Screening method and application of lactic acid bacterium with antioxidant capacity
A technology of antioxidant capacity and screening method, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as lactic acid bacteria that do not involve antioxidant properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1: bacterial strain screening:
[0034] (1) Lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional pickled vegetables
[0035] Take 1g of traditional pickled vegetables in Northeast China, dilute it with sterilized saline at a ratio of 1:10, bathe in 75°C water for 15 minutes, and then dilute it with sterile water 10 times gradient, select 10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 、10 -6 For four dilution gradients, draw 100 μL of the bacterial suspension and spread it on the MRS plate, at least 3 plates for each dilution gradient, culture at 37°C for about 48 hours to obtain a single colony, separate and purify by streaking, and obtain pure isolated lactic acid bacteria strains Several.
[0036] (2) Preliminary screening of lactic acid bacteria with hydrogen peroxide tolerance
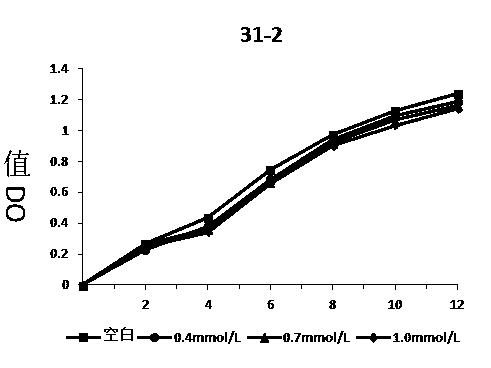
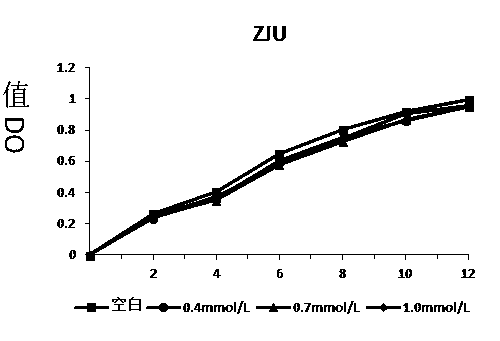
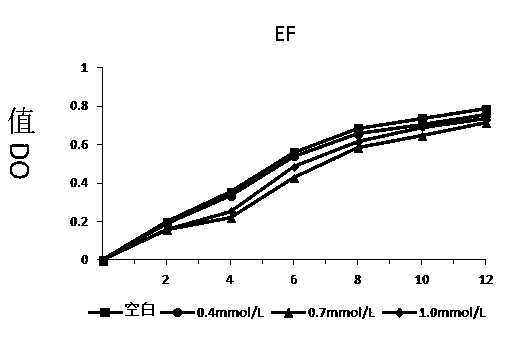
[0037] Add 10ml of MRS medium into a stoppered test tube, and add an appropriate amount of hydrogen peroxide solution, so that the initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide in the medium is 0, 0.4, 0.7, 1.0...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Example 2: Physiological and biochemical characteristics and strain screening of Pediococcus pentosaceae ZJUAF-4
[0064] Table 4 Physiological and biochemical characteristics of bacterial strain ZJUAF-4 of the present invention
[0065]
[0066] Note: "+" means positive, "-" means negative
[0067] Identification of 16S rDNA of strain ZJUAF-4 of the present invention
[0068] The 16S rDNA of the bacterial strain ZJUAF-4 of the present invention was sequenced, and compared with the NCBI database by Blast, the results showed that the homology between ZJUAF-4 and the model strain Pediococcus pentosaceus NWAFU5032 reached 99%, and the homology with the model strain Pediococcus pentosaceus SD 7013 was 99%, and 99% homology with the model strain Pediococcuspentosaceus PEP1, so the strain was determined to be Pediococcus pentosaceus.
[0069] Strain ZJUFA-4 was deposited on November 21, 2018 at No. 3, Yard No. 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, General Mic...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Embodiment 3: Application of Pediococcus pentosaceae ZJUAF-4 to prepare fermented feed
[0071] 1) Preparation of fermentation broth
[0072] Inoculate ZJUAF-4 in MRS liquid medium, and culture it statically for 24 hours, so that the concentration of bacteria solution reaches 1.0×10 9 ~1.0×10 10 CFU / mL, to prepare ZJUAF-4 fermentation broth;
[0073] 2) Preparation of fermented feed
[0074] Add 5% of the fermentation broth prepared in step 1) to the fermentation raw materials (including 10g of corn, 10g of soybean meal, 24g of bran, and 6g of soybean hulls), and then add and insert an appropriate amount of warm water so that the total moisture content accounts for 10% of the total mass of the fermentation system. 35% to 40%, stir and mix to obtain a fermentation system, leave it to ferment for 24 to 48 hours, and obtain a fermented feed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com