Novel rotor applied to high-speed permanent magnet motor
A technology for permanent magnet motors and rotors, which is applied in the direction of magnetic circuit rotating parts, electric components, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of low operating reliability, low power density, and low structural strength of permanent magnet motors, and achieve good heat dissipation , large electromagnetic torque, and the effect of improving operational reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
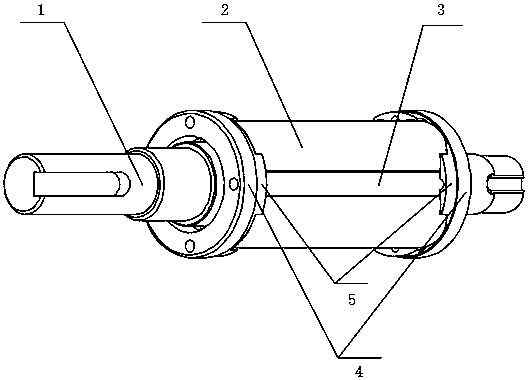
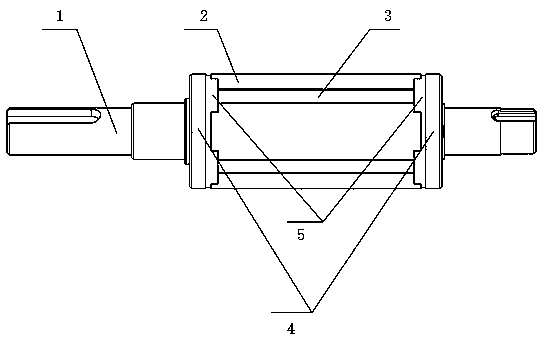
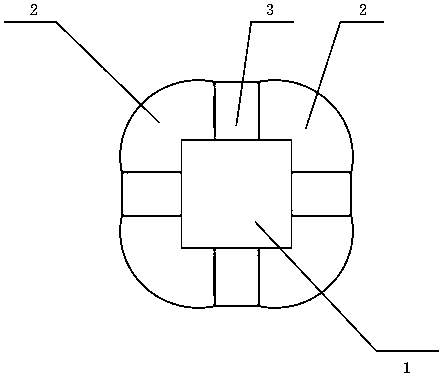
[0019] see Figure 1 to Figure 4 , a new type of rotor applied to high-speed permanent magnet motors, including a rotating shaft 1, a main permanent magnet 2, a transverse magnetization permanent magnet 3 and a magnetic isolation copper ring 4, characterized in that: the rotating shaft 1 is a polygonal rotating shaft, and the polygonal top Embedding the main permanent magnet 2 at an angle and fixing the main permanent magnet 2 circumferentially, on the one hand, increasing the adsorption force between the main permanent magnet 2 and the rotating shaft, can enhance the radial fixing of the permanent magnet to resist the centrifugal force at high speed; on the other hand On the one hand, the waveform of the air gap magnetic field is improved, and the loss is reduced; the magnetic isolation copper ring 4 is an approximate cup-shaped structure, and the magnetic isolation fixed wall 5 on it is tightly fastened to the two axial ends of the main permanent magnet 2, so as to realize th...
Embodiment 2
[0021] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the special features are as follows:
[0022] The combination of the transverse magnetism gathering structure and the surface-mounted rotor is used to gather magnetism through a transverse magnetism gathering permanent magnet 3 between the two main permanent magnets 2, and utilize the magnetic monopole characteristic of the magnetism gathering structure, that is, the transverse magnetism gathering The magnetic field distribution on both sides of the structure is extremely uneven, and the magnetic field intensity on the side close to the air gap is significantly higher than that on the side close to the rotating shaft; therefore, the magnetic field lines enter the main magnetic pole from the transverse magnetic accumulation permanent magnet 3 through the contact surface of the adjacent permanent magnet This means that the magnetic field strength at the center of the contact surface between the main magnetic pole a...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown in the figure, the traditional circular shaft is changed to the polygonal shaft 1 in the figure, and the permanent magnet 2 with the opposite magnetization direction is embedded in the vertex of the polygonal shaft to fix the permanent magnet 2 to avoid damage caused by the huge centrifugal force at high speed. . By adding transverse magnetization permanent magnet 3 between permanent magnets 2 to form a transverse magnetic field structure for magnetization concentration, the thickness of the rotor core can be greatly weakened or even completely eliminated, thereby reducing the size of the rotor and finally realizing the size of the motor shrinking.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com