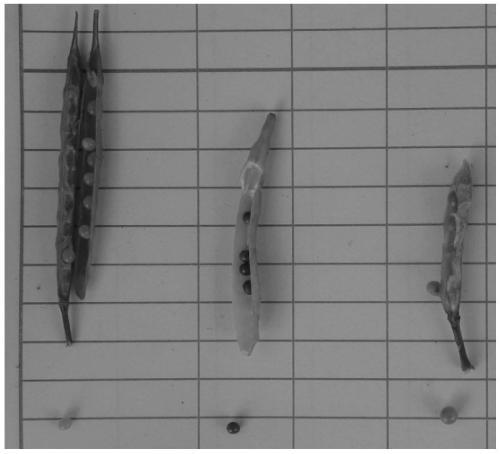
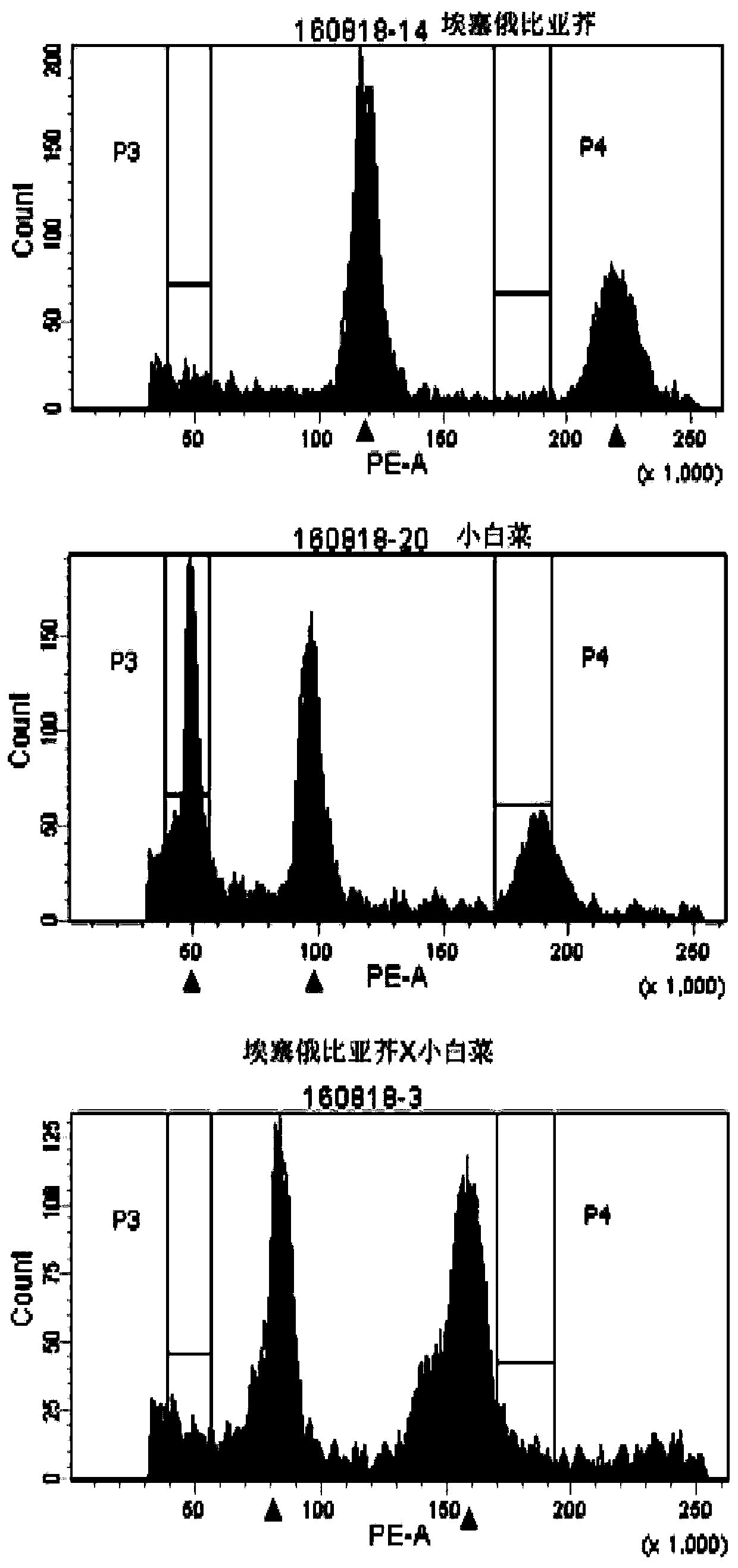
Molecular marker for identifying interspecific hybrids of Chinese cabbage and brassica carinata and separation conditions of A10 and C09 chromosomes of progeny materials
A molecular marker and chromosome technology, applied in the field of genetics and breeding, can solve problems such as time-consuming and labor-intensive, and achieve the effect of simple, fast, cost-effective, simple operation, and rich vegetable types.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 This example identifies the hybrid F between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard 1 plant
[0043] 1.1 Extract the F to be detected 1 Genomic DNA of the plant and its parents.
[0044] 1.2 Synthetic primers:
[0045] C09D-F: 5'-TGACAGCATATGAAGCCTGC-3' (SEQ ID No.1);
[0046] C09D-R: 5'-GATCCTGCCACAAGAATTTGA-3' (SEQ ID No. 2).
[0047] 1.3PCR amplification. To be detected F 1 Plants and their parental DNA are used as templates, and the above primers are used for PCR amplification reaction. The reaction system is 10 μL, including: 1×PCR Buffer (containing Mg + ), 0.5ng template DNA, 0.2mM dNTPs, 0.5μM primer C09D-F, 0.5μM primer C09D-R, 1U Taq enzyme. PCR reaction conditions: 94°C for 3min; 94°C for 30s, 56.1°C for 30S, 72°C for 30S, 35 cycles; 72°C for 5min.
[0048] 1.4 The above PCR products were detected by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Configure 8% polypropylene gel, run electrophoresis at 180 volts for 1.5 hours, and end the electrophoresi...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 This example identifies the hybrid backcross progeny between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard (BC 2 )Material
[0056] 1.1 Extract the genomic DNA of the plants to be tested and their parents.
[0057] 1.2 Synthetic primers:
[0058] C09D-F: 5'-TGACAGCATATGAAGCCTGC-3' (SEQ ID No.1);
[0059] C09D-R: 5'-GATCCTGCCACAAGAATTTGA-3' (SEQ ID No. 2).
[0060] 1.3PCR amplification. Taking the plant to be detected and its parental DNA as a template, the PCR amplification reaction is carried out with the above primers. The reaction system is 20 μL, including: 1×PCR Buffer (containing Mg + ), 1ng template DNA, 0.2mM dNTPs, 0.5μM primer C09D-F, 0.5μM primer C09D-R, 1U Taq enzyme. PCR reaction conditions: 95°C for 3min; 95°C for 30s, 56.1°C for 30S, 72°C for 30S, 35 cycles; 72°C for 10min.
[0061] 1.4 The above PCR products were detected by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Configure 8% polypropylene gel, electrophoresis at 180 volts for 2 hours, and end the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com