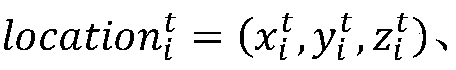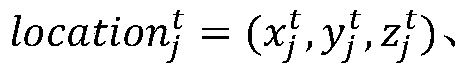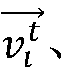A method for selecting an adaptive routing protocol of a mobile ad hoc network
A mobile self-organization and routing protocol technology, applied in data exchange networks, digital transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as inability to respond and adjust strategies, network performance constraints, and nodes not being able to adapt to topology changes well
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0192] The result of Example 1 shows that after using the routing protocol selection method of the present invention, some aspects of the performance of the ad hoc network can be improved.
[0193] Simulation example 2 compares the network performance after using different routing strategies.
[0194] The three different routing strategies in simulation example 2 are:
[0195]
[0196] It can be seen from the simulation results that in Example 2, using the routing protocol selection method of TARCS1, no matter what speed the node moves, the network packet transmission rate is the largest, as shown in Figure 11 shown.
[0197] It can be seen from the simulation results that in Example 2, the order of network throughput is: TARCS1>TARCS2>TARCS3, such as Figure 12 shown.
[0198] It can be seen from the simulation results that in Example 3, regardless of the node speed, the average end-to-end delay of TARCS3 is the smallest, as Figure 13 shown.
[0199] It can be seen ...
example 2
[0200] The results of Example 2 show that different routing strategies can improve different aspects of network performance.
[0201] In actual scenarios, due to the uncertainty of the target and the complexity of the environment, the trajectory and movement of nodes will change at any time. The significance of the present invention is to allow nodes to perceive and respond to these changes, so that the network performance is affected by these changes as little as possible. The present invention provides an adaptive routing protocol selection method by using the perceived changes in topology state between nodes in the network, so that nodes can quickly adapt to changes in mobility patterns, and prevent network performance from being affected by changes in node mobility patterns. reduce.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com