Method of Processing Polygonal Parts Using Cycloidal Rotation Technology
A part processing and polygonal technology, applied in metal processing equipment, manufacturing tools, planer/slotting machine, etc., can solve the problems that the quality of positioning data needs to be further improved, the gap of high-precision positioning results is large, and the reliability of positioning results is low. Reduce the manual debugging process, prolong the service life, and facilitate the effect of one-time molding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
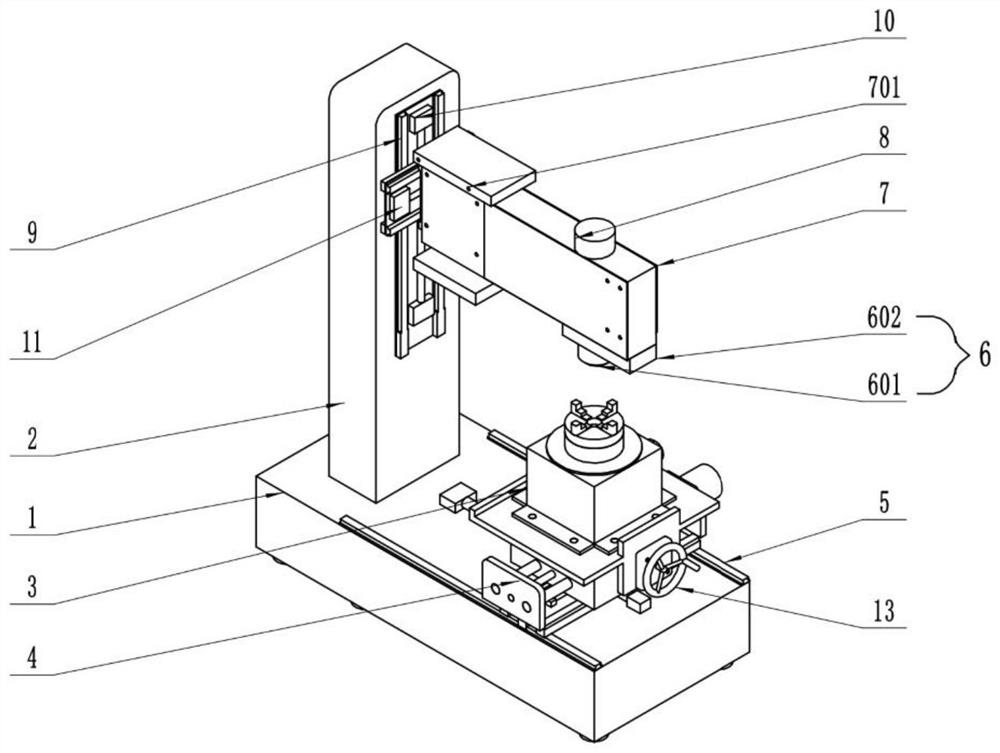
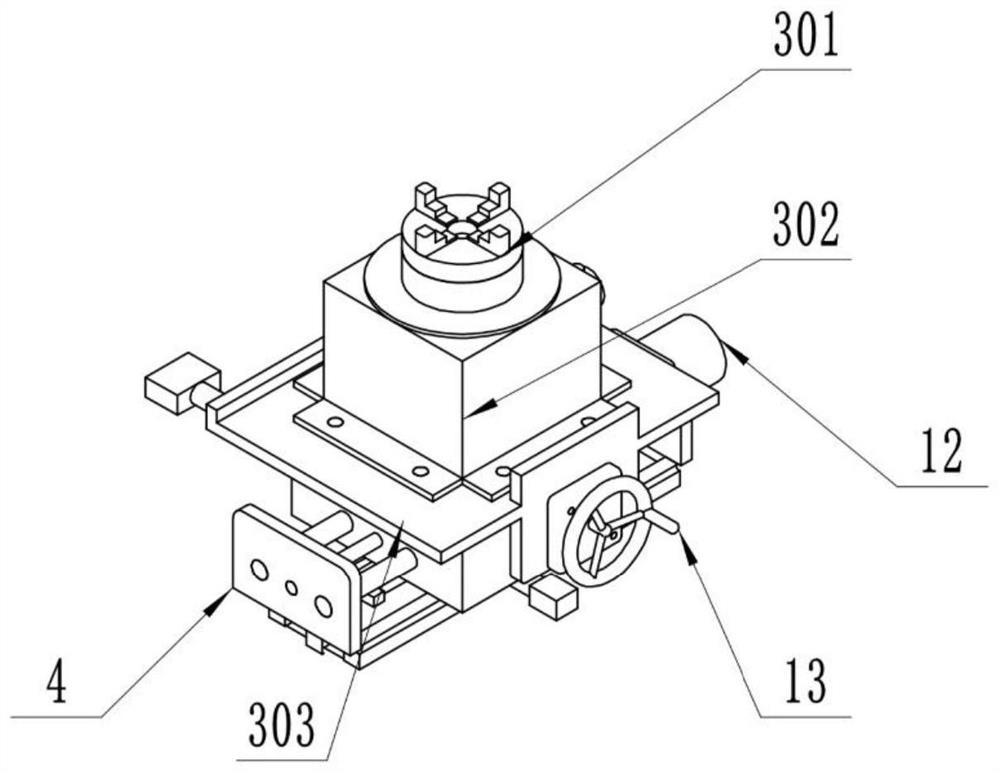
[0073] The embodiment is basically as attached figure 1 Shown: A device for processing polygonal parts using cycloidal rotation technology, including a horizontally placed base 1 and a vertical column 2, and a bearing device 3 is installed in the opposite direction of the column 2, and the bearing device 3 includes threads from top to bottom Connected chuck 301, support platform 302 and transition plate 303, under the transition plate 303 is slidably connected with a cross-section of the “凵”-shaped sliding plate 4, the sliding plate 4 includes two vertical plates parallel to each other and placed horizontally The horizontal plate, the horizontal horizontal slide rail 5 is welded between the two vertical plates, the right side of the sliding plate 4 is electrically connected to the fourth motor 12 that controls the horizontal movement of the sliding plate 4, and the model of the fourth motor 12 is HST80ST -M02430. The front of the sliding plate 4 is connected with a shaker 13 ...
Embodiment 2
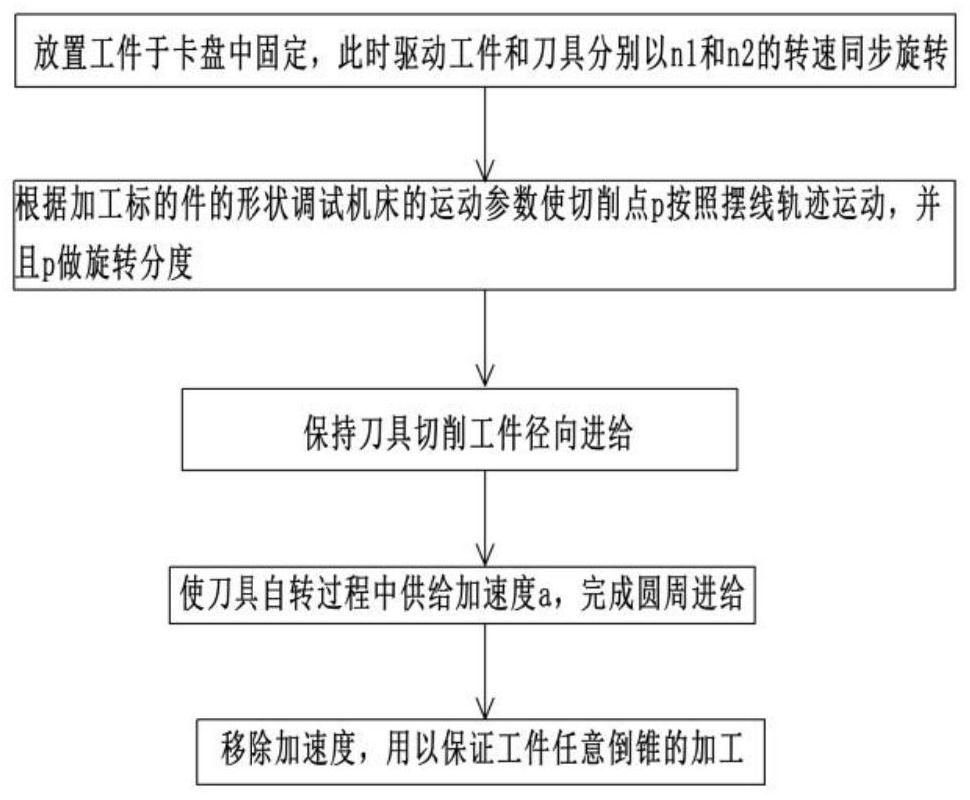
[0085] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that when the maximum radius of gyration is 43 mm, and it is required to process regular quadrilateral parts with a side length of 14 mm and an accuracy of 0.03 mm, or straight groove parts, the operator will engage the raw material on the chuck In 301, the raw material and the milling head 601 are then driven to rotate synchronously at speeds n1 and n2, respectively.
[0086] At this time, the operator adjusts according to the parameters, so that the parameters satisfy the motion trajectory equation of the cutting point p follows the following equation, where t is a reference variable, t∈[a,b], a1 is the radius of the base circle of the cycloid, R 2 is the radius of the occurrence circle, where A, B, R 1 and R 2 is a constant, t is the revolution angle of the cycloid, A is the distance from point p to the center of the circle, and B is the initial angle of the cycloid; the parameter equation is
[008...
Embodiment 3
[0091] The difference between this implementation and the above-mentioned embodiment lies in the processing of heptagonal parts. Given a round bar with a diameter of 21mm, it is required to process a heptagon with a circumcircle radius of 10mm and an accuracy of 0.01mm. Take A=12.5mm, R 1 =32mm,R 2 =16mm, B=0, α=42, the cycloid trajectory is obtained as Figure 11 As shown, the measured machining accuracy is 0.005mm, which meets the machining requirements.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com