Sorbent for dialysis device and dialysis system
An adsorbent, dialysate technology, used in dialysis systems, selective adsorption, ion exchange treatment devices, etc., can solve problems such as defects, low toxin removal levels, and rare pH evolution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
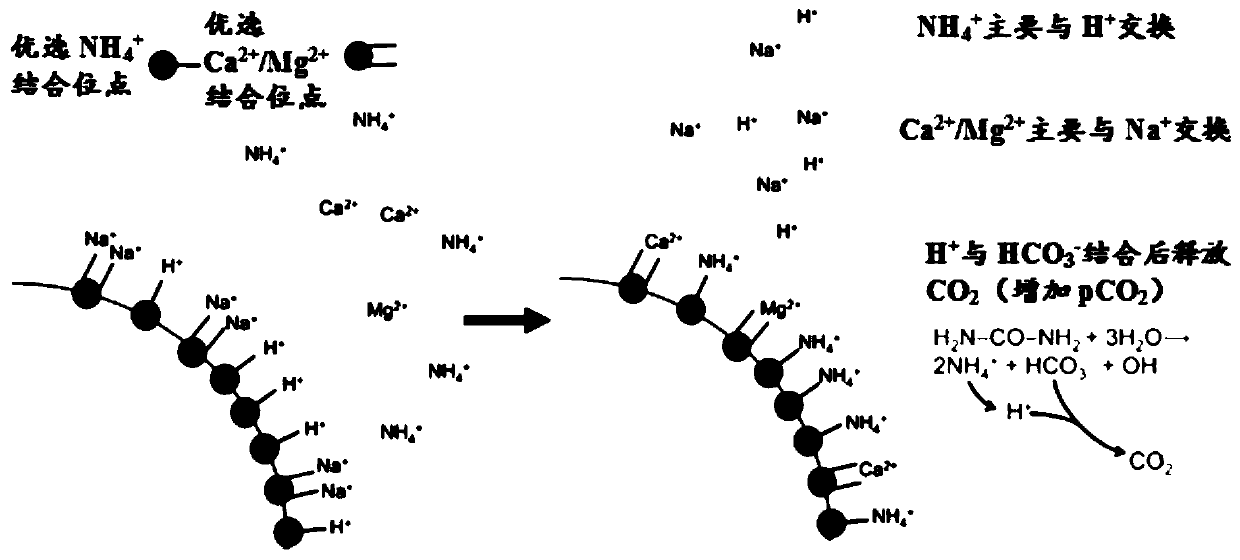
[0114] The present invention also provides a method for preparing an adsorbent, comprising: combining immobilized uremic toxin-treating enzyme particles for converting urea into ammonium ions with an ammonium ion mainly exchanged for hydrogen ions and an essential cation mainly exchanged for sodium ions. cation exchange particles; providing a source of sodium; and optionally, mixing in anion exchange particles and / or organic compound adsorption particles.
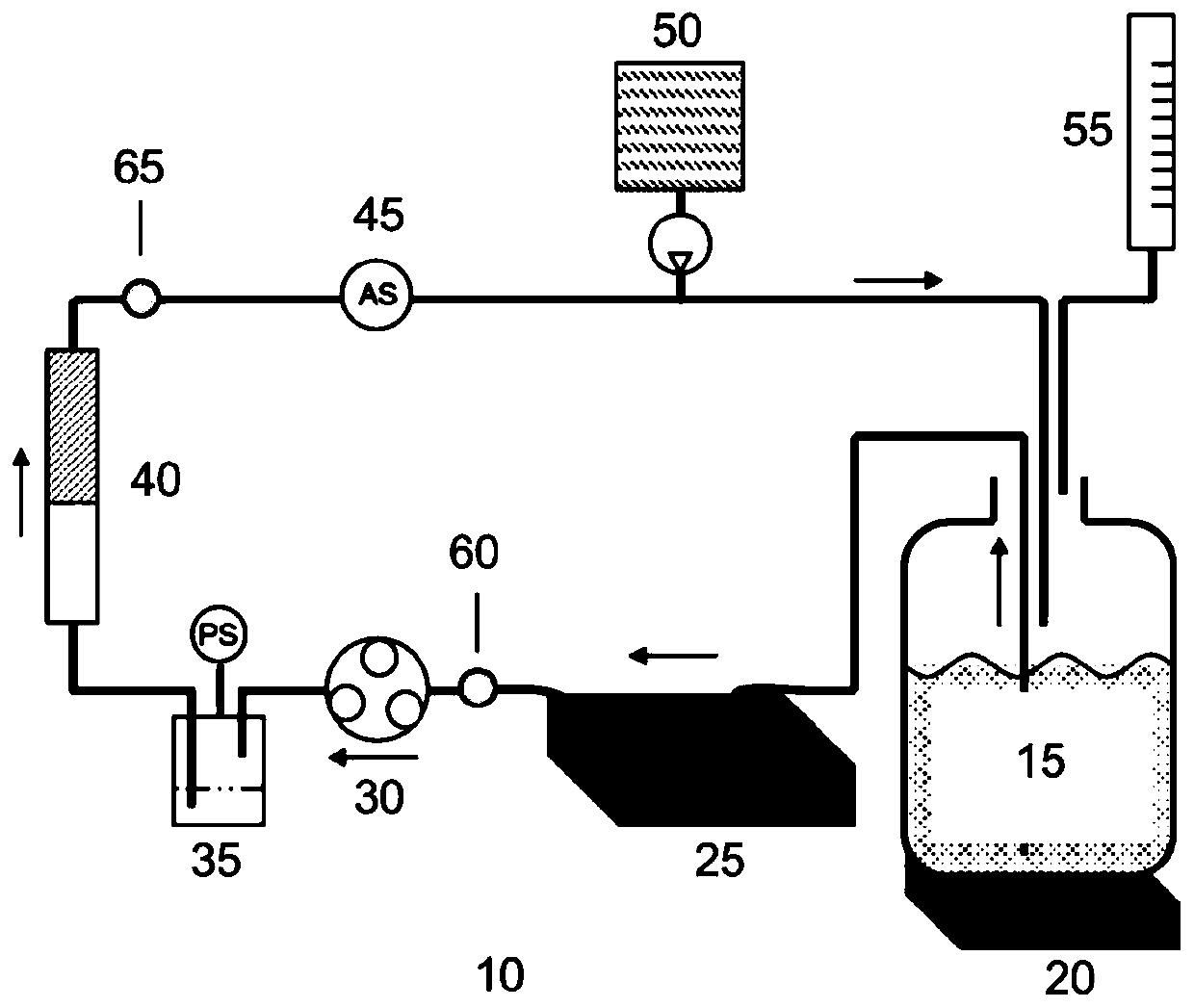
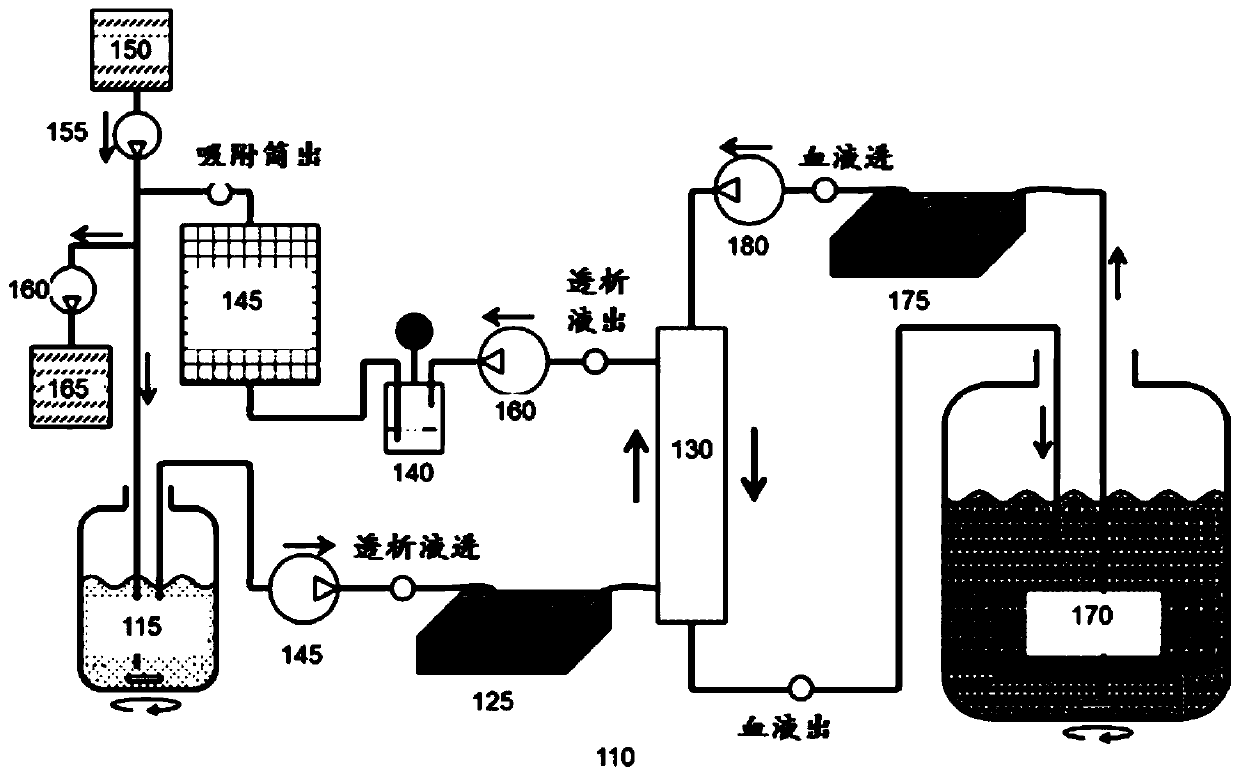
[0115] In one embodiment, the sorbent is contained in at least one sorption cartridge. The sorption cartridge can be configured for easy removal from the dialysis device. The cartridges are available in a compact design and are made of wear-resistant materials. The cartridge can be made of chemically and biologically inert elastic material. The adsorption cartridge may also have the ability to withstand the pressure of the fluid flow system in the dialysis device without leakage. The cartridge can be made of materials ca...
Embodiment 1
[0139] Embodiment 1: the preparation of zirconium phosphate
[0140] Zirconium phosphate is synthesized by existing methods, for example, according to the US Patent No. US3850835, by reacting an aqueous mixture of basic zirconium sulfate and phosphoric acid, or by carbonic acid Reaction synthesis of sodium zirconium and aqueous mixtures of phosphoric acid.
[0141] The resulting product was titrated to pH 4.5. Wherein, 5M sodium hydroxide solution is gradually added to the aqueous slurry of zirconium phosphate until the pH value reaches 4.5. After titration, the zirconium phosphate was first washed until the filtrate was within the acceptable leachable range and then air dried.
Embodiment 2
[0142] Embodiment 2: the preparation of hydrated zirconia
[0143]Hydrated zirconia is synthesized by existing methods, for example, by reacting an aqueous mixture of sodium zirconium carbonate and sodium hydroxide according to the method described in US Patent No. US4256718. After the hydrous zirconia is synthesized, the resulting product is titrated to a pH of 12 to 13. Wherein, an aqueous slurry of hydrated zirconia can be prepared and titrated with 5M sodium hydroxide until the pH value of the slurry reaches 12-13. In some cases, the hydrated zirconia is also washed until the leachate concentration in the filtrate is within acceptable levels, and then it is air dried. Alternatively, the hydrated zirconia can be recovered directly from the slurry and air dried. The hydrated zirconia that has undergone the washing step is called "washed hydrated zirconia", and the hydrated zirconia recovered directly from the titration slurry is called "unwashed hydrated zirconia".
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com