Key protein recognition method based on tensor random walking
A technology of random walk and identification method, applied in the field of systems biology, can solve the problem of poor prediction performance of key proteins, and achieve the effect of good prediction performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
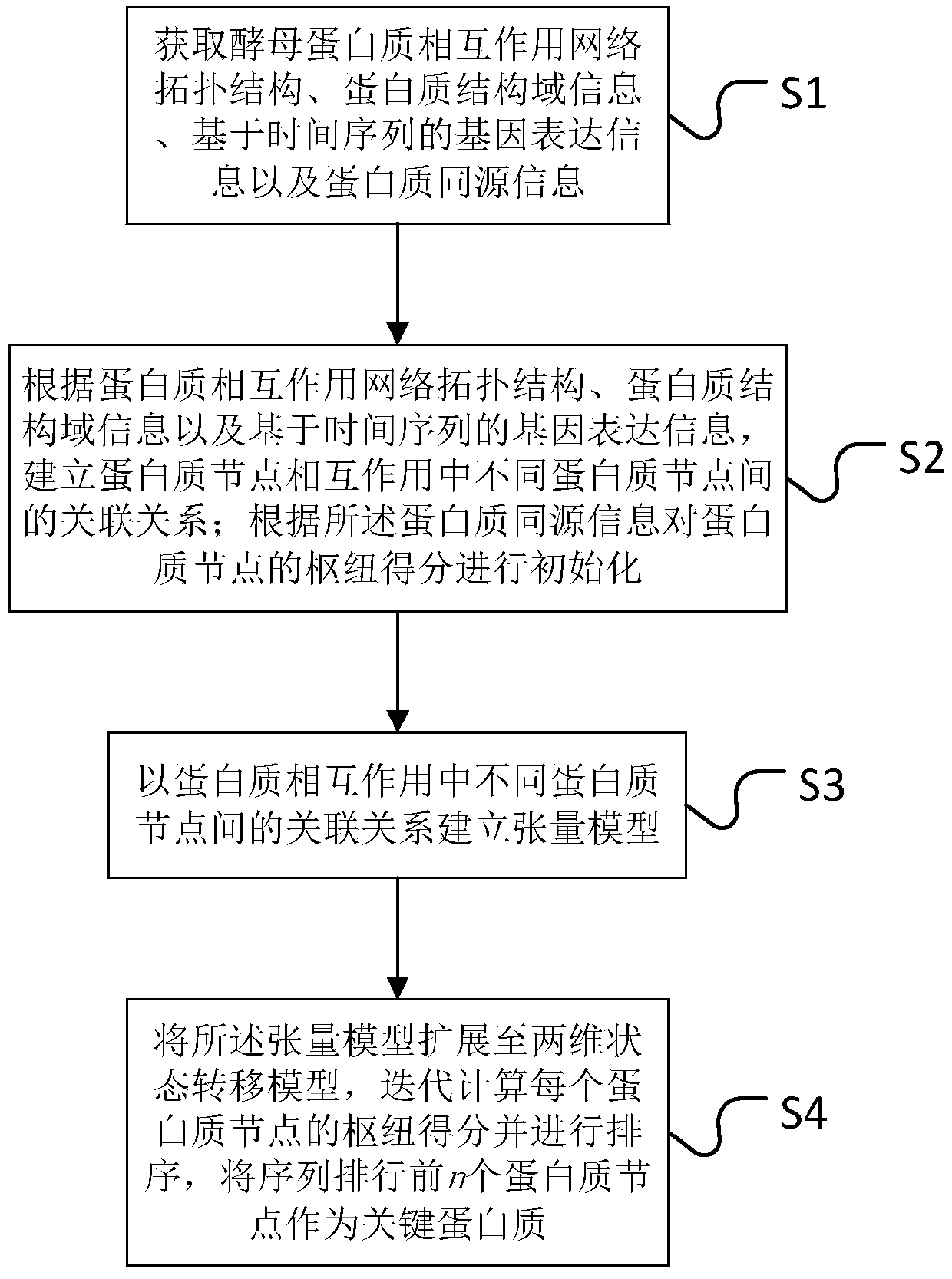
[0047] see figure 1 , the present invention firstly provides a key protein identification method based on tensor random walk, comprising the following steps:
[0048] S1: Obtain protein interaction network topology, protein domain information, time-series-based gene expression information, and protein homology information.
[0049] The above three kinds of data all come from public databases on the Internet. Protein interaction networks derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker's yeast) have been well characterized by gene knockout experiments and have been widely used for the assessment of key proteins. The protein domain data were downloaded from the Pfam database, containing 1107 distinct domains involving 3,056 proteins in the PPI network. The gene expression data contains a total of 6,776 gene products (proteins) sampling data at 36 different times.
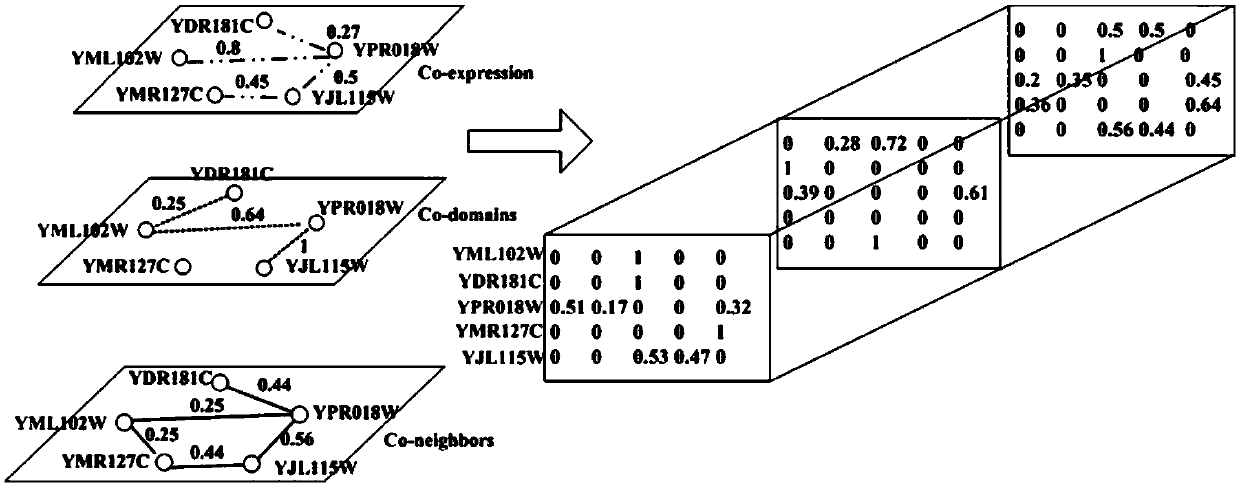
[0050] S2: According to the protein interaction network topology, protein domain information and gene expression inf...
Embodiment 2
[0088] In order to verify the effectiveness of the key protein identification method proposed in the present invention, we run this method and other ten current key protein identification methods on the yeast protein interaction network. The protein interaction network used for the experiments is derived from the DIP database, which consists of 5,023 proteins and 22,570 edges. Self-interactions and repeated interactions have been removed from the network. The gene expression data of yeast contains the sampling data of 6,776 gene products (proteins) at 36 different times. Of the 6,776 proteins, 4,902 proteins were included in the DIP dataset. image 3It is the method proposed by the present invention and other ten key protein prediction methods DC, IC, BC, CC, SC, NC, CoEWC, Pec, POEM, ION respectively predict the top 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600 key proteins Accuracy comparison chart of (ie n=100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com