Method for forming hard carbon anode material lithium ion battery
A technology of lithium-ion batteries and formation methods, which is applied in the field of battery formation, and can solve problems affecting the cycle stability of hard carbon negative electrode materials lithium-ion batteries, potential safety hazards, and risks of lithium analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
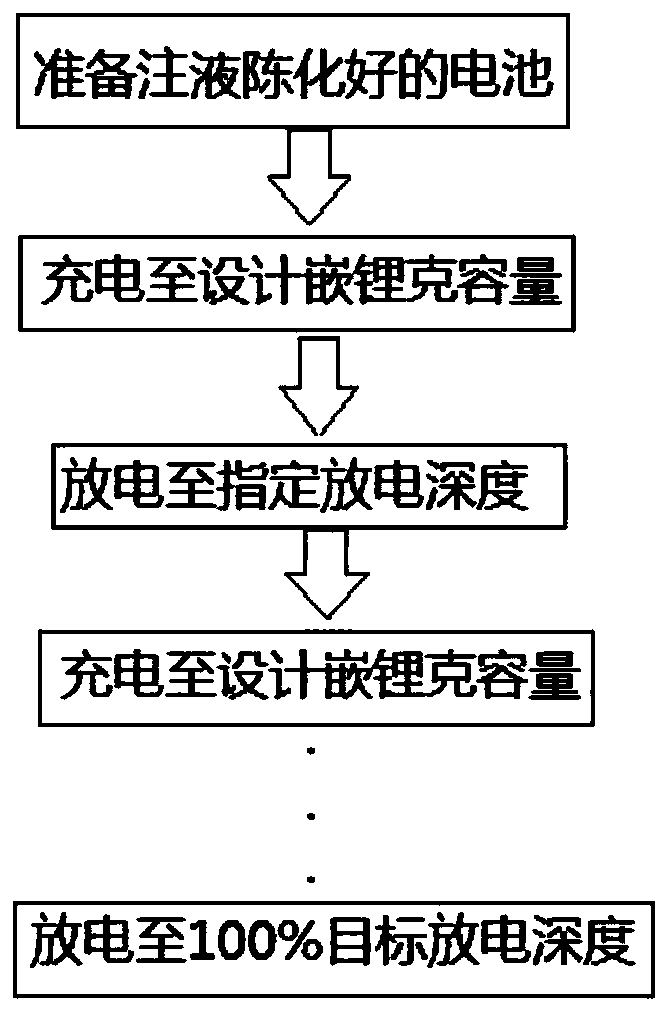
[0026] In the embodiment of the present invention, the preparation method of the liquid-injected and aged battery preferably includes: according to the manufacturing process of the conventional button battery, the metal lithium sheet is used as the counter electrode, that is, the negative electrode in the button battery.
[0027] According to the conventional button battery manufacturing process, the hard carbon negative electrode material, conductive agent SP, and binder SBR / CMC are prepared into a slurry, which is evenly and continuously coated on the copper foil, dried and rolled to form a positive electrode. Pole piece: The mass ratio of the hard carbon, SP, SBR and CMC is preferably 95:2:2:1.
[0028] The positive and negative pole pieces, electrolyte and separator were assembled into a button battery, and then aged at 25°C for 24 hours to obtain a liquid-injected aged battery.
[0029] In the present invention, the battery that has been aged by liquid injection is subjec...
Embodiment 1
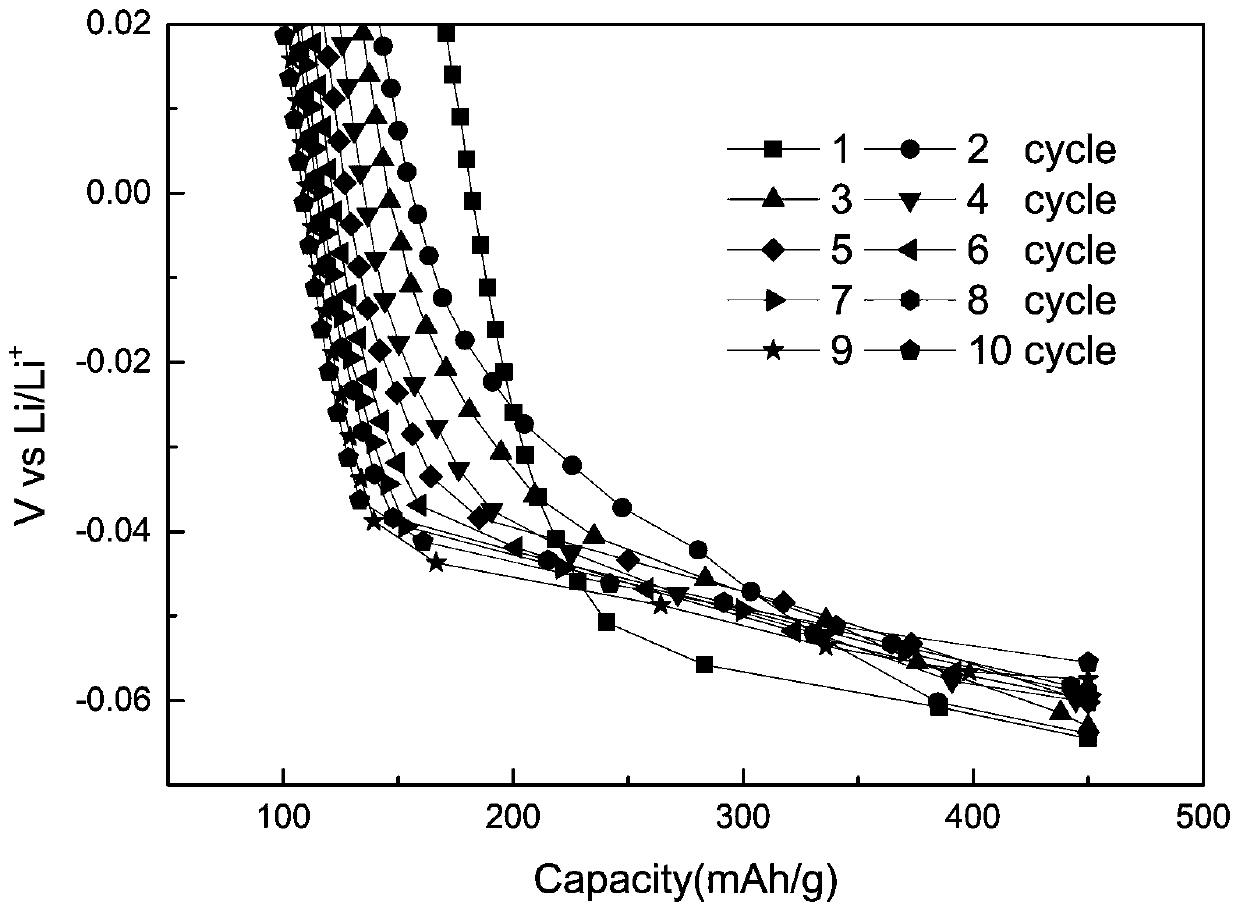
[0037] A method for the formation of a hard carbon negative electrode material lithium-ion battery, performing formation treatment on the battery that has been aged by liquid injection; the formation temperature is 25°C; the designed lithium intercalation gram capacity (hereinafter referred to as SOC) is 450mAh / g, The target depth of discharge (hereinafter referred to as DOD) is 450mAh / g;
[0038] The process of the chemical conversion treatment includes:
[0039] Intercalate lithium at a rate of 0.2C to 100% SOC in the first week, and then delithiate at a rate of 0.2C to 55% DOD;
[0040] In the second week, intercalate lithium at a rate of 0.2C to 100% SOC, and then delithiate at a rate of 0.2C to 60% DOD;
[0041] In the third week, insert lithium at a rate of 0.2C to 100% SOC, and then delithiate at a rate of 0.2C to 65% DOD;
[0042] In the fourth week, intercalate lithium at a rate of 0.2C to 100% SOC, and then delithiate at a rate of 0.2C to 70% DOD;
[0043] In the ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] A method for forming a hard carbon negative electrode material lithium-ion battery, which involves forming a battery that has been aged by liquid injection; the formation temperature is 25°C; the designed lithium intercalation gram capacity is 450mAh / g, and the target discharge depth is 382.5mAh / g;
[0055] The process of the chemical conversion treatment includes:
[0056] In the first week, lithium was intercalated to 450mAh / g at a rate of 0.2C, and then delithiated at a rate of 0.2C to 382.5mAh / g.
[0057] The preparation method of the liquid-injected aged battery is the same as that in Example 1.
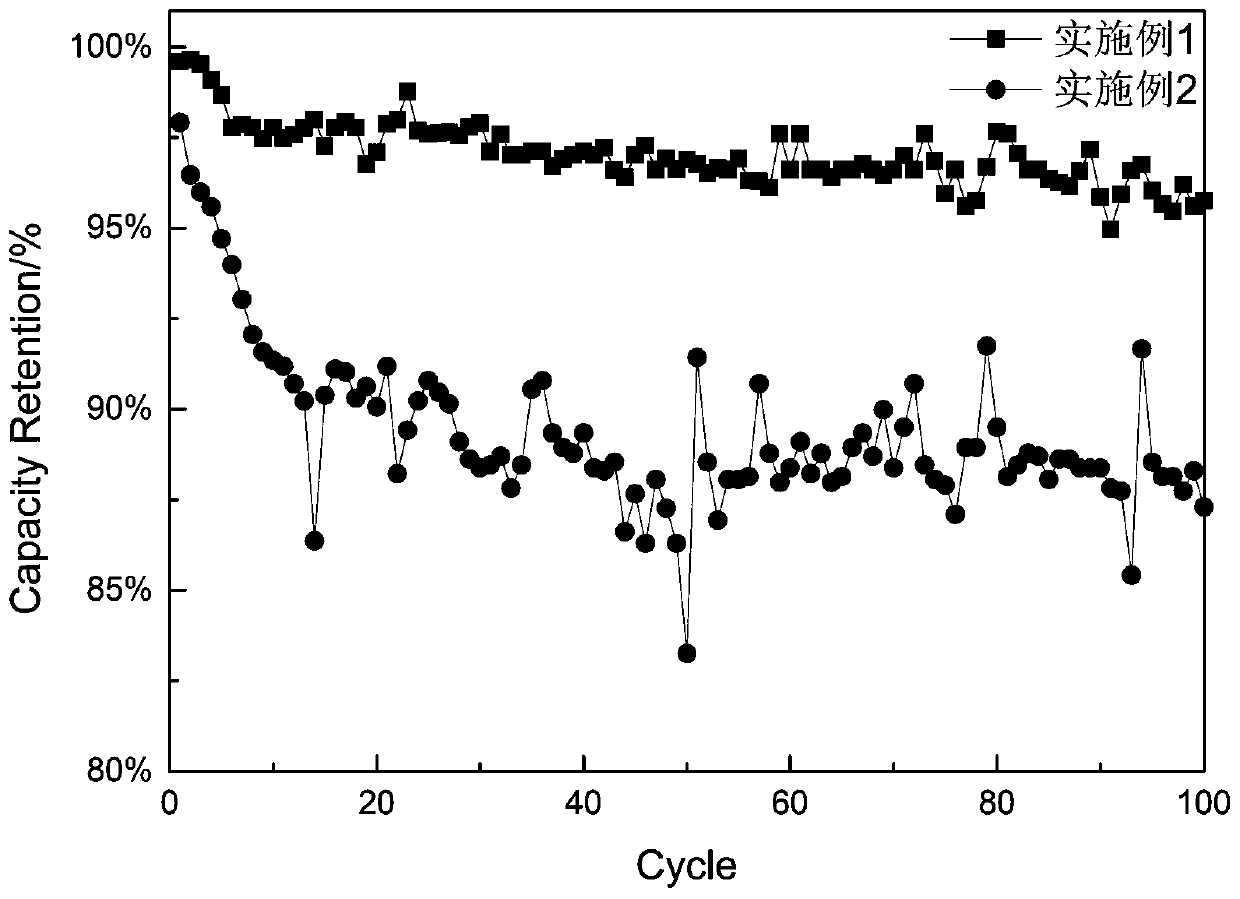
[0058] With 0.5C magnification, the formation battery in embodiment 1 and 2 is charged and discharged 100 times, and the 100 cycle performance of the formation battery in research embodiment 1 and 2 is studied, and the results are as follows figure 2 shown. from figure 2 It can be seen that the irreversible Li in the positive electrode is reduced by gradually incre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com