Method for forming liquid rubber composite node with damping through hole and node
A liquid rubber, damping hole technology, applied in the shock absorber-spring combination, spring/shock absorber design features, shock absorbers, etc. The effect of expanding the volume space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
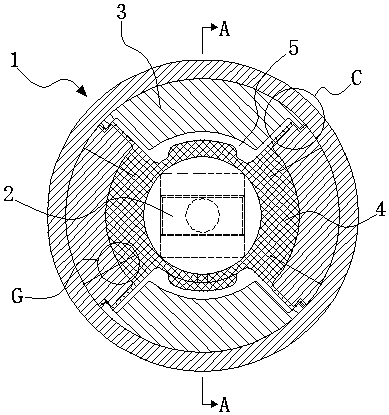
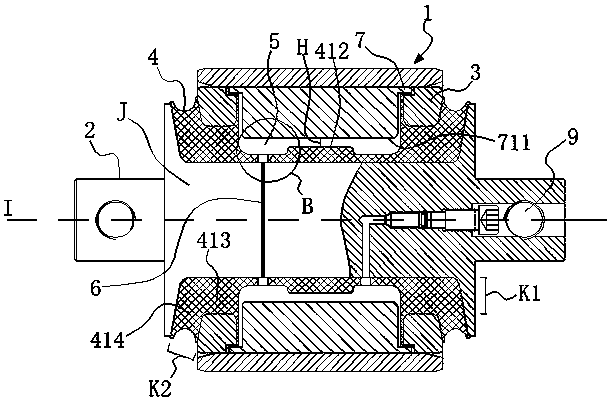
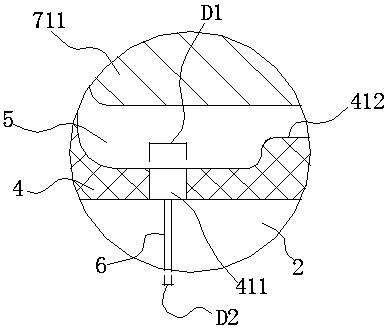
[0040] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, a method of forming a liquid rubber composite node with an intermediate damping hole, which is to add an intermediate spacer 3 between the outer casing 1 and the mandrel 2, and vulcanize and bond the intermediate spacer 3 and the mandrel 2 through rubber 4 Together, the integrated intermediate spacer and the mandrel are assembled into the outer casing 1; the mandrel 2 is provided with a damping through hole passing through the mandrel 2, and the middle spacer 3 is hollowed out to form multiple spaces. After vulcanization, the rubber 4 and the multiple spaces are used to form a plurality of liquid cavities 5 that are independent of each other. Liquids (not shown in the figure) are arranged in the plurality of liquid cavities 5 and pass through the plurality of liquid cavities 5. The damping through holes 6 communicate with each other. The liquid rubber composite joint formed by the above method can provide smaller radia...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2: as Figure 9 As shown, compared with Example 1, the difference is that in order to enable the liquid rubber to provide nonlinear stiffness characteristics, this embodiment adopts the following scheme: the inner peripheral arc surface of the arc-shaped cover plate 7 in this embodiment No bumps are set on the top, but a mandrel bump 211 is set on the mandrel 2, and the rubber 4 is covered on the mandrel 2 and the mandrel bump 211 and formed along it. Under the action of load, the arc-shaped cover plate 7 first contacts the rubber 4 located in the liquid cavity, and the node begins to provide nonlinear stiffness characteristics. The contact forms a hard stop limit protection function. In this embodiment, there are corresponding protruding mandrel protrusions 211 on the outer peripheral surface of the mandrel 2 corresponding to the two arc-shaped cover plates 7, and the two mandrel protrusions 211 are respectively located in the two liquid cavities. 5 in.
Embodiment 3
[0056] Embodiment 3: as Figure 10 As shown, compared with Embodiment 1, the difference is that in order to enable the liquid rubber to provide nonlinear stiffness characteristics, this embodiment adopts the following scheme: on the arc-shaped cover plate 7 and the mandrel 2 in this embodiment No projections are provided, and only rubber projections 415 protruding toward the arc-shaped cover plate 7 are provided on the rubber 4 covering the outer peripheral surface of the mandrel 2 in the liquid cavity. When using the arc-shaped cover plate 7 and the rubber projection 415 When in contact, the node begins to provide a non-linear stiffness characteristic, but in this embodiment, the node has no hard stop limit protection function. In this embodiment, the two rubber bumps 415 are respectively located in the two liquid cavities 5 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com