Chemical method for microbial clogging treatment in artificial recharging process
A chemical method and microbial technology are applied in the field of microbial blockage control in the process of artificial recharge, which can solve the problems of low recharge rate, microbial blockage, and high equipment maintenance cost, achieve less dosage, low cost, and improve recharge efficiency. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
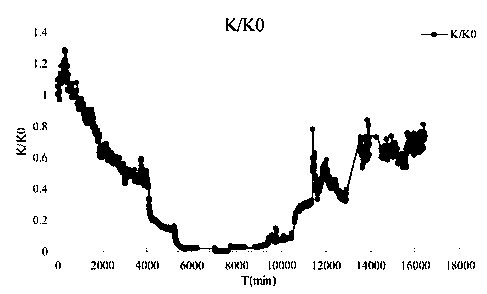
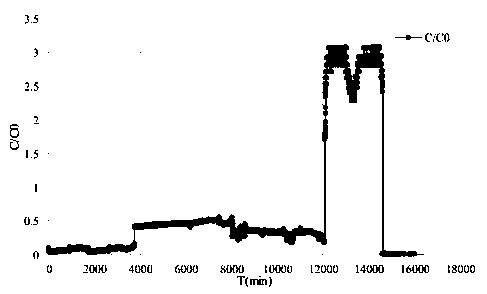
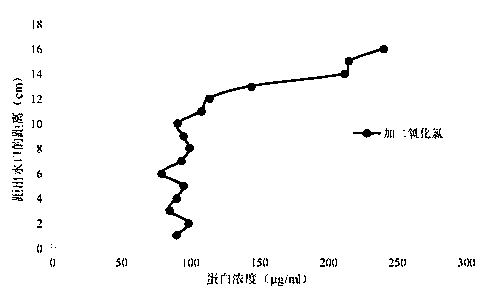
[0049] (1): After the medium is blocked (the permeability coefficient is reduced to the initial 0.01%), the chlorine dioxide solution of 0.1mg / L is passed into the experimental sand column from top to bottom at a speed of 5m / d.
[0050] (2): Continuously inject 100ml of chlorine dioxide solution, then stop injecting and let it stand for 12 hours.
[0051] (3): After 12 hours, start to feed ultrapure water into the experimental sand column at a speed of 5m / d.
[0052] (4): According to the recovery of the permeability coefficient, intermittently inject 0.1 mg / L chlorine dioxide solution into the sand column for 4 times, rinse with ultrapure water, and the permeability coefficient of the porous medium will recover to 60% of the initial permeability coefficient in 5 days .
Embodiment 2
[0054] (1): After the medium is blocked (the permeability coefficient is reduced to the initial 0.01%), the chlorine dioxide solution of 0.5mg / L is passed into the experimental sand column from top to bottom at a speed of 5m / d.
[0055] (2): Continuously inject 100ml of chlorine dioxide solution, then stop injecting and let it stand for 12 hours.
[0056] (3): After 12 hours, start to feed ultrapure water into the experimental sand column at a speed of 5m / d.
[0057] (4): According to the restoration of permeability coefficient, 0.5 mg / L chlorine dioxide solution was intermittently passed into the sand column for 7 times, and washed with ultrapure water. The permeability coefficient of the porous medium recovered to 74% of the initial permeability coefficient in 5 days. .
Embodiment 3
[0059] (1): After the medium is blocked (the permeability coefficient is reduced to the initial 0.01%), the chlorine dioxide solution of 0.8mg / L is passed into the experimental sand column from top to bottom at a speed of 5m / d.
[0060] (2): Continuously inject 100ml of chlorine dioxide solution, then stop injecting and let it stand for 12 hours.
[0061] (3): After 12 hours, start to feed ultrapure water into the experimental sand column at a speed of 5m / d.
[0062] (4): According to the restoration of the permeability coefficient, intermittently inject 0.8 mg / L chlorine dioxide solution into the sand column for 4 times, rinse with ultrapure water, and the permeability coefficient of the porous medium returns to 82% of the initial permeability coefficient in 5 days .
[0063] current technology
[0064] Most of the existing microbial blockage treatment methods are replacing the surface medium and adding hydrolytic enzymes. The formula for solution preparation is to inject h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com