In-situ multiplex nucleic acid detection method
A technology of multiple nucleic acids and detection methods, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve problems such as marker limitations and achieve good specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 Human skin fibroblasts were used as experimental samples to investigate the in situ detection of cellular ACTB mRNA by double junction probe method.
[0027] (1) Cell culture and fixation:
[0028] The breast cancer cell line SK-BR-3 was cultured in DMEM (containing 10% FBS) for 24-48 hours, treated with trypsin to form suspended cells, planted on sterile glass slides, and cultured again for 12-24 hours. Rinse with DEPC-PBS, 3×3min; fix with 3% PFA prepared in DEPC-PBS at room temperature for 30min; rinse with DEPC-PBS again, and dehydrate with gradient ethanol: 70%, 85%, and 100%, respectively, for 5min each. Air dry.
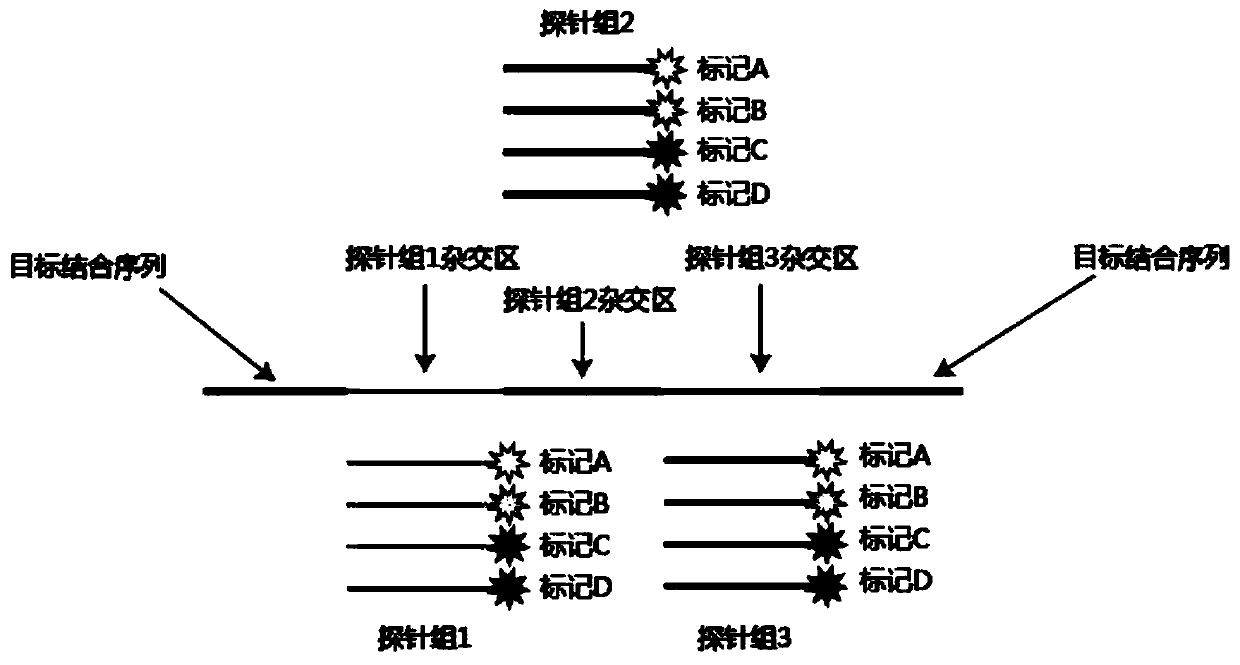
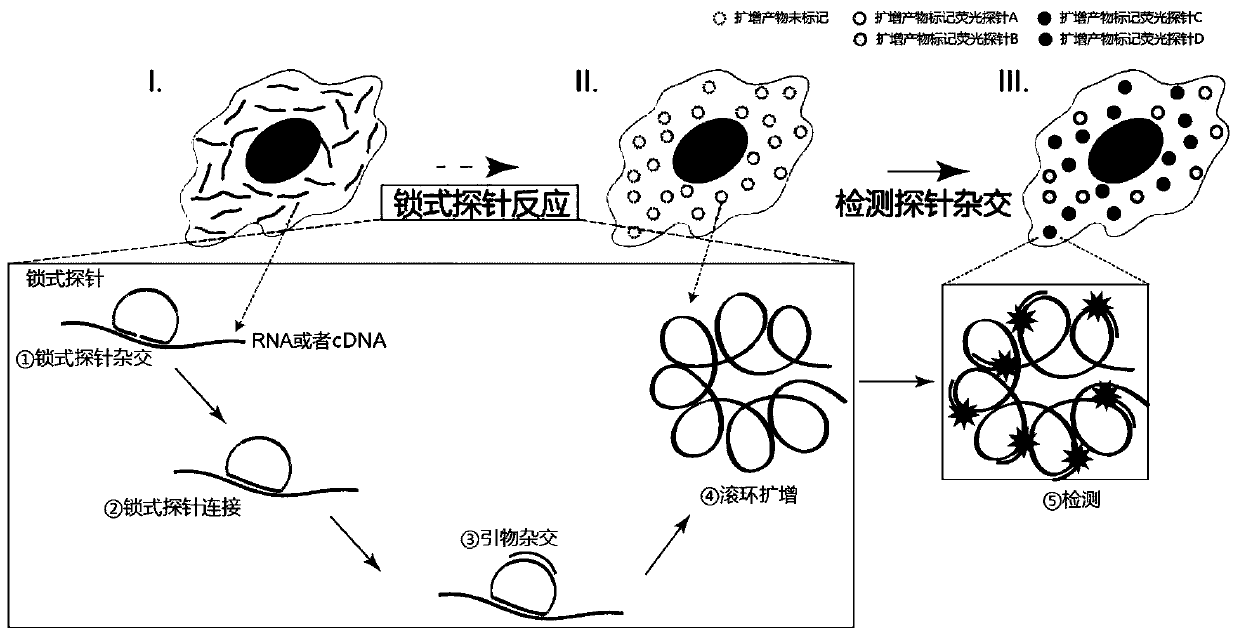
[0029] (2) In situ nucleic acid detection, such as Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0030] (1) padlock probe hybridization
[0031] The cell membrane of the breast cancer cell line SK-BR-3 was punched through the membrane, and 0.1M HCl was added to the sample and incubated at room temperature ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com