A model iteration updating method and device
An iterative update and model technology, applied in the computer field, can solve the problem that retraining and updating the knowledge base takes a lot of time, saving time and money costs, improving use efficiency, and reducing the amount of updates.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
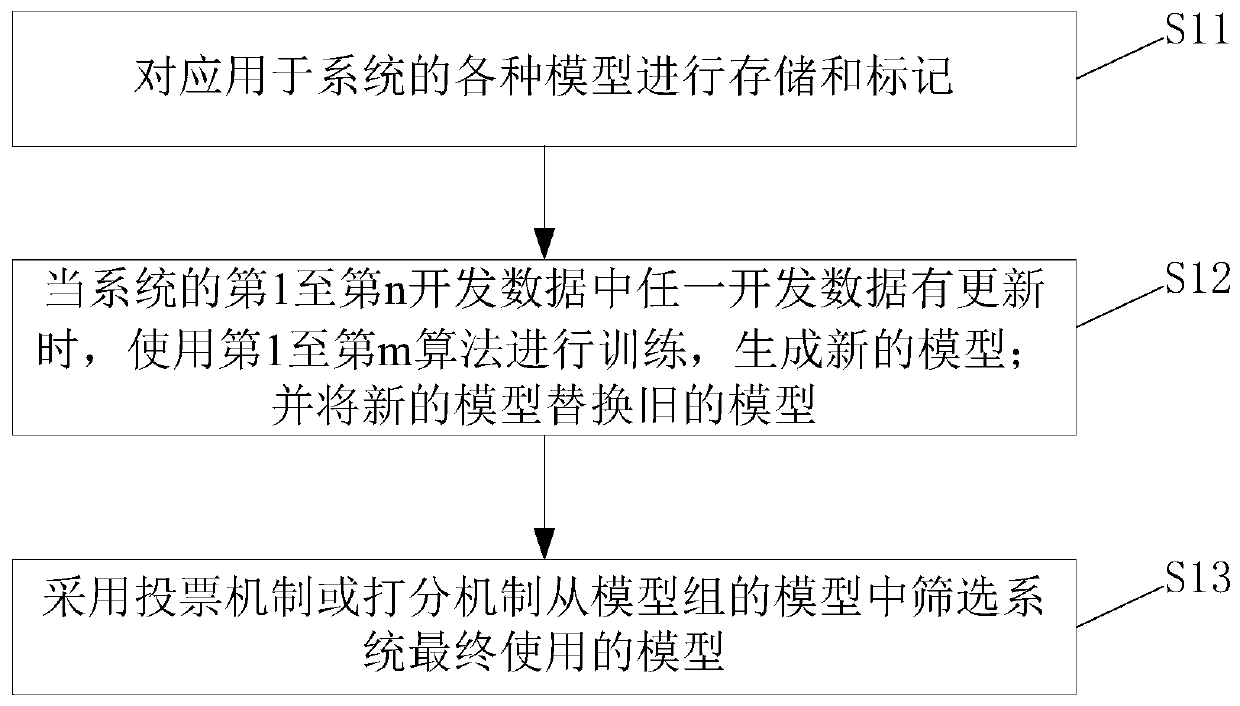
[0028] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for iteratively updating a model, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0029] Step S11, storing and labeling various models applied to the system. The system includes m algorithms and n sets of development data, and trains the 1st to mth algorithms respectively through the 1st to nth development data to obtain the training After the model group, the model group is marked as Md11, Md12, ..., Md1n, Md21, Md22, ..., Md2n, ..., Mdm1, Mdm2, ..., Mdmn, where n and m are positive integers and n≥1, m ≥1, m represents the serial number of the algorithm, and n represents the serial number of the development data; the first development data trains the 1st to mth algorithms respectively, and respectively obtains the model Md11, model Md12, ..., model Md1n; the second development data respectively trains the first The mth algorithm is trained to obtain the model Md21, the model Md22, ..., the model Md2n respectiv...
Embodiment 2
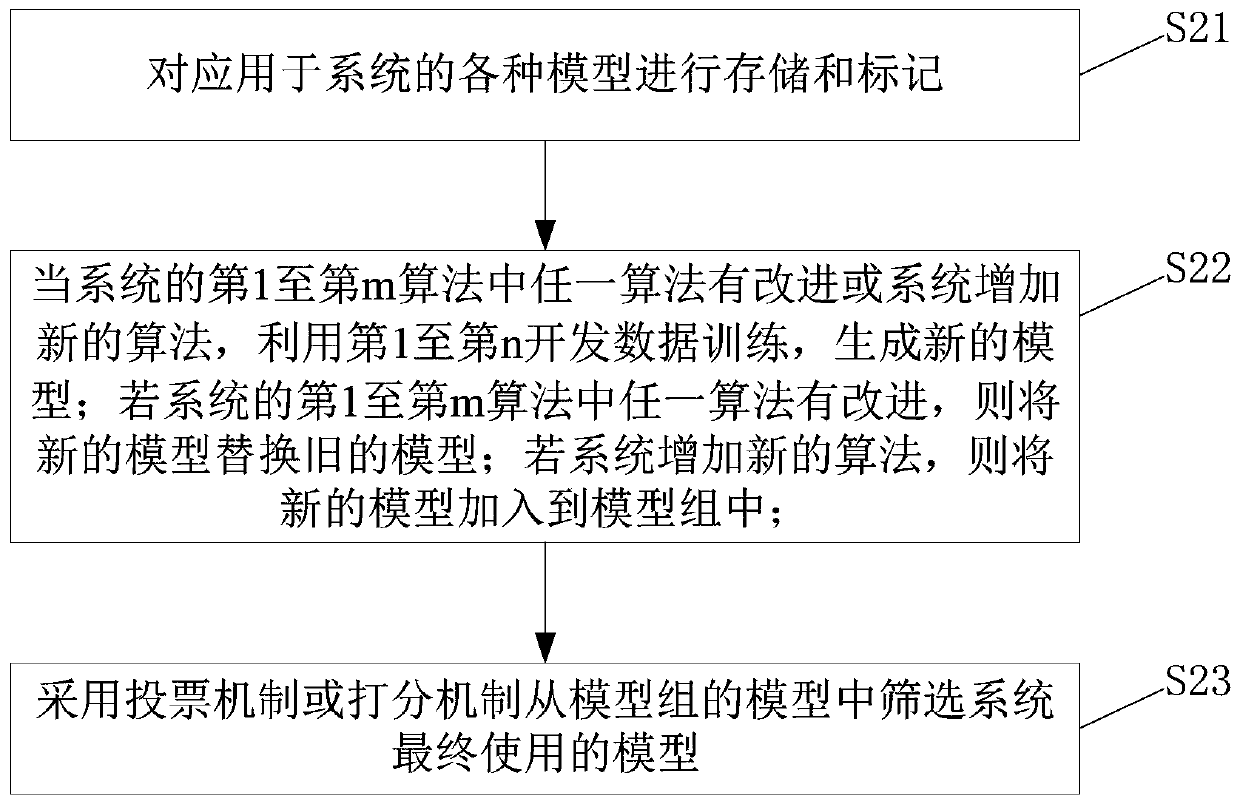
[0039] The embodiment of the present invention provides another method for iteratively updating the model, which specifically includes the following:
[0040] Step S21, storing and labeling various models applied to the system. The system includes m algorithms and n sets of development data, and trains the 1st to mth algorithms respectively through the 1st to nth development data to obtain the training After the model group, the model group is marked as Md11, Md12, ..., Md1n, Md21, Md22, ..., Md2n, ..., Mdm1, Mdm2, ..., Mdmn, where n and m are positive integers and n≥1, m ≥1, m represents the serial number of the algorithm, and n represents the serial number of the development data;
[0041] In the enumerated examples of the present invention, three kinds of algorithms are applied in a certain set of systems, respectively denoted as A1, A2, A3; the three kinds of algorithms are trained respectively with the first development data D1 and the second development data D2 , the tr...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The present invention also provides that the model iterative update device is applied to the model iterative update method; the model iterative update method is the same as the first and second embodiments, and will not be repeated here. The model iterative updating device has at least one processor; and a memory connected in communication with the at least one processor; wherein, the memory stores instructions executable by the at least one processor, and the instructions are executed by the at least one processor A processor executes to cause the at least one processor to execute the steps of the iterative model updating method.
[0051] The model iterative updating method of the present invention can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. The above-mentioned software functional units are stored in a storage medium, and include several instructions to enable a computer device (which may be a personal computer, server or network device, etc.) or a processor t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com