Method for analyzing lead pollution source in water body deposit
A sediment and pollution source technology, applied in the field of environmental geology, to achieve accurate calculation results, reduce the amount of data, and simplify the traceability process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] This embodiment provides a method for analyzing the source of lead pollution in water body sediments, comprising the following steps:
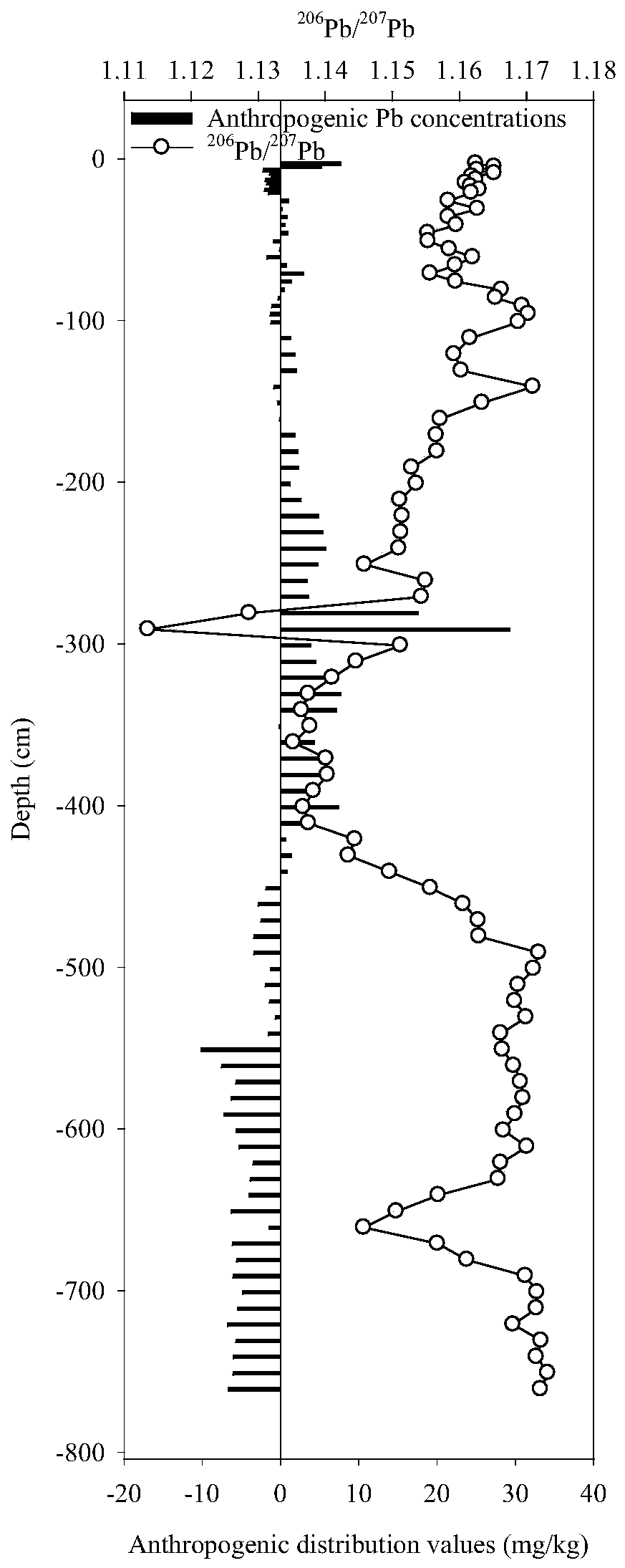
[0029] S0, using geochemical baselines to differentiate natural and anthropogenic sources of lead in sediments;
[0030] S1, using a standardized method to establish a geochemical baseline model of lead in sediments in the area to be studied;
[0031] S2, calculating the lead geochemical baseline value of the research area and the corresponding lead geochemical baseline value of each sample based on the baseline model described in step S1;
[0032] S3, according to the sediment lead geochemical baseline value calculated in step S2 and the corresponding lead geochemical baseline value of each sample, calculate the average value of the anthropogenic contribution concentration and the corresponding anthropogenic contribution rate at each sampling point, and screen out The point corresponding to man-made lead, the lead concentration of the...
Embodiment 2
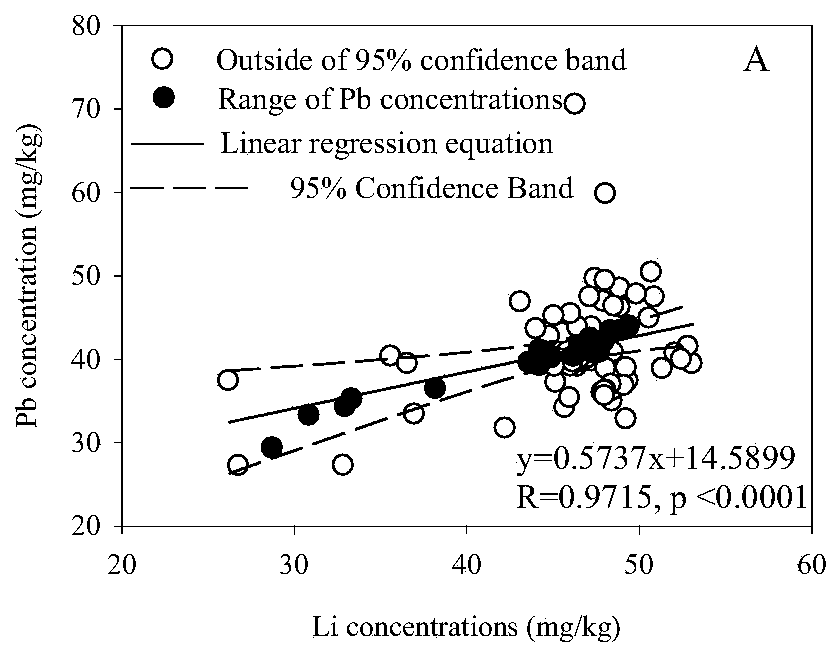
[0040] In this example, Daheiting Reservoir was taken as the research area, and a 7m-long sediment columnar sample was collected in a deep silted area, and cut into 92 sediment samples. Firstly, pre-treat the sediment, dry it with a freeze dryer, pass it through a 0.25mm nylon sieve, and then digest the mixed acid to measure the concentration of lead (Pb), lithium (Li) and other metals on the machine, and Pb is the target element , Li is an inert element and is used as a calibration element in the standardization method.
[0041] Sediment samples and columnar samples from the pretreated study area were analyzed for lead sources using the following procedure.
[0042] 1. First, according to the contents of Li and Pb in the 92 samples, a binary regression equation was made to determine the 95% confidence interval, and the points falling within the 95% confidence interval were screened out, and the concentration of Li and Pb was further A standardized method is used to establish...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com