A software reliability growth model for introducing faults based on Weibull distribution
A growth model and reliability technology, applied in the field of software reliability growth model
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
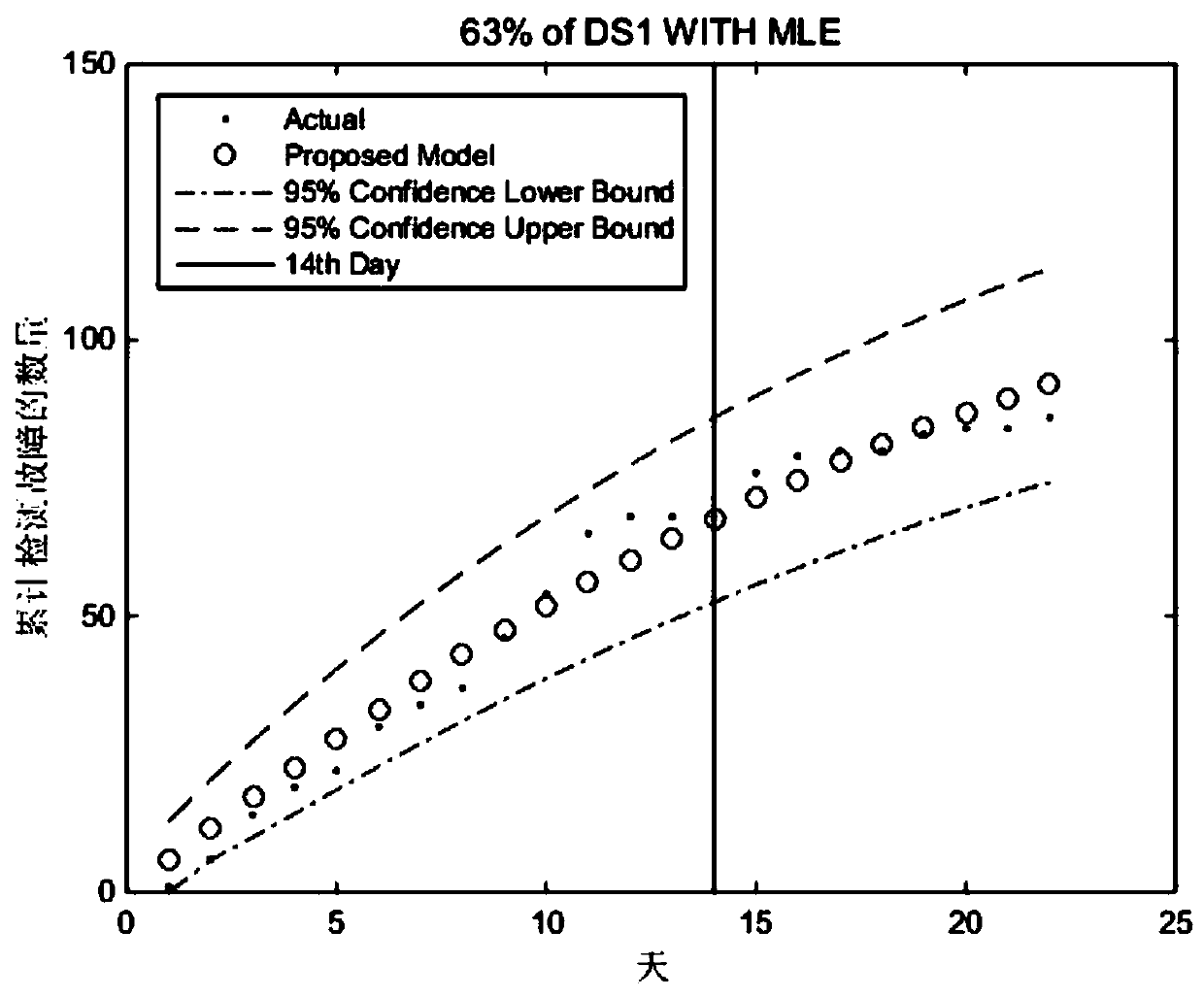
Embodiment 1
[0109] A software reliability growth model based on Weibull distribution introducing faults is characterized by comprising the following steps:
[0110] (1) The function of the total number of faults is expressed by the following formula:
[0111] a(t)=aF(t)+C (3)
[0112] Among them, a(t) represents the function of the total number of faults, a represents the total number of faults that are expected to be introduced in the end, F(t) is the distribution function of faults introduced, and C is the number of faults in the initially expected software;
[0113] (3) The fault introduction intensity function is expressed by the following formula:
[0114] η(t)=aF'(t) (4)
[0115] where η(t) means F'(t) means
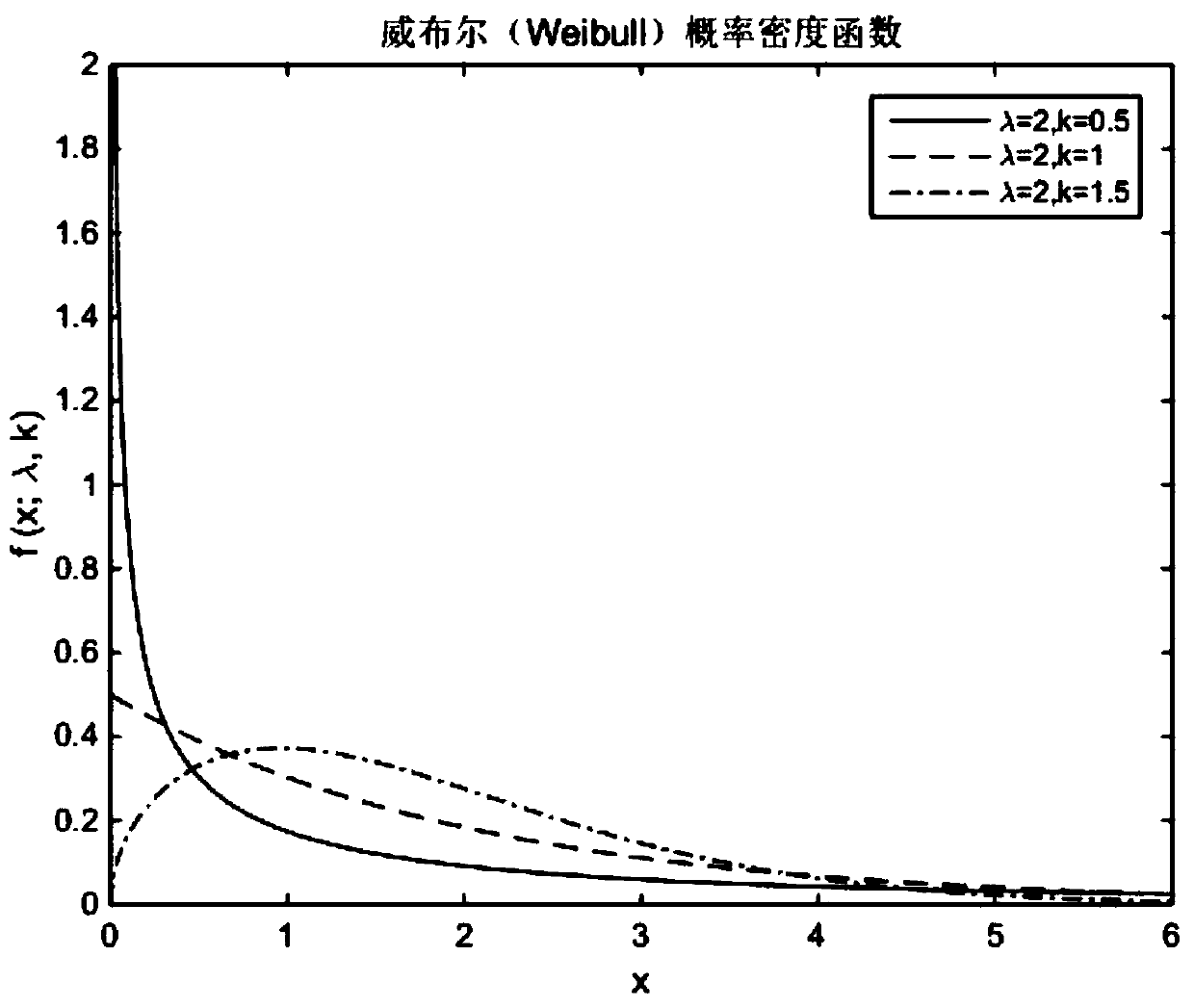
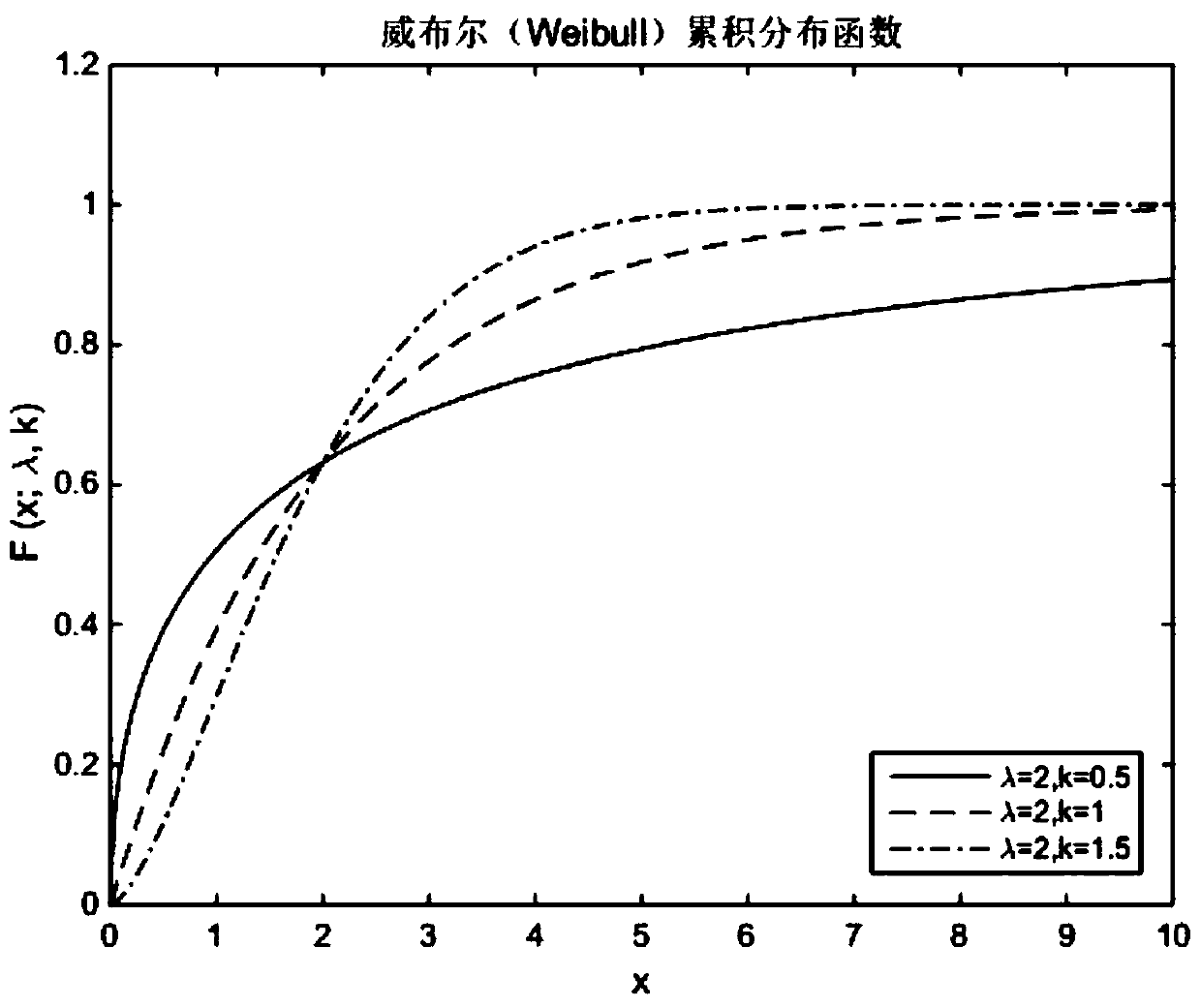
[0116] (3) Assuming that the total number of faults function (3) obeys the Weibull distribution, that is, the total number of faults function a(t) and the fault introduction intensity function η(t) can be expressed as:
[0117] a(t)=aF(t)+C=a[1-exp(-αt d )]+C (5)
[0118...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com