Amide copolymer hydrate kinetic inhibitor and application thereof
A kinetic inhibitor, hydrate technology, applied in drilling compositions, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of insignificant enhancement of inhibitory performance, small controllability of molecular structure, general molecular weight distribution, etc. Wide application range and conditions, small molecular dispersion coefficient, high yield effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Take 10.297g of vinylcaprolactam and 5.107g of N-isopropylacrylamide into a three-necked flask, and then connect the three ports of the flask with a thermometer, a condenser tube, and a rubber hole plug, and the upper end of the condenser tube is connected to the gas path. After evacuating, pass nitrogen gas to initially remove the air in the pipeline. Weigh 0.308g of azobisisobutyronitrile and 100mL of N,N-dimethylformamide, dissolve azobisisobutyronitrile in dimethylformamide, inject it into the flask from the hole of the rubber stopper with a syringe, and seal it. Then evacuate and circulate nitrogen for three times to ensure anaerobic operating conditions. Turn on the condensed water circulation, turn on the magnetic stirring at 300rpm, and turn on the oil bath at 85°C. After reacting for 12 h, the oil bath and stirring were turned off, and the solution was cooled to room temperature. The solution was rotary evaporated at 80°C until the precipitation was complete....
Embodiment 2
[0030] Same as Example 1, the difference is:
[0031] The reaction temperature is 70°C and the reaction time is 20h. Cool the reacted solution to room temperature, dry and cool at 70°C, then drop the solution into anhydrous ether, wash and dry the obtained solid to obtain the target product; vinylcaprolactam and N- The mass ratio of isopropylacrylamide is 1:1; the mass ratio of total monomer mass to azobisisobutyronitrile is 50:1, and the mass ratio of azobisisobutyronitrile to N,N-dimethylformamide The ratio is 1:100.
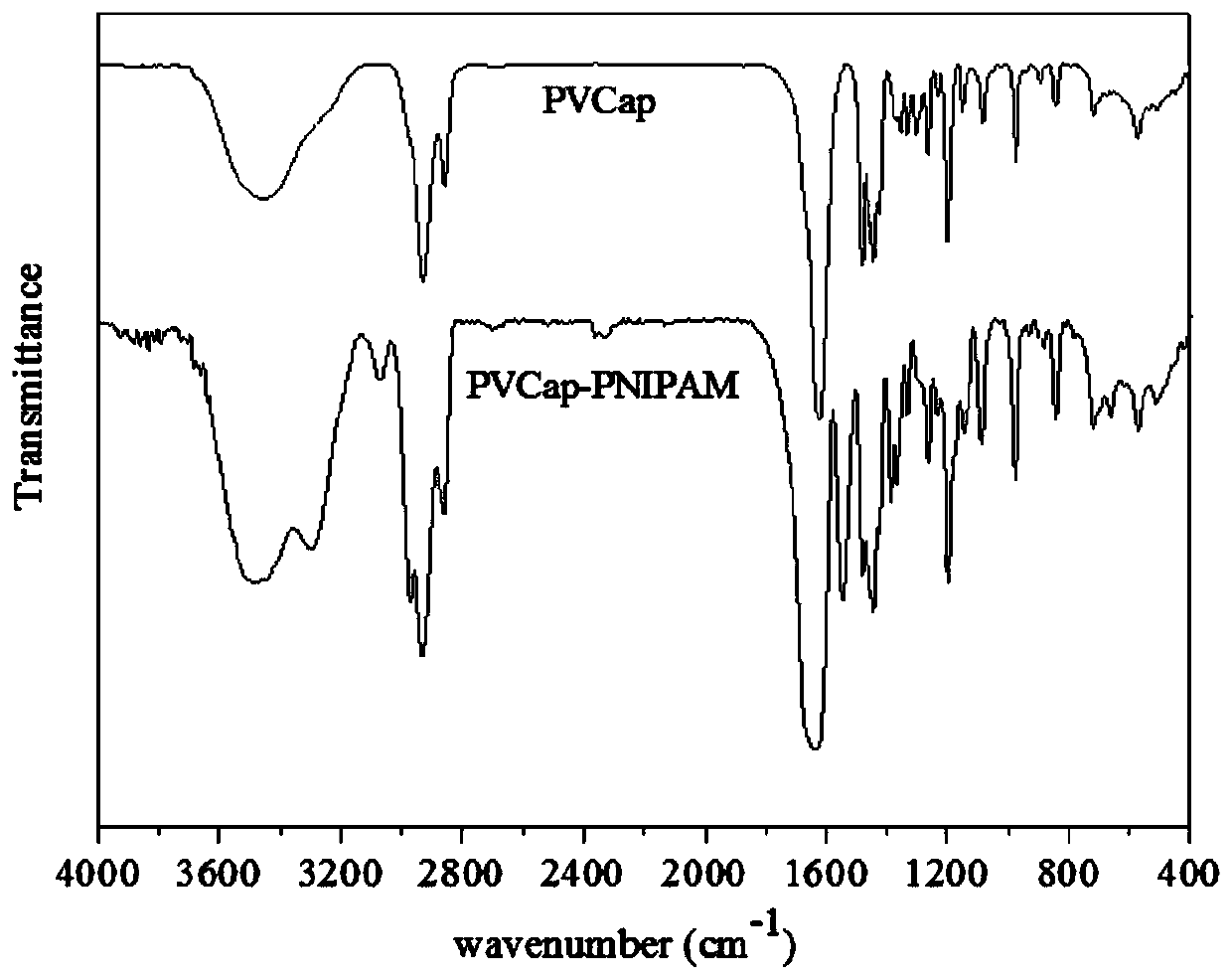
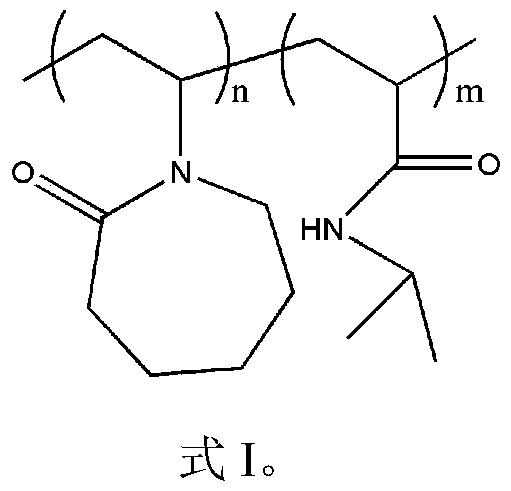
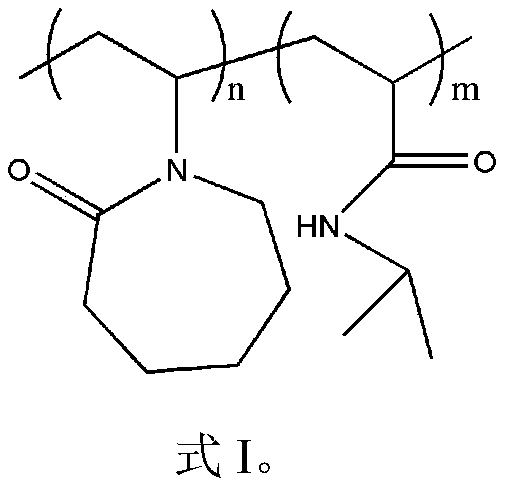
[0032] The characteristic peaks of the characteristic structure were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectrum and hydrogen spectrum of nuclear magnetic resonance to determine the synthetic substance, and the molecular weight of the synthetic substance was characterized by gel permeation chromatography. It was determined that the product prepared in this example was poly(vinyl caprolactam-isopropylacrylamide), and the weight average molecular weigh...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Same as Example 1, the difference is:
[0035] The reaction temperature is 90°C and the reaction time is 6h. The reacted solution is cooled to room temperature, dried and cooled at 95°C, and the solution is dropped into anhydrous ether, and the obtained solid is washed and dried to obtain the target product; vinyl caprolactam and N- The mass ratio of isopropylacrylamide is 20:1; the mass ratio of total monomer mass to azobisisobutyronitrile is 200:1, and the mass ratio of azobisisobutyronitrile to N,N-dimethylformamide The ratio is 1:500.
[0036] The characteristic peaks of the characteristic structure were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectrum and hydrogen spectrum of nuclear magnetic resonance to determine the synthetic substance, and the molecular weight of the synthetic substance was characterized by gel permeation chromatography. It is determined that the product prepared in this example is poly(vinyl caprolactam-isopropylacrylamide), and the weigh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com