Method and device for obtaining aerosol extinction coefficient
An extinction coefficient, aerosol technology, used in measurement devices, climate sustainability, particle and sedimentation analysis, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in achieving very high accuracy and large limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
[0104] Specific embodiment one (the 2nd identification point is measuring point),
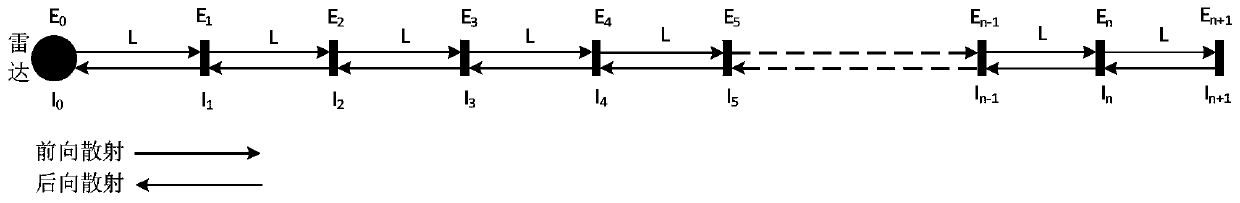
[0105]First, take the position where the lidar is located as the origin, and set n+1 equidistant marker points on the detection path of the lidar (such as figure 2 shown), and take the second mark point on the detection path starting from the origin as the measurement point. In addition, as an optional embodiment, the distance L between two adjacent marking points is 15 meters (m).
[0106] The aerosol extinction coefficient α at the measurement point is obtained by measuring the atmospheric integral turbidimeter at the second mark point 2 and the backscatter coefficient β 2 , and calculate the atmospheric correction parameter A. For example, as an optional embodiment, α 2 =1*10 -5 , β 2 =2*10 -6 , A=1.
[0107] Use the laser radar to launch the laser pulse into the atmosphere along the detection path, and measure the intensity I of the backscattered light at each mark point on the det...
specific Embodiment 2
[0118] Specific embodiment two (the nth marking point is a measuring point),
[0119] First, take the position where the lidar is located as the origin, and set n+1 equidistant marker points on the detection path of the lidar (such as figure 2 shown), and take the nth mark point on the detection path starting from the origin as the measurement point. In addition, as an optional embodiment, the distance L between two adjacent marking points is 15 meters (m).
[0120] The aerosol extinction coefficient α at the measurement point is obtained by measuring the atmospheric integral turbidimeter at the nth mark point n and the backscatter coefficient β n , and calculate the atmospheric correction parameter A. For example, as an optional embodiment, α n =1.5*10 -5 , β n =2.3*10 -6 , A=1.1.
[0121] Use the laser radar to launch the laser pulse into the atmosphere along the detection path, and measure the intensity I of the backscattered light at each mark point on the detecti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com