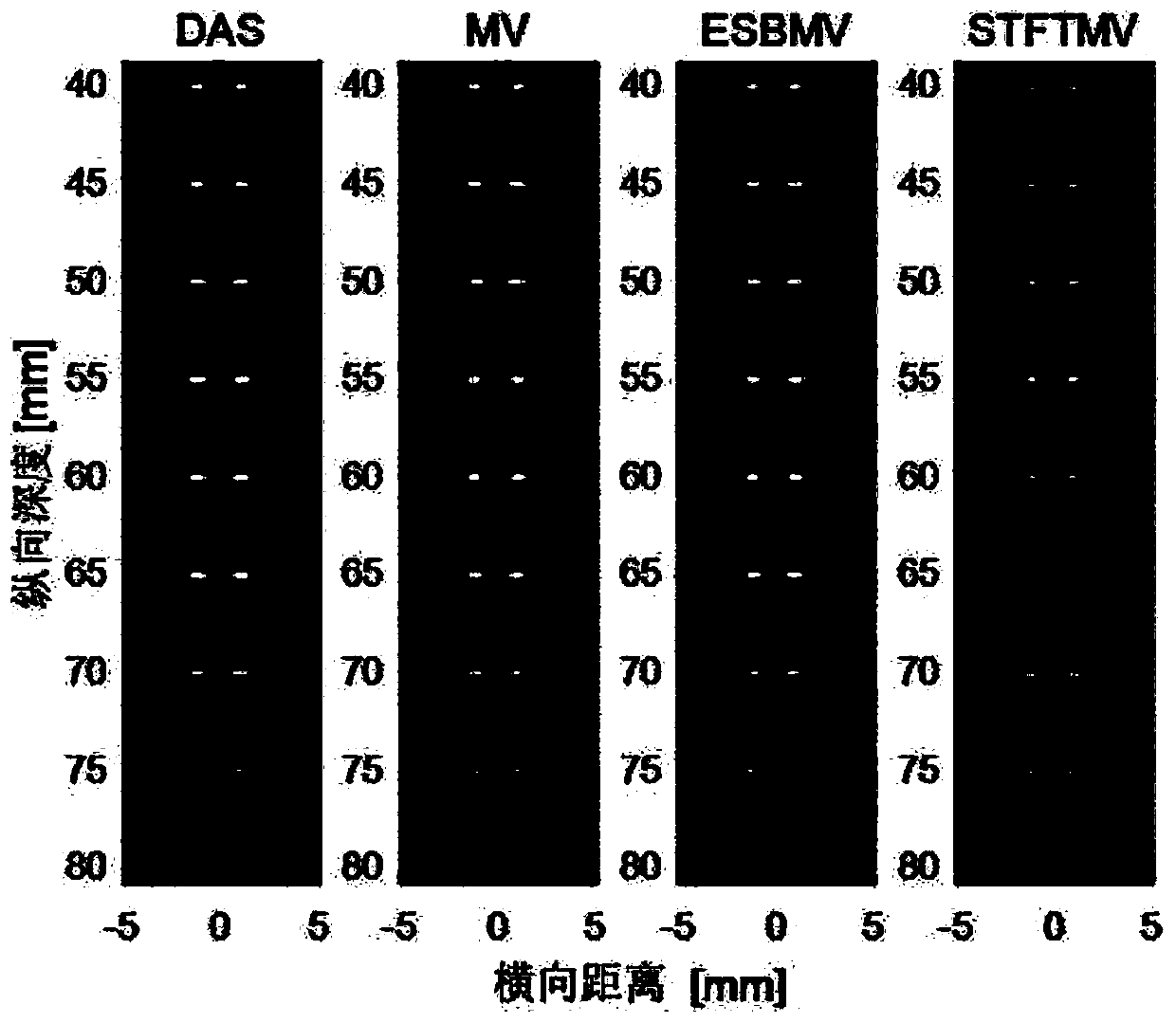
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0073] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
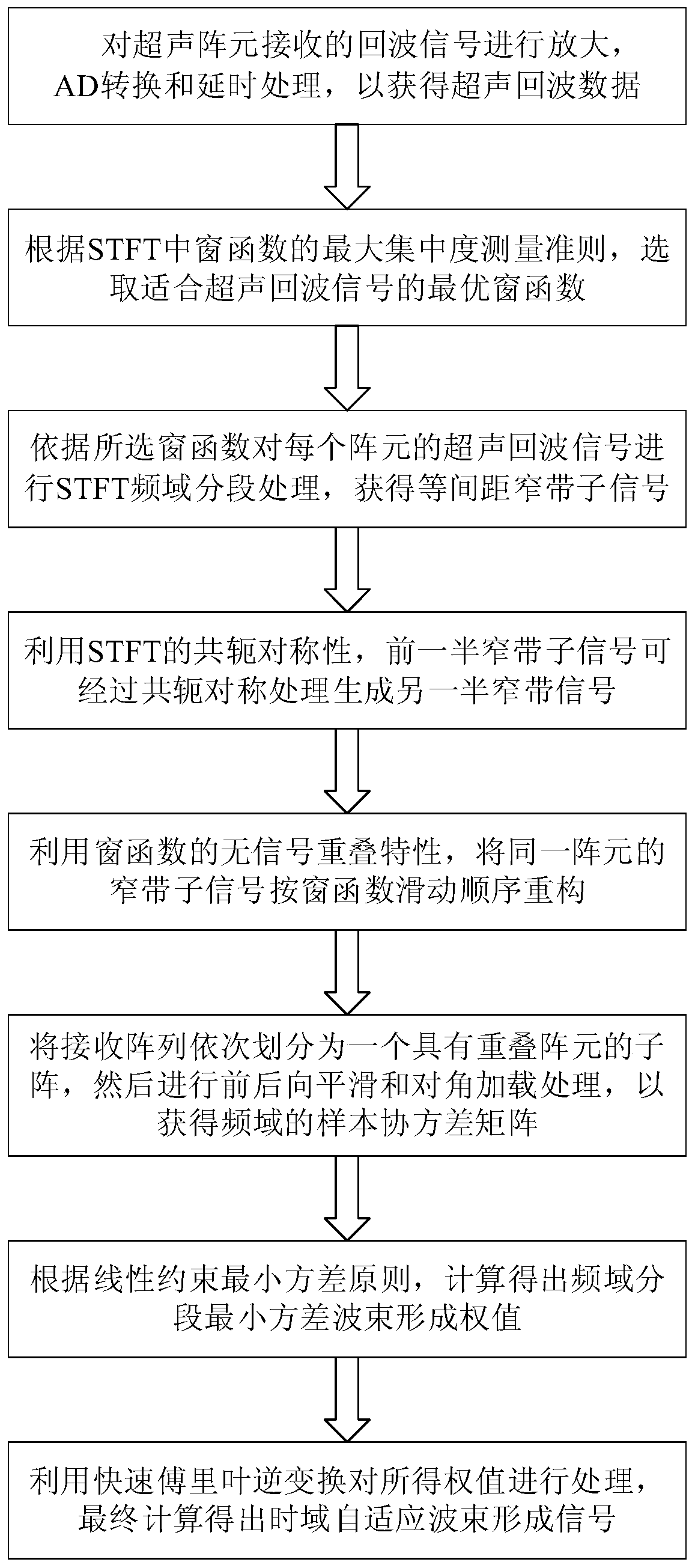
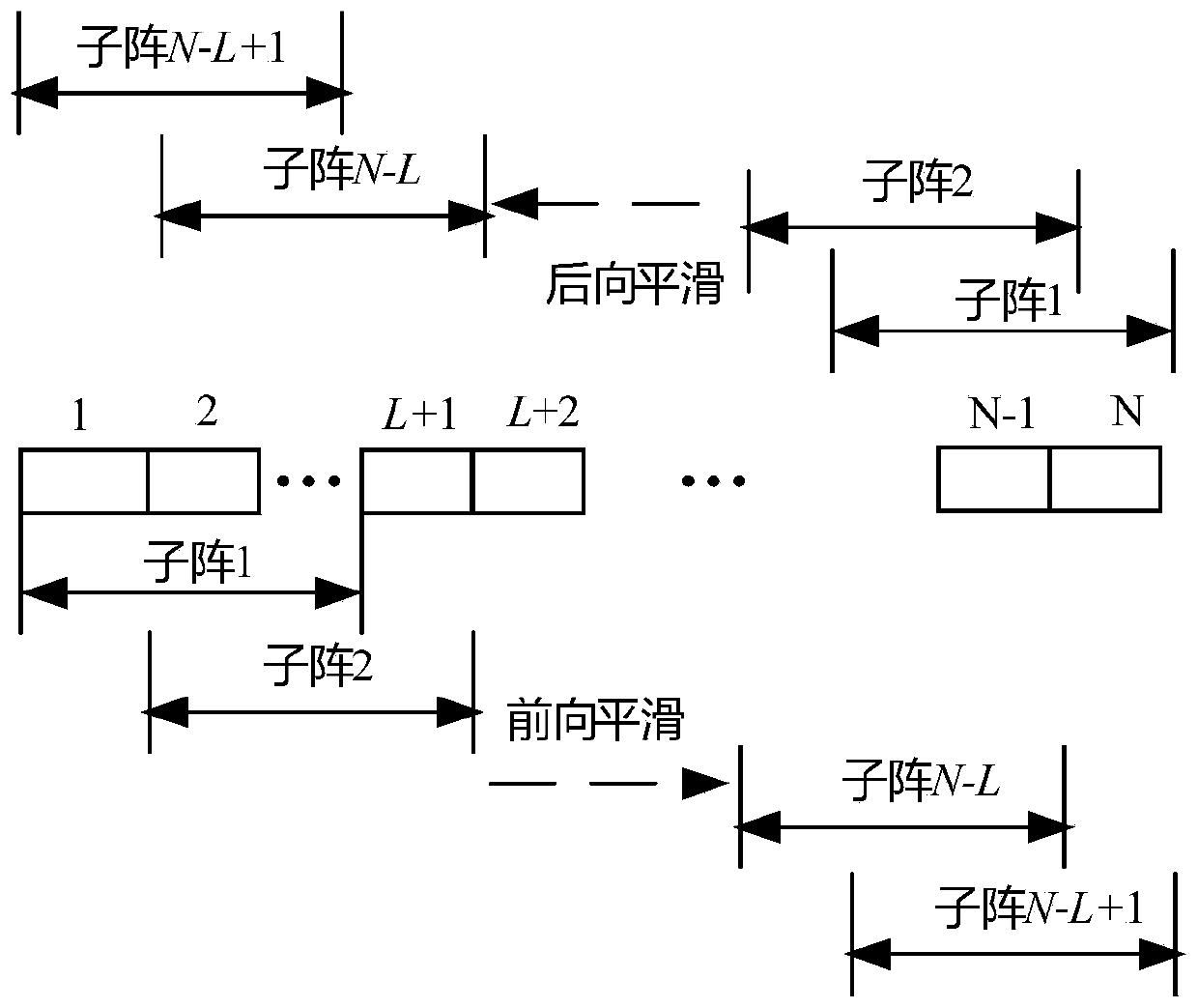
[0074] figure 1 It is a flowchart of the method of the present invention, figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of forward and backward spatial smoothing algorithm. As shown in the figure, the present invention provides a high-resolution minimum variance ultrasonic imaging method based on time-frequency segmentation, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0075] Step S1: Perform amplification, AD conversion and delay processing on the echo signal received by the ultrasonic array element to obtain ultrasonic echo data; obtain the signal x(τ)=[x 1 (τ),x 2 (τ),...x N (τ)], x 1 (τ)...x N (τ) respectively represent the echo signals received by each array element, N represents the number of ultrasonic array elements, and τ represents the sampling time corresponding to the depth;
[0076] Step S2: According to the maximum concentra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com