Oral care compositions for promoting gum health
A technology of oral care and composition, which is applied in the field of oral care composition, can solve problems such as adverse side effects, achieve the effect of promoting gum health, improving the beneficial effect of gum health, and stabilizing product quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 to 10
[0161] Examples 1 to 10 are dentifrice compositions as shown below, wherein the amounts of the components are in % by weight. They can be suitably prepared by conventional methods selected by the formulator. Examples 1 to 6 are preparations of the present invention according to the present invention, respectively prepared with two concentrations of stannous ion source (such as stannous chloride) and a single antifibrinolytic agent (such as TA, EACA or PAMBA). Example 7 is a formulation of the invention prepared with stannous chloride and two antifibrinolytic agents such as TA and EACA. At the same time, Comparative Formulation Examples 8 to 10 were prepared. Example 8 was prepared without a source of stannous ions, Example 9 was prepared without an antifibrinolytic agent, and Example 10 was prepared without any components. All compositions were prepared from mixtures of the ingredients in Tables 1 and 2 in the proportions indicated.
Embodiment 1 to 7
[0163]
[0164]
[0165] Table 2: Comparative Composition Examples 8 to 10
[0166]
Embodiment 11
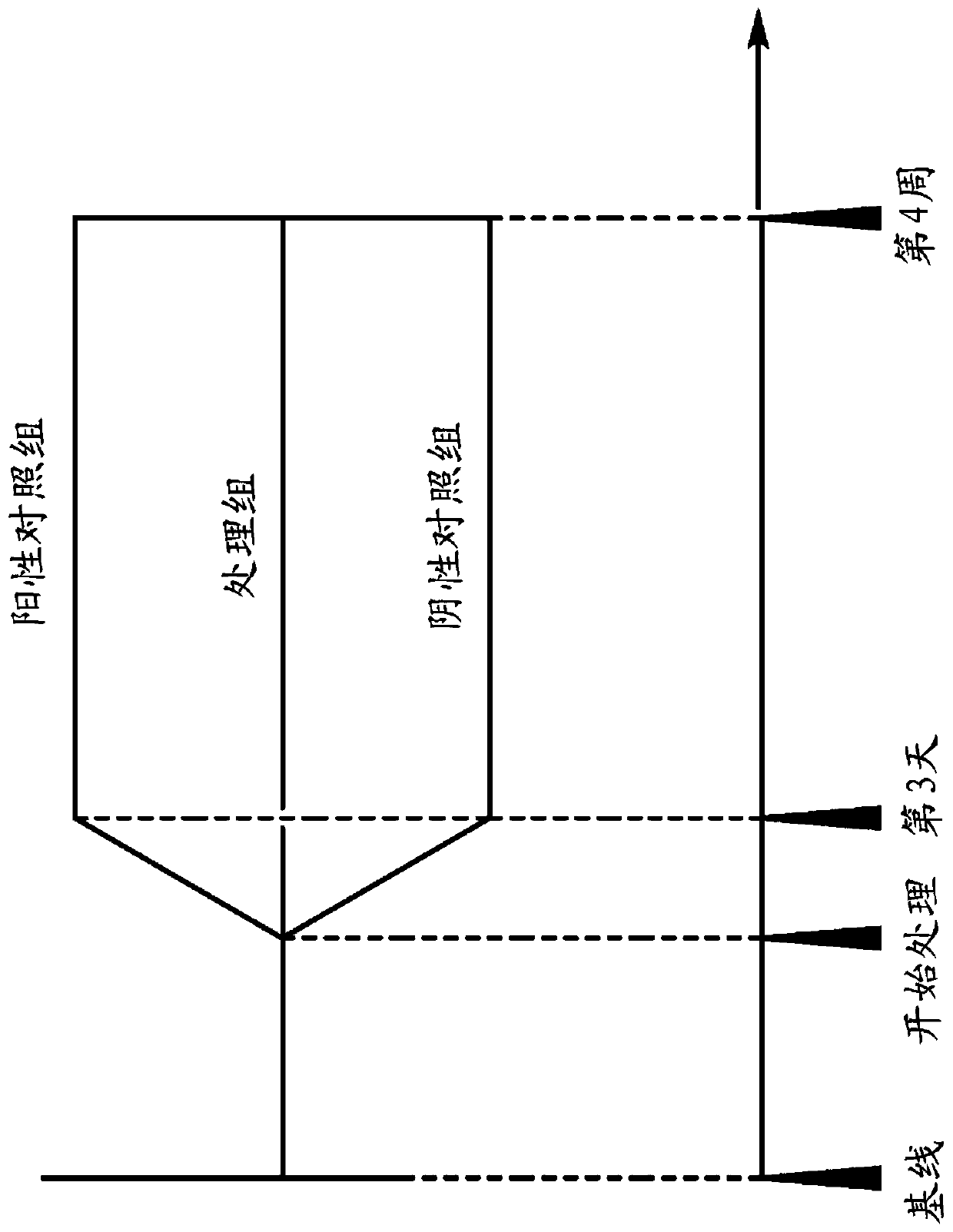
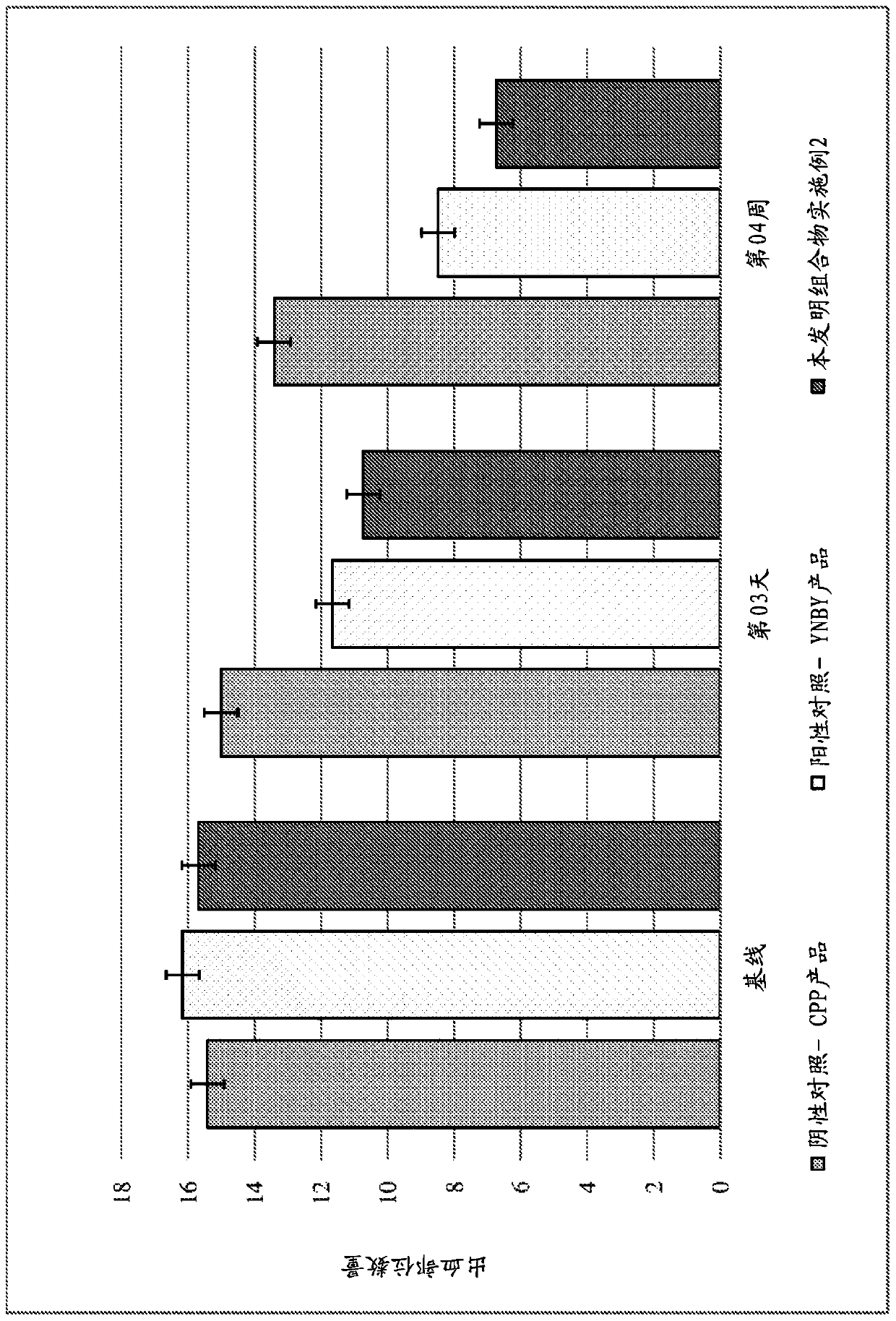
[0167] Example 11 - Assay for Measuring Improved Gingival Wound Healing in the Oral Mouth
[0168] The following assays were used to determine the improvement in gingival wound healing in the oral cavity for oral care compositions of the invention and control oral care compositions. This assay involves gentle probing of the gingival crevices to assess for bleeding. Gingivitis was assessed according to Mazza's Papapilla Bleeding Index on Probing ("PBI", with a modification of Muhlemann, H.R.: J. Prev. Dent. 1977; 4:6), otherwise known as the "Mazza Index", to determine Number of bleeding sites (defined by Mazza, 1981). For this measurement, a maximum of 56 sites on the medial and distal lingual surface of each tooth were probed. Place the probe in the gingival sulcus to a depth of approximately 0.5 mm to 1.0 mm and scan the tip of the interdental papilla from its insertion point along the soft tissue direction of the sulcus. Scan all of the face or tongue in each quadrant ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com