Non-invasive human body thermal comfort AI sensing method
A non-invasive, thermal comfort technology, applied in the fields of machine learning, building physics, and computer vision, can solve the problems that users cannot know the temperature and cannot control it, and achieve the elimination of restricted human activities, good operability, and reduced complexity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
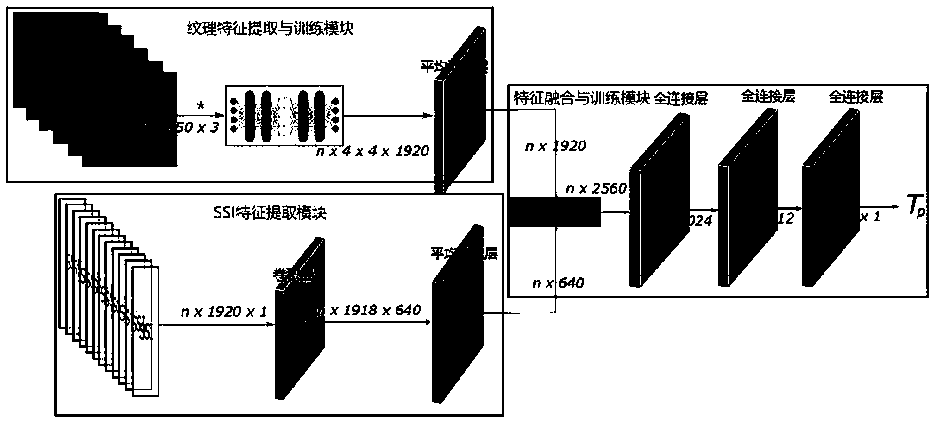
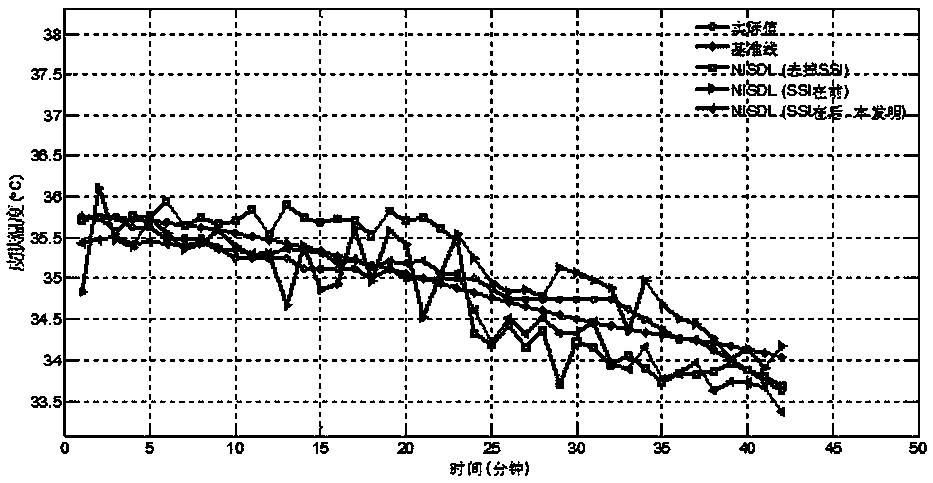
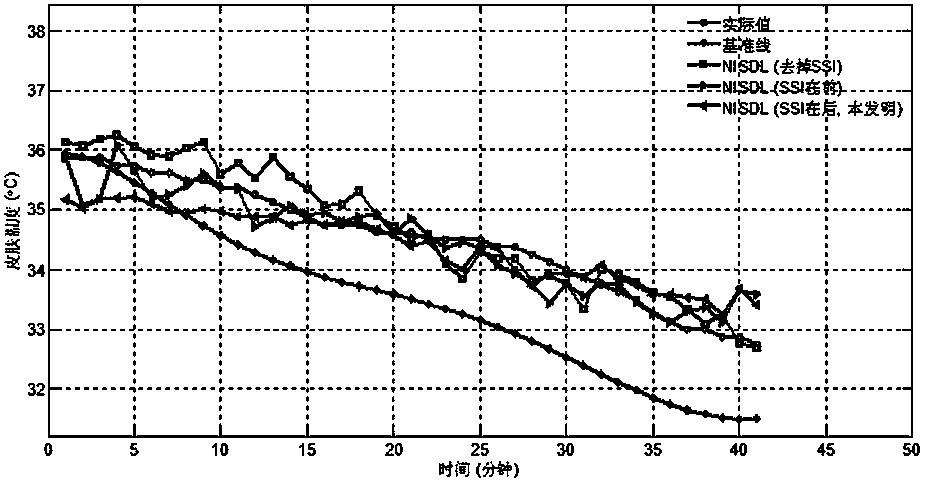
[0039] The shortcomings of the existing technology on human thermal comfort detection methods and the obvious application experience of HAVC system control fixation or manual participation are inspected. Relying on the development of computer vision and machine learning, the inventor is committed to adding "tactile and visual" capabilities to heating and cooling systems, real-time perception of human comfort, and thus providing real-time and effective feedback signals to participate in the automatic operation of thermostats. On the basis of massive data, it continuously learns user behavior habits and realizes the prediction function, so as to achieve adjustment in advance, meet the thermal comfort needs of users as much as possible, and finally realize people-oriented in the true sense.
[0040] For this reason, the present invention develops a brand new branch, and innovatively proposes a non-invasive AI perception method for human body thermal comfort. The technical implemen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com