High-speed train braking force optimal distribution method
A technology for optimizing allocation and high-speed trains, applied in brakes, railway braking systems, braking transmissions, etc., can solve problems such as less consideration of adhesion limit differences, train slippage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] 1 Optimal distribution strategy of air braking force based on maximum adhesion utilization
[0057] 1.1 Objective function
[0058] The coefficient of adhesion μ that would normally be utilized in the locomotive adhesion concept L The ratio to the available stickiness coefficient μ is defined as sticky utilization:
[0059]
[0060] The available sticking coefficients and the used sticking coefficients are expressed as follows:
[0061]
[0062]
[0063] From formula (1) (2) (3), the equivalent expression of adhesion utilization rate can be obtained
[0064]
[0065] In the formula: F is the adhesion force (KN) utilized, F max is the maximum adhesion force (KN) that can be produced between the wheel and rail, and p is the vertical static load (KN).
[0066] According to the requirements of braking force distribution, it is necessary to maximize η, which is equivalent to (1-η) 2 minimum. The air braking force distribution of 4 vehicles is taken as an ex...
Embodiment 2
[0121] 1 Simulation and experiment
[0122] 1.1 Simulation results and analysis
[0123] Aiming at the distribution of braking force during the train braking process, the simulation model of fast braking conditions is established by using MATLAB / SIMULINK as follows: figure 1 authenticating.
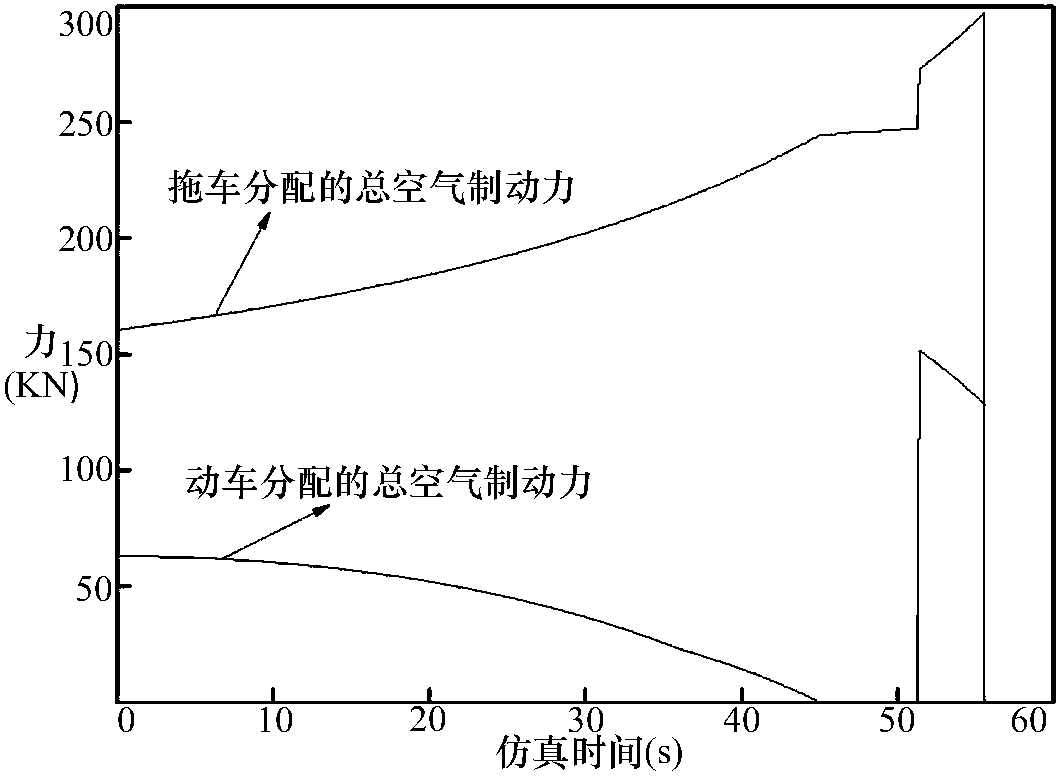
[0124] Such as image 3 Shown is the total air braking force distributed by the motor car and the trailer during the braking process. It can be seen that the total air braking force distributed by the trailer has been increasing, and the motor car has been decreasing accordingly until it is zero. After 50s, since the electric braking force is zero, the trailer can no longer meet the braking requirements, and the air braking force of the train needs to be supplemented.
[0125] Such as Figure 4-7 Shown is the comparison of air braking force distribution and load-to-weight ratio distribution of 4 trailers using the optimal distribution algorithm of the present invention, by Figure 4-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com