Motion intention recognition device for lower extremity exoskeletons and method thereof
A technology for motion intentions and recognition devices, applied in applications, medical science, manipulators, etc., can solve problems such as increased cost, large size, and complex recognition models
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0079] The specific implementation manners of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
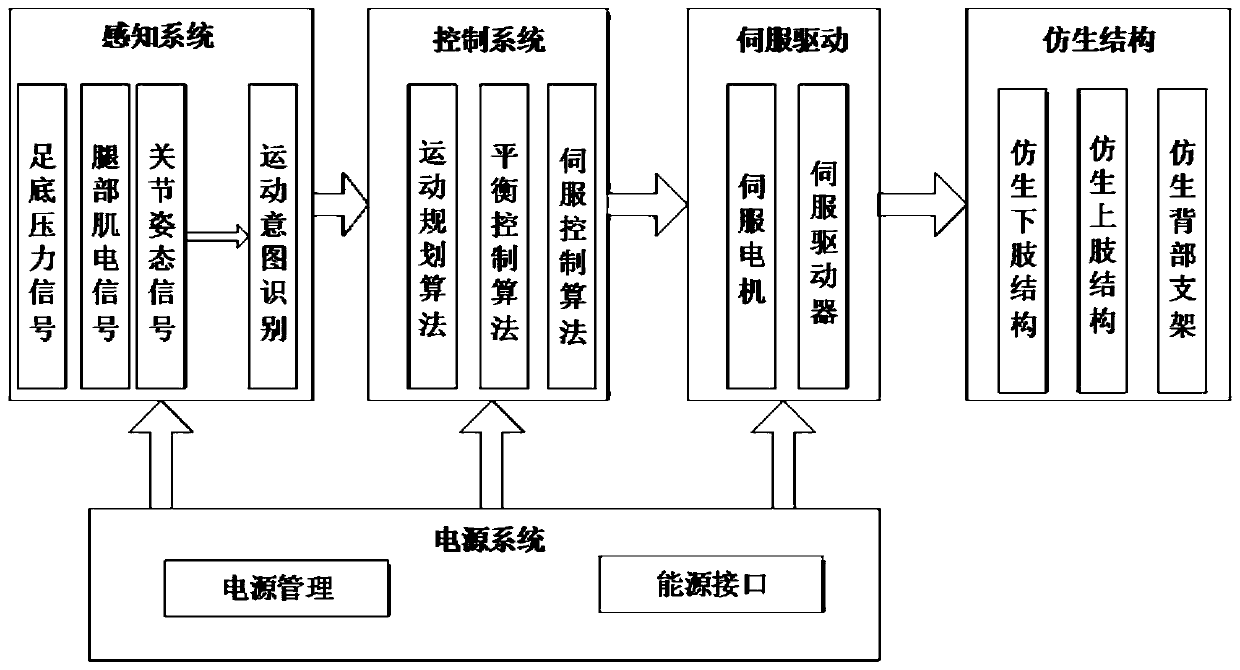
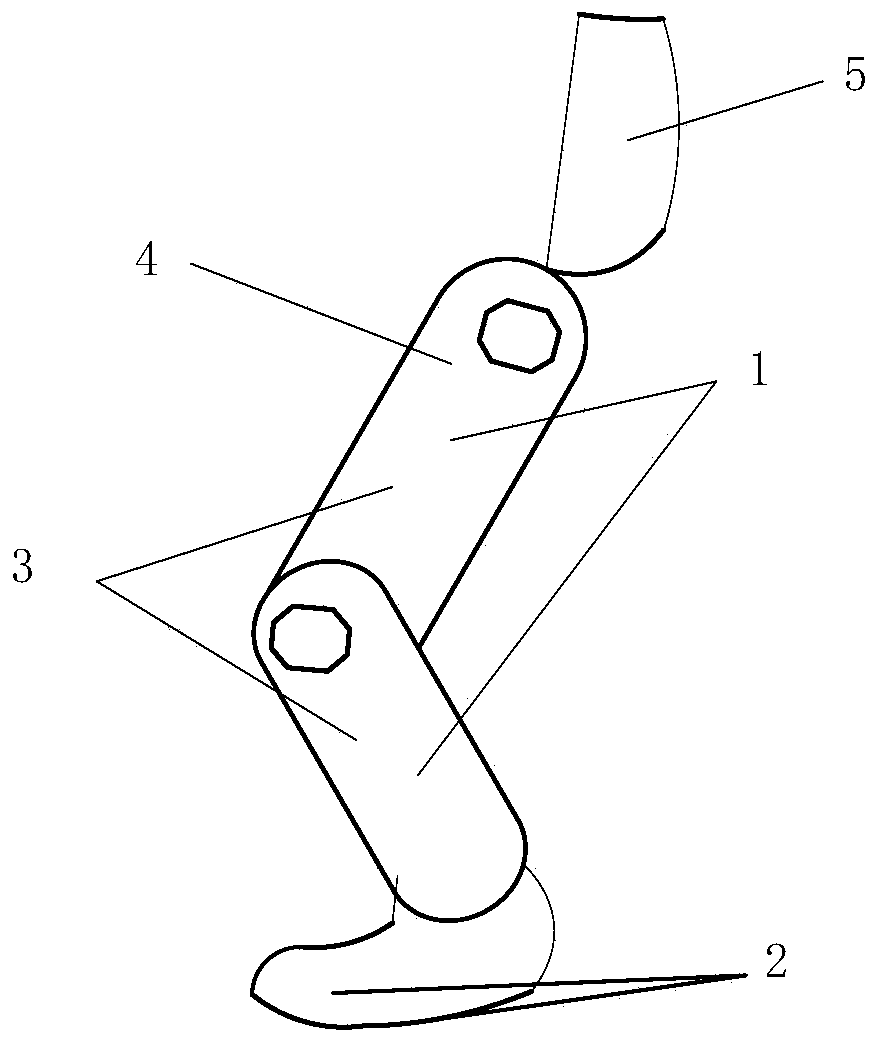
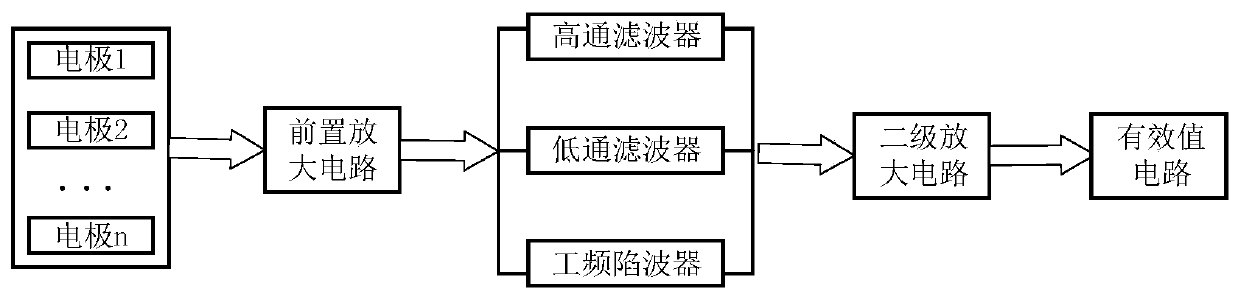
[0080] Lower limb assist exoskeleton system such as figure 1 As shown, it includes exoskeleton bionic mechanism system, perception system, control system, power supply system and drive system. Among them, the bionic mechanism system includes the bionic lower limb structure, the bionic upper limb structure, and the bionic back support; the perception system includes the acquisition of plantar pressure signals, leg myoelectric signals, joint posture signals, and movement intention recognition; the control system includes motion planning algorithms, balance Control algorithm, servo control algorithm; power system includes power management system and energy interface; servo ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com